Today`s Marketers Need to be DIVERSE
... • How firm’s can prepare a simple, one-page strategic plan for building business for their firm • Why marketing professionals are your firm’s biggest competitive advantage and your best ally for driving business • How extracting key elements from your firm’s strategic plan and aligning them with mar ...
... • How firm’s can prepare a simple, one-page strategic plan for building business for their firm • Why marketing professionals are your firm’s biggest competitive advantage and your best ally for driving business • How extracting key elements from your firm’s strategic plan and aligning them with mar ...
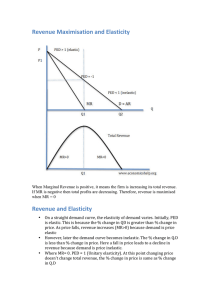
Revenue Maximisation and Elasticity Revenue
... Managers in charge may pursue other objectives. Legal Barriers. A key patent may prevent other firms developing a strong brand name. Alternatively some industries may be a legal monopoly like Royal Mail ...
... Managers in charge may pursue other objectives. Legal Barriers. A key patent may prevent other firms developing a strong brand name. Alternatively some industries may be a legal monopoly like Royal Mail ...
walt-disney-case-study
... usually for everybody to see and experience (although they are mainly for children) and before Eisner, there were not a very important cost reduction policy. Product quality was always on top and Disney tried to always have the best. Many forms of competitive advantage cannot be sustained indefinite ...
... usually for everybody to see and experience (although they are mainly for children) and before Eisner, there were not a very important cost reduction policy. Product quality was always on top and Disney tried to always have the best. Many forms of competitive advantage cannot be sustained indefinite ...
Managerial Economics
... behavior & structure of firms & industries • Provides foundation for understanding strategic decisions through application of game theory ...
... behavior & structure of firms & industries • Provides foundation for understanding strategic decisions through application of game theory ...
Evaluating a Firm`s Internal Capabilities
... • how do these strengths & weaknesses compare to competitors? ...
... • how do these strengths & weaknesses compare to competitors? ...
Unit 4, Lesson 10 Competition
... take a piece of the pie Competition lowers the price until it just covers the costs (opportunity cost of capital included) ...
... take a piece of the pie Competition lowers the price until it just covers the costs (opportunity cost of capital included) ...
Lecture 1 Practice Question Answers
... 5. In the diagram below, dark lines indicate the starting position. The lighter lines (with prime symbols next to them) indicate the final position. Notice that in the final position, the price line goes through the very lowest point on the ATC curve, which means the firm is making zero profits. ...
... 5. In the diagram below, dark lines indicate the starting position. The lighter lines (with prime symbols next to them) indicate the final position. Notice that in the final position, the price line goes through the very lowest point on the ATC curve, which means the firm is making zero profits. ...
defence economic trends in the pacific
... resources (eg, unique core competencies or superior dynamic capabilities) It stresses that differences in firms’ resource endowments cause differences in economic performance and that sustainable competitive advantage (as demonstrated by the stream of economic rents) results from the possession of ...
... resources (eg, unique core competencies or superior dynamic capabilities) It stresses that differences in firms’ resource endowments cause differences in economic performance and that sustainable competitive advantage (as demonstrated by the stream of economic rents) results from the possession of ...
Perfect Competition Script
... business there is a perfect substitute ready to take your place and if you raise your prices than people would just shop elsewhere. ...
... business there is a perfect substitute ready to take your place and if you raise your prices than people would just shop elsewhere. ...
Motorcycle for the would-be Ferrari driver : Italian, fast and, of course
... Museum, events, stores, racing, advertising and Ducati owners club ...
... Museum, events, stores, racing, advertising and Ducati owners club ...
Managerial Economics
... behavior & structure of firms & industries • Provides foundation for understanding strategic decisions through application of game theory ...
... behavior & structure of firms & industries • Provides foundation for understanding strategic decisions through application of game theory ...
Strategy - BYU Marriott School
... II. Operational planning-- looking at current decisions. marketing mix decisions after start up of product. ...
... II. Operational planning-- looking at current decisions. marketing mix decisions after start up of product. ...
Selecting a Marketing Strategy
... There is no perfect marketing strategy. The key is that the firm develops its strengths and tries to eliminate its weaknesses (whilst still taking account of opportunities and threats which may arise). In short, the marketing strategy should match a firm’s internal strengths and external market oppo ...
... There is no perfect marketing strategy. The key is that the firm develops its strengths and tries to eliminate its weaknesses (whilst still taking account of opportunities and threats which may arise). In short, the marketing strategy should match a firm’s internal strengths and external market oppo ...
Recl 3p40 Lecture 9
... -not everyone is the same, and they do not all want the same thing -Health care, in theory but doesn’t really work -single-segmented segmentation selecting a single segment to target -if the segment is small, this may be considered a “niche” strategy -small businesses , don’t have money for mixed ma ...
... -not everyone is the same, and they do not all want the same thing -Health care, in theory but doesn’t really work -single-segmented segmentation selecting a single segment to target -if the segment is small, this may be considered a “niche” strategy -small businesses , don’t have money for mixed ma ...
Competitive Advantage Management Level
... collaboration among staff, customers and suppliers. Basically it builds upon the relationship architecture of the firm ...
... collaboration among staff, customers and suppliers. Basically it builds upon the relationship architecture of the firm ...
03 - CANVAS- Environmental factors
... The external forces that directly or indirectly influence a firm’s acquisition and allocation of resources and its creation of products ...
... The external forces that directly or indirectly influence a firm’s acquisition and allocation of resources and its creation of products ...
download
... needs and wants: Government, social change, economic shifts, technology etc. • These factors are often noncontrollable but can have a major impact on purchasing decisions ...
... needs and wants: Government, social change, economic shifts, technology etc. • These factors are often noncontrollable but can have a major impact on purchasing decisions ...
Strategic Marketing Planning
... Developing Marketing strategies Planning Marketing Programs Managing the Marketing Effort ...
... Developing Marketing strategies Planning Marketing Programs Managing the Marketing Effort ...
Business Strategy
... Explain the nature and value of a market focus strategy Illustrate how a firm can pursue both low-cost and differentiation strategies Identify requirements for business success at different stages of industry evolution Determine good business strategies in fragmented and global industries Decide whe ...
... Explain the nature and value of a market focus strategy Illustrate how a firm can pursue both low-cost and differentiation strategies Identify requirements for business success at different stages of industry evolution Determine good business strategies in fragmented and global industries Decide whe ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... care centers and palliative medicine. Similarly, the Technological advances have an impactful role on the growth and profitability of healthcare providers. In the healthcare industry at large and in hospital settings in particular, technological growth is key in providing medical care. Hospitals that ...
... care centers and palliative medicine. Similarly, the Technological advances have an impactful role on the growth and profitability of healthcare providers. In the healthcare industry at large and in hospital settings in particular, technological growth is key in providing medical care. Hospitals that ...
download soal
... a. Data captured by legacy systems produces primarily information describing what happened in the past. b. Data captured by legacy systems is still valuable. c. Legacy data cannot be converted to new technologies. d. Some legacy data may only exist as paper printouts. 12. The standard bit mapped ima ...
... a. Data captured by legacy systems produces primarily information describing what happened in the past. b. Data captured by legacy systems is still valuable. c. Legacy data cannot be converted to new technologies. d. Some legacy data may only exist as paper printouts. 12. The standard bit mapped ima ...
Economics
... Human Resources Affect on Business How do employers deal with a shortage of workers for a certain job or profession? ...
... Human Resources Affect on Business How do employers deal with a shortage of workers for a certain job or profession? ...
Chapter 14: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
... • Since in long-run, the monopolistically competitive firm produces on the downward sloping portion of ATC, MC is below ATC. Since P=ATC in long-run, MC < ATC = P and thus MC < P. Monopolistic competition and the welfare of society Is monopolistic competition desirable from the standpoint of society ...
... • Since in long-run, the monopolistically competitive firm produces on the downward sloping portion of ATC, MC is below ATC. Since P=ATC in long-run, MC < ATC = P and thus MC < P. Monopolistic competition and the welfare of society Is monopolistic competition desirable from the standpoint of society ...