Presentation
... For each inherited character, an individual has two copies of a gene– one from each parent.(Pair Principle) There are alternative forms of a gene (alleles) that control different traits. When the two alleles occur together, one may be completely expressed (dominant) and one may have no observable ef ...
... For each inherited character, an individual has two copies of a gene– one from each parent.(Pair Principle) There are alternative forms of a gene (alleles) that control different traits. When the two alleles occur together, one may be completely expressed (dominant) and one may have no observable ef ...
Gene Section TRIAP1 (TP53 regulated inhibitor of apoptosis 1)
... unspliced form that encodes good proteins (see figure ...
... unspliced form that encodes good proteins (see figure ...
pGLO Bacterial Transformation- Pre-Lab
... Consideration 3: The Genes Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Scientist ...
... Consideration 3: The Genes Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Scientist ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 7 __________ dominance results in the blending of genes in the hybrid. Give an example using flower color. 8 What is another term for a heterozygous genotype? 9 The _____________ is the physical feature such as round peas that results from a genotype. 10How many traits are involved in a monohybrid c ...
... 7 __________ dominance results in the blending of genes in the hybrid. Give an example using flower color. 8 What is another term for a heterozygous genotype? 9 The _____________ is the physical feature such as round peas that results from a genotype. 10How many traits are involved in a monohybrid c ...
pGLO Bacterial Transformation- Pre-Lab
... Consideration 3: The Genes Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Scientist ...
... Consideration 3: The Genes Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Scientist ...
This is a paper I wrote for a documentary
... very new to me. While I thought I knew a good bit of genetics, and how they work, I was astounded by how much I did not know. The very idea that a slight change in the makeup of our genetic code can be life changing is mind boggling to me. Development of an entire new human being has always been int ...
... very new to me. While I thought I knew a good bit of genetics, and how they work, I was astounded by how much I did not know. The very idea that a slight change in the makeup of our genetic code can be life changing is mind boggling to me. Development of an entire new human being has always been int ...
Directed evolution
... revealed that they can be grouped onto families that are similar in size and amino acid sequence. Enzyme belonging to the same family have evolved from a common ancestor to acquire a new catabolic function through various genetic events, such as gene transfer, recombination, duplication, multiple po ...
... revealed that they can be grouped onto families that are similar in size and amino acid sequence. Enzyme belonging to the same family have evolved from a common ancestor to acquire a new catabolic function through various genetic events, such as gene transfer, recombination, duplication, multiple po ...
It`s All in the Genes
... fascinating inherited traits in humans, from top to toes. Genes control whether hair is blond, brown, or black, whether or not it has red highlights, and whether it is straight, curly, or kinky. Widow’s peaks, cowlicks, a whorl in the eyebrow, and white forelocks run in families, ...
... fascinating inherited traits in humans, from top to toes. Genes control whether hair is blond, brown, or black, whether or not it has red highlights, and whether it is straight, curly, or kinky. Widow’s peaks, cowlicks, a whorl in the eyebrow, and white forelocks run in families, ...
Grade 9 Science – Unit 1 – Biology
... organisms, including internal processes. Physiology includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells and biomolecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. By comparing these processes, the degree of genetic similarity can be assessed. DNA Evidence of Rela ...
... organisms, including internal processes. Physiology includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells and biomolecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. By comparing these processes, the degree of genetic similarity can be assessed. DNA Evidence of Rela ...
PS Webquest
... 2. What protein copies the luc gene into messenger RNA? ___________________________________ 3. What is the process of making RNA copies of DNA (genes) called? ______________________________ 4. After the mRNA copy of luc gene moves into the cytoplasm; what organelle is going to read it to make it int ...
... 2. What protein copies the luc gene into messenger RNA? ___________________________________ 3. What is the process of making RNA copies of DNA (genes) called? ______________________________ 4. After the mRNA copy of luc gene moves into the cytoplasm; what organelle is going to read it to make it int ...
Lab5CysticFibroShort
... 5. Every person has a different sequence of bases for 13, 14 & 15 yet only Leah and Richard Have CF. Why doesn’t Josina’s difference cause CF? 6. Use a colored pencil to circle the amino acid differences between the 4 people in your table. 7. Compare Leah’s amino acid sequence to that of Norma and ...
... 5. Every person has a different sequence of bases for 13, 14 & 15 yet only Leah and Richard Have CF. Why doesn’t Josina’s difference cause CF? 6. Use a colored pencil to circle the amino acid differences between the 4 people in your table. 7. Compare Leah’s amino acid sequence to that of Norma and ...
Genome Annotation
... – Related to this is the concept that paired regions (stems) will be conserved across species lines even if the individual bases aren’t conserved. That is, if there is an A-U pairing on one species, the same position might be occupied by a G-C in another species. • This is an example of concerted ev ...
... – Related to this is the concept that paired regions (stems) will be conserved across species lines even if the individual bases aren’t conserved. That is, if there is an A-U pairing on one species, the same position might be occupied by a G-C in another species. • This is an example of concerted ev ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... that this last discovery proved to be helpful in profiling suspects using DNA evidence. One isolated gene was found to produce a protein causing blue eyes while the normal form (allele) of the gene caused brown eyes. It was discovered that the mutant blue-eye colour was the result of any mutation in ...
... that this last discovery proved to be helpful in profiling suspects using DNA evidence. One isolated gene was found to produce a protein causing blue eyes while the normal form (allele) of the gene caused brown eyes. It was discovered that the mutant blue-eye colour was the result of any mutation in ...
The genetic basis of behavior
... Receptors Nerve growth factor Structural proteins (such as muscle) Enzymes involved in metabolic pathways that synthesize key substances such as neurotransmitters, steroid hormones, eye pigments, etc… Regulatory proteins that turn other genes on and off ...
... Receptors Nerve growth factor Structural proteins (such as muscle) Enzymes involved in metabolic pathways that synthesize key substances such as neurotransmitters, steroid hormones, eye pigments, etc… Regulatory proteins that turn other genes on and off ...
Control of Gene Expression and Cancer
... – Heterochromatin-inactive genes located within darkly staining portions of chromatin ex: Barr body – Euchromatin-loosely packed areas of active genes » Euchromatin still needs processing before transcription occurs » Chromatin remodeling complex pushes aside histone ...
... – Heterochromatin-inactive genes located within darkly staining portions of chromatin ex: Barr body – Euchromatin-loosely packed areas of active genes » Euchromatin still needs processing before transcription occurs » Chromatin remodeling complex pushes aside histone ...
Mendelian Genetics Activity Reference Sheet
... Of or relating to any chromosome other than the sex chromosomes; a characteristic inherited on any gene pair other than the sex chromosomes. Chromosome Pair (Homologous pair): A pair of chromosomes that are similar in form and function, but may vary in genetic composition due to allelic differences ...
... Of or relating to any chromosome other than the sex chromosomes; a characteristic inherited on any gene pair other than the sex chromosomes. Chromosome Pair (Homologous pair): A pair of chromosomes that are similar in form and function, but may vary in genetic composition due to allelic differences ...
teach-eng-mod2
... • No longer sees “genes” as static or simple phenomena • Genes interact dynamically with one another and with cellular and extracellular components to regulate body and brain functions • Genes turn on and off (“are expressed”) • Regulation of gene expression may be as important a contributor to dise ...
... • No longer sees “genes” as static or simple phenomena • Genes interact dynamically with one another and with cellular and extracellular components to regulate body and brain functions • Genes turn on and off (“are expressed”) • Regulation of gene expression may be as important a contributor to dise ...
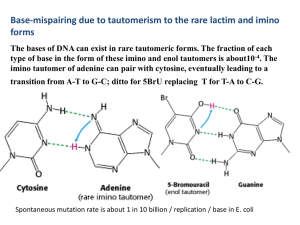
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... the natural hexoses in the same way that RNA relates to ribose, none exhibit discernible Watson-Crick base pairing between adenine and uracil Instead, some purine-purine self-pairing occurs, although much weaker than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent ...
... the natural hexoses in the same way that RNA relates to ribose, none exhibit discernible Watson-Crick base pairing between adenine and uracil Instead, some purine-purine self-pairing occurs, although much weaker than in homo-DNA. Guanine-cytosine pairing is far weaker than in RNA, hence incompetent ...
12-1 Chromosomes and Inheritance patterns
... • Each percent of the time they get split up is one map unit. • By comparing many genes scientists can figure out the order they are in ...
... • Each percent of the time they get split up is one map unit. • By comparing many genes scientists can figure out the order they are in ...
Object 4: Genetic fingerprinting
... to charge the suspect with the crime. Genetic fingerprinting also helps scientists identify bodies, by comparing their DNA to those of missing people or their relatives. It can also be used to work out whether people are related to each other, such as paternity testing. Pathology Genetics is the pat ...
... to charge the suspect with the crime. Genetic fingerprinting also helps scientists identify bodies, by comparing their DNA to those of missing people or their relatives. It can also be used to work out whether people are related to each other, such as paternity testing. Pathology Genetics is the pat ...
PDF - SystemsX.ch
... healthy life. “We will then compare these results with the human genome”, says Deplancke. Flies share around 60 percent of their genes with humans, and mice 80 percent, meaning that many of these results will be relevant for us, too. ...
... healthy life. “We will then compare these results with the human genome”, says Deplancke. Flies share around 60 percent of their genes with humans, and mice 80 percent, meaning that many of these results will be relevant for us, too. ...
3-8-heredity_and_environment
... if animals with trait are interbred with those that don’t, more of their offspring should have the trait then in a normal population ...
... if animals with trait are interbred with those that don’t, more of their offspring should have the trait then in a normal population ...
Genetics - MrGalusha.org
... if animals with trait are interbred with those that don’t, more of their offspring should have the trait then in a normal population ...
... if animals with trait are interbred with those that don’t, more of their offspring should have the trait then in a normal population ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.