From DNA sequence to application: possibilities and
... knowledge relates both to the assignments of open reading frames (ORF's) and the function of non-coding DNA sequences.Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequencesof several LAB bacteriophages has revealed that their chromosomeshave a fixed, modular structure, each module having a set of genesinvo ...
... knowledge relates both to the assignments of open reading frames (ORF's) and the function of non-coding DNA sequences.Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequencesof several LAB bacteriophages has revealed that their chromosomeshave a fixed, modular structure, each module having a set of genesinvo ...
! Mendel`s Law of Independent Assortment
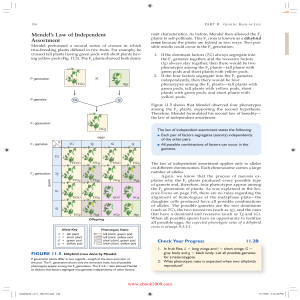
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
Use what you learned in Module 5 to construct a gene model for tra
... Genes track are exons and the thin lines with arrowheads show the locations of the introns. Notice that the diagrams for the first and second RNA-Seq Exon Junctions tracks have the same 5’ splice site but different 3’ splice sites. Let’s see what we can find out about these splice sites. First, we n ...
... Genes track are exons and the thin lines with arrowheads show the locations of the introns. Notice that the diagrams for the first and second RNA-Seq Exon Junctions tracks have the same 5’ splice site but different 3’ splice sites. Let’s see what we can find out about these splice sites. First, we n ...
Arabidopsis Gene and cDNA Encoding Cell
... thaliana. In Atbfructl and both tomato genes, exon 2 is only 9 bp long and encodes part of a highly conserved region found in a11 known invertase proteins (NDPNG). By way of contrast, in the D. carota gene this short nucleotide sequence is included in exon 1. There is one conflict between the gene s ...
... thaliana. In Atbfructl and both tomato genes, exon 2 is only 9 bp long and encodes part of a highly conserved region found in a11 known invertase proteins (NDPNG). By way of contrast, in the D. carota gene this short nucleotide sequence is included in exon 1. There is one conflict between the gene s ...
The Genetics of Eye Color
... of pigment within a small number of melanosomes. Irises from green–hazel eyes show moderate pigment levels and melanosome number, while brown eyes are the result of high melanin levels stored across many melanosomes (see figure two). To date, eight genes have been identified which impact eye color. ...
... of pigment within a small number of melanosomes. Irises from green–hazel eyes show moderate pigment levels and melanosome number, while brown eyes are the result of high melanin levels stored across many melanosomes (see figure two). To date, eight genes have been identified which impact eye color. ...
Something`s Fishy
... You have learned that DNA is a linear sequence of nucleotides made up of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. This sequence of A, T, G, and C is unique to each individual. Restriction enzymes cut DNA. Each restriction enzyme recognizes a specific group of “target” base pairs and makes a cut with ...
... You have learned that DNA is a linear sequence of nucleotides made up of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. This sequence of A, T, G, and C is unique to each individual. Restriction enzymes cut DNA. Each restriction enzyme recognizes a specific group of “target” base pairs and makes a cut with ...
1 © 2013 AIMS Education Foundation Topic Heredity Key Question
... • Many characteristics of an organisms are inherited from the parents of the organisms, but other characteristics result from an individual’s interactions with the environment. Inherited characteristics include the color of flowers and the number of limbs of an animal. Other features, such as the a ...
... • Many characteristics of an organisms are inherited from the parents of the organisms, but other characteristics result from an individual’s interactions with the environment. Inherited characteristics include the color of flowers and the number of limbs of an animal. Other features, such as the a ...
Simplex sigillum veri New approaches to the analysis of
... expression levels (mRNA concentrations) •relative or absolute values ...
... expression levels (mRNA concentrations) •relative or absolute values ...
Comprehension Question - We can offer most test bank and solution
... accepted by scholars of that time? Include in your answer some evidence in favor of the idea, observations that seemed to support the idea, or other rationale for accepting the idea. Answer: Answers will vary but should include specific evidence or observations that support the idea. Examples: Pange ...
... accepted by scholars of that time? Include in your answer some evidence in favor of the idea, observations that seemed to support the idea, or other rationale for accepting the idea. Answer: Answers will vary but should include specific evidence or observations that support the idea. Examples: Pange ...
Mendel and Heredity
... • Gregor Mendel (1850’s)– Austrian monk that bred pea plants and from his experiments he formed the basis of GENETICS: study of heredity • Used peas because they had easily distinguishable forms of various traits: flower color, pod shape/color, seed shape/color, plant height and flower placement • E ...
... • Gregor Mendel (1850’s)– Austrian monk that bred pea plants and from his experiments he formed the basis of GENETICS: study of heredity • Used peas because they had easily distinguishable forms of various traits: flower color, pod shape/color, seed shape/color, plant height and flower placement • E ...
DNA THIS ONE
... 2. RNA and DNA are both types of Nucleic Acids. What are the 3 main differences between RNA and DNA? ...
... 2. RNA and DNA are both types of Nucleic Acids. What are the 3 main differences between RNA and DNA? ...
Build Your Own Baby
... genetic code, gene "A" translates into a protein called melanin. This dark pigment is like a natural UV blocker. The greater the number of dominant genes one has, the greater the amount of melanin, the darker the skin, and the more UV protection a person has. These genes have been selected-for near ...
... genetic code, gene "A" translates into a protein called melanin. This dark pigment is like a natural UV blocker. The greater the number of dominant genes one has, the greater the amount of melanin, the darker the skin, and the more UV protection a person has. These genes have been selected-for near ...
Karyotyping, FISH and CGH array
... Karyotyping vs array CGH and SNP array In principle, both karyotyping and arrays are genome-wide technologies which can be used to assess the presence of genomic imbalance such as copy number variations (CNVs). Although they may look like very different technologies, the primary difference between t ...
... Karyotyping vs array CGH and SNP array In principle, both karyotyping and arrays are genome-wide technologies which can be used to assess the presence of genomic imbalance such as copy number variations (CNVs). Although they may look like very different technologies, the primary difference between t ...
DNA-free CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering in
... The CRISPR-Cas9 system permits researchers to quickly edit genes for functional protein knockout in mammalian, fish and plant genomes, among others, and consequently has dramatically transformed biological research. The CRISPR-Cas9 system requires exogenous Cas9 nuclease to be delivered into the cel ...
... The CRISPR-Cas9 system permits researchers to quickly edit genes for functional protein knockout in mammalian, fish and plant genomes, among others, and consequently has dramatically transformed biological research. The CRISPR-Cas9 system requires exogenous Cas9 nuclease to be delivered into the cel ...
B/B a/a - kcpe-kcse
... 1. Genes can have alternate versions called alleles. 2. Each offspring inherits two alleles, one from each parent. 3. If the two alleles differ, the dominant allele is expressed. The recessive allele remains hidden unless the dominant allele is absent. 4. The two alleles for each trait separate duri ...
... 1. Genes can have alternate versions called alleles. 2. Each offspring inherits two alleles, one from each parent. 3. If the two alleles differ, the dominant allele is expressed. The recessive allele remains hidden unless the dominant allele is absent. 4. The two alleles for each trait separate duri ...
Page 517 Duplication of the S. cerevisiae genome
... Beadle and Tatum chose N. crassa as a model organism to study gene-protein relationships. The genome sequence was reported: 39 Mb, 7 chromosomes, 10,082 ORFs (Galagan et al., 2003). ...
... Beadle and Tatum chose N. crassa as a model organism to study gene-protein relationships. The genome sequence was reported: 39 Mb, 7 chromosomes, 10,082 ORFs (Galagan et al., 2003). ...
Lecture 6 - U of L Class Index
... Positive (the most common in eukaryotes, but can be found in bacteria as well): an activator protein is needed to activate the gene expression ...
... Positive (the most common in eukaryotes, but can be found in bacteria as well): an activator protein is needed to activate the gene expression ...
File - Mr. Doyle SUIS Science
... • Hemoglobin is a protein that binds oxygen in the lungs and carries it to cells throughout the body • The hemoglobin molecule consists of four polypeptides (globins) folded around iron-containing hemes – oxygen molecules bind to the iron atoms • Defects in polypeptide chains can cause anemia, in wh ...
... • Hemoglobin is a protein that binds oxygen in the lungs and carries it to cells throughout the body • The hemoglobin molecule consists of four polypeptides (globins) folded around iron-containing hemes – oxygen molecules bind to the iron atoms • Defects in polypeptide chains can cause anemia, in wh ...
Y chromosome: Structure and Biological Functions
... Y chromosome is the smallest haploid sex chromosome. Although Y chromosome is poor in genes, it comprises several important genes which plays essential role in different biological functions- Sex determination, regulation of spermatogenesis as well as in male infertility. This paper details about th ...
... Y chromosome is the smallest haploid sex chromosome. Although Y chromosome is poor in genes, it comprises several important genes which plays essential role in different biological functions- Sex determination, regulation of spermatogenesis as well as in male infertility. This paper details about th ...
Comparison of DNA isolation methods and storage conditions for
... Colton, L., and J.B. Clark. Department of Zoology, Weber State University, Ogden UT 84408-2505 USA. Correspondence: [email protected]. ...
... Colton, L., and J.B. Clark. Department of Zoology, Weber State University, Ogden UT 84408-2505 USA. Correspondence: [email protected]. ...
1 - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Meiosis differs from mitosis in that A. it occurs only in the reproductive tissues that produce gametes. B. the chromosomes are duplicated twice. C. the resulting cells are polyploid. D. the chromosome pairs do not separate. Answer:A ...
... Meiosis differs from mitosis in that A. it occurs only in the reproductive tissues that produce gametes. B. the chromosomes are duplicated twice. C. the resulting cells are polyploid. D. the chromosome pairs do not separate. Answer:A ...
b - nnhschen
... Mendel and Genetics Law of Segregation: • Two alleles for a trait separate during ...
... Mendel and Genetics Law of Segregation: • Two alleles for a trait separate during ...
Protein World
... • The best, however not completely convincing, result was found using PCP and not ME: ...
... • The best, however not completely convincing, result was found using PCP and not ME: ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.