Specific biomolecules serve various functions in the body.
... b. It clamps onto messenger RNA and uses its information to assemble amino acids. c. It transports amino acids to the ribosomes to be assembled into proteins. d. It creates another molecule of DNA through replication. ...
... b. It clamps onto messenger RNA and uses its information to assemble amino acids. c. It transports amino acids to the ribosomes to be assembled into proteins. d. It creates another molecule of DNA through replication. ...
The MAOA Gene Predicts Credit Card Debt ∗ London School of Economics
... At conception individuals inherit one half of their DNA from each parent, with one copy of each gene coming from the mother and one copy from the father. Some genes come in different versions, known as “alleles”—for example, sickle cell disease results from a particular allele coding for abnormal r ...
... At conception individuals inherit one half of their DNA from each parent, with one copy of each gene coming from the mother and one copy from the father. Some genes come in different versions, known as “alleles”—for example, sickle cell disease results from a particular allele coding for abnormal r ...
El Proyecto Genoma Humano
... • BioProject is an administrative object (defined by goal, target, funding, collaboration) • Genome is a biological object defining an organism at molecular level • Genome assembly is a complex data structure that defines the structure, relative position (scaffold) and chromosome placement of DNA se ...
... • BioProject is an administrative object (defined by goal, target, funding, collaboration) • Genome is a biological object defining an organism at molecular level • Genome assembly is a complex data structure that defines the structure, relative position (scaffold) and chromosome placement of DNA se ...
7th Grade Science Formative Assessment #6 Multiple Choice
... A. All four offspring received all of their genetic information only from Parent 1 and are therefore identical to that parent. B. All four offspring received all of their genetic information only from Parent 2 and are therefore identical to that parent. C. Each of the offspring is genetically unique ...
... A. All four offspring received all of their genetic information only from Parent 1 and are therefore identical to that parent. B. All four offspring received all of their genetic information only from Parent 2 and are therefore identical to that parent. C. Each of the offspring is genetically unique ...
Correction of copy number induced false positives in
... Overall, LDO removes the copy number effect beyond the YAP1 amplicon in sf268 and in mkn45 cell lines, as shown in Fig. 3. The number of guides with log2(CNA) larger than 2 and LogFC below -0.5 is decreased from 84 to 25 guides in mkn45 and 274 to 50 guides in sf268. Library design and guide quality ...
... Overall, LDO removes the copy number effect beyond the YAP1 amplicon in sf268 and in mkn45 cell lines, as shown in Fig. 3. The number of guides with log2(CNA) larger than 2 and LogFC below -0.5 is decreased from 84 to 25 guides in mkn45 and 274 to 50 guides in sf268. Library design and guide quality ...
Supplementary document Trehalose/2
... method (Falicia Goh et al 2011). Cell pellets were washed three times in a sterile isotonic ...
... method (Falicia Goh et al 2011). Cell pellets were washed three times in a sterile isotonic ...
Lecture9_10_extra2 - Welcome to people.pharmacy.purdue.edu!
... HLA-DQ, HLA-DP, HLA-DR Each MHC II locus encodes a gene for the chain and a gene for the chain: e.g. HLA-DQA, HLA-DQB => MHC II isoforms HLA-DPA, HLA-DPB => MHC II isoforms HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB => MHC II isoforms ...
... HLA-DQ, HLA-DP, HLA-DR Each MHC II locus encodes a gene for the chain and a gene for the chain: e.g. HLA-DQA, HLA-DQB => MHC II isoforms HLA-DPA, HLA-DPB => MHC II isoforms HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB => MHC II isoforms ...
Is COPD in adulthood really so far removed from early development? EDITORIAL
... genetic alteration in the genes involved in early development may disturb normal structural formation and function in one or more affected organs/systems, and hence cause clinically diagnosed congenital diseases in children. In addition to the genetic alterations described previously, genetic change ...
... genetic alteration in the genes involved in early development may disturb normal structural formation and function in one or more affected organs/systems, and hence cause clinically diagnosed congenital diseases in children. In addition to the genetic alterations described previously, genetic change ...
Name: Per: _____ Intro to Mendelian Genetics Webquest Go to the
... Click on Concept 5, Genetic Inheritance follows Rules. 1. What problem was presented when Mendel proposed that each trait is determined by a pair of genes? Mendel deduced that _________ cells contained only ____ parental gene each __________. Mendel found that different ___________ __________ from p ...
... Click on Concept 5, Genetic Inheritance follows Rules. 1. What problem was presented when Mendel proposed that each trait is determined by a pair of genes? Mendel deduced that _________ cells contained only ____ parental gene each __________. Mendel found that different ___________ __________ from p ...
Intro to Mendelian Genetics Webquest
... Click on Concept 5, Genetic Inheritance follows Rules. 1. What problem was presented when Mendel proposed that each trait is determined by a pair of genes? Mendel deduced that _________ cells contained only ____ parental gene each __________. Mendel found that different ___________ __________ from p ...
... Click on Concept 5, Genetic Inheritance follows Rules. 1. What problem was presented when Mendel proposed that each trait is determined by a pair of genes? Mendel deduced that _________ cells contained only ____ parental gene each __________. Mendel found that different ___________ __________ from p ...
Minireview Shifty Ciliates: Frequent Programmed
... The frequency of this frameshift is as much as 10,000fold greater than the estimated rate of spontaneous translational frameshifting. The sequence of the region in and around the site of frameshifting stimulates this impressive increase in “error.” Among the simplest types of programmed frameshifts ...
... The frequency of this frameshift is as much as 10,000fold greater than the estimated rate of spontaneous translational frameshifting. The sequence of the region in and around the site of frameshifting stimulates this impressive increase in “error.” Among the simplest types of programmed frameshifts ...
Differential Regulation of Antagonistic Pleiotropy in Synthetic and
... in both S. cerevisiae and S. paradoxus. These results suggest that in unicellular organisms, ...
... in both S. cerevisiae and S. paradoxus. These results suggest that in unicellular organisms, ...
DNA notes
... Determine probability of traits that can be inherited 11. What is the process that involves one cell dividing two times to create four new cells with half the number of chromosomes? Meiosis 12. What type of cells undergo meiosis? Sperm and Egg 13. How many chromosomes are in a human egg cell? ...
... Determine probability of traits that can be inherited 11. What is the process that involves one cell dividing two times to create four new cells with half the number of chromosomes? Meiosis 12. What type of cells undergo meiosis? Sperm and Egg 13. How many chromosomes are in a human egg cell? ...
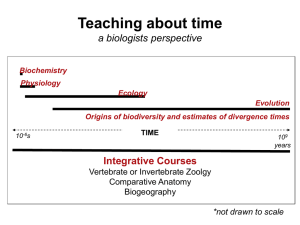
Teaching deep time through macroevolution and
... Biologist’s general modus operandus • We had no training on how to teach about deep time other than memorizing the chart • We focus on teaching biological processes, not so much the time scales during which they proceed • We make modest attempts to talk about deep time ...
... Biologist’s general modus operandus • We had no training on how to teach about deep time other than memorizing the chart • We focus on teaching biological processes, not so much the time scales during which they proceed • We make modest attempts to talk about deep time ...
Doubling Down on Genomes: Polyploidy and Crop Plants
... wheat, reduction in genome size may occur relatively rapidly, after only a few generations in some synthetic lines (Eilam et al., 2008, 2010), serving to exemplify the “revolutionary” (Feldman and Levy, 2009) pace of genomic alterations that impact allopolyploid genomes. What ...
... wheat, reduction in genome size may occur relatively rapidly, after only a few generations in some synthetic lines (Eilam et al., 2008, 2010), serving to exemplify the “revolutionary” (Feldman and Levy, 2009) pace of genomic alterations that impact allopolyploid genomes. What ...
Protein Synthesis PowerPoint
... – adenine always pairs with a thymine – guanine always pairs with a cytosine complementary – The strictness of base-pairing results in two strands that contain complementary base pairs. • base-pairing rules in RNA – adenine always pairs with a uracil – guanine always pairs with a cytosine Chapter me ...
... – adenine always pairs with a thymine – guanine always pairs with a cytosine complementary – The strictness of base-pairing results in two strands that contain complementary base pairs. • base-pairing rules in RNA – adenine always pairs with a uracil – guanine always pairs with a cytosine Chapter me ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... The plants were a cross between two parents that show different forms of a trait 7. Mendel concluded _______ factors controlled each trait. The difference forms of the genes are called _____________. Two, alleles 8. When Mendel crossed a tall pea plant with a short pea plant, why were all of the off ...
... The plants were a cross between two parents that show different forms of a trait 7. Mendel concluded _______ factors controlled each trait. The difference forms of the genes are called _____________. Two, alleles 8. When Mendel crossed a tall pea plant with a short pea plant, why were all of the off ...
apgenetics1206
... 11) A genetic disease known as Marfan Syndrome is caused by a dominant allele. In this disease the fingers and toes are excessively long. This and other skeletal defects are often accompanied by a misplaced eye lens and defects of the heart. Some individuals with this syndrome may have all the defec ...
... 11) A genetic disease known as Marfan Syndrome is caused by a dominant allele. In this disease the fingers and toes are excessively long. This and other skeletal defects are often accompanied by a misplaced eye lens and defects of the heart. Some individuals with this syndrome may have all the defec ...
Type-2 fuzzy Approach for Disease-Associated Gene Identification on Microarrays Yan-Fei Wang
... consideration to analyze DNA microarrays. Liang et al. [1] proposed a fuzzy set theory based approach, namely a fuzzy membership test (FM-test), for disease genes identification and obtained better results by applying their approach on diabetes and lung cancer microarrays. However, some limitations ...
... consideration to analyze DNA microarrays. Liang et al. [1] proposed a fuzzy set theory based approach, namely a fuzzy membership test (FM-test), for disease genes identification and obtained better results by applying their approach on diabetes and lung cancer microarrays. However, some limitations ...
Session 5 - Annenberg Learner
... THAT MAKE UP THE HUMAN GENOME. DNA IS THE STUFF OF HEREDITY. IT IS THE CHEMICAL MATERIAL WHICH PASSES ON THE INFORMATION THAT DETERMINES WHAT A CREATURE WILL BE, HOW IT WILL FUNCTION, AND HOW IT WILL REPRODUCE. IT IS A LONG, THREAD-LIKE MOLECULE IN WHICH THE INFORMATION THAT TELLS THE ORGANISM WHAT ...
... THAT MAKE UP THE HUMAN GENOME. DNA IS THE STUFF OF HEREDITY. IT IS THE CHEMICAL MATERIAL WHICH PASSES ON THE INFORMATION THAT DETERMINES WHAT A CREATURE WILL BE, HOW IT WILL FUNCTION, AND HOW IT WILL REPRODUCE. IT IS A LONG, THREAD-LIKE MOLECULE IN WHICH THE INFORMATION THAT TELLS THE ORGANISM WHAT ...
Transcription and Translation
... nitrogen bases in a complementary fashion (mRNA is made from the DNA template) ...
... nitrogen bases in a complementary fashion (mRNA is made from the DNA template) ...
PDF
... frequency from 17.4% to 78.2% (P = 0.00011), which is significantly higher (P = 0.00665) than that achieved with the Zfy1 transgene (47.2%). Thus the Zfy2 transgene promotes meiosis II more effectively than the Zfy1 transgene. Both transgenes are single copy and inserted on the X chromosome, but we ...
... frequency from 17.4% to 78.2% (P = 0.00011), which is significantly higher (P = 0.00665) than that achieved with the Zfy1 transgene (47.2%). Thus the Zfy2 transgene promotes meiosis II more effectively than the Zfy1 transgene. Both transgenes are single copy and inserted on the X chromosome, but we ...
Models for homologous recombination
... meiotic recombination Many protein function together to promote meiotic recombination ...
... meiotic recombination Many protein function together to promote meiotic recombination ...
Hardy-Weinberg Questions
... A cat breeder who wished to produce tortoiseshell cats crossed a black female cat with a ginger male. Complete the genetic diagram and predict the percentage of tortoiseshell kittens expected from this cross. ...
... A cat breeder who wished to produce tortoiseshell cats crossed a black female cat with a ginger male. Complete the genetic diagram and predict the percentage of tortoiseshell kittens expected from this cross. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.