![ch10-Energy [Repaired]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008777902_1-68ae696e4b65996dd46398516c774b8d-300x300.png)
Derivation of the BET and Langmuir Isotherms
... low pressures the nitrogen molecules begin to fill the slots. As the pressure increases, more nitrogen gets adsorbed as can be seen in the near linear low pressure part of the na /nm vs P curve. As the pressure continues to increase, the slots fill up and eventually the surface is covered. At this p ...
... low pressures the nitrogen molecules begin to fill the slots. As the pressure increases, more nitrogen gets adsorbed as can be seen in the near linear low pressure part of the na /nm vs P curve. As the pressure continues to increase, the slots fill up and eventually the surface is covered. At this p ...
Precision Assessment of Surface Coating Roughness Height
... To compare E{St } with the corresponding rough surface profile parameter let’s examine an isotropic surface case, when c=1. The curves given on Fig. 1 show the average absolute maximums of surface (a) and its profile (b). We see that the total height of profile Rt, which is set on the determined len ...
... To compare E{St } with the corresponding rough surface profile parameter let’s examine an isotropic surface case, when c=1. The curves given on Fig. 1 show the average absolute maximums of surface (a) and its profile (b). We see that the total height of profile Rt, which is set on the determined len ...
Calculus 3 Lecture Notes, Section 12.1
... information about a surface z f x, y that lives in 3D space. A contour plot consists of a number of level curves for the surface. Specifically, given a function of two variables, z f x, y , a level curve is the (2D) graph of the curve f x, y c , for some constant c. This amounts to in ...
... information about a surface z f x, y that lives in 3D space. A contour plot consists of a number of level curves for the surface. Specifically, given a function of two variables, z f x, y , a level curve is the (2D) graph of the curve f x, y c , for some constant c. This amounts to in ...
This exam covers Ahrens Chapters 7, 8, 10, and 12, plus related
... 1. The merging of liquid cloud droplets by collision is called: a. coalescence b. riming c. accretion d. deposition 2. The amount of pressure change that occurs over a given horizontal distance is called the: a. pressure tendency b. Coriolis parameter c. pressure gradient d. potential gradient e. sl ...
... 1. The merging of liquid cloud droplets by collision is called: a. coalescence b. riming c. accretion d. deposition 2. The amount of pressure change that occurs over a given horizontal distance is called the: a. pressure tendency b. Coriolis parameter c. pressure gradient d. potential gradient e. sl ...
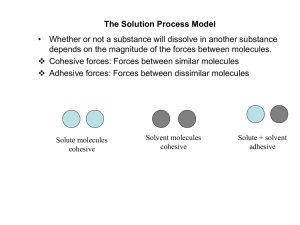
Surface tension
Surface tension is the elastic tendency of liquids which makes them acquire the least surface area possible. Surface tension is an important property that markedly influences many ecosystems. Surface tension is responsible, for example, when an object or insect (e.g. water striders) that is denser than water is able to float or run along the water surface.At liquid-air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of water molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). The net effect is an inward force at its surface that causes water to behave as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. Because of the relatively high attraction of water molecules for each other, water has a high surface tension (72.8 millinewtons per meter at 20 °C) compared to that of most other liquids. Surface tension is an important factor in the phenomenon of capillarity.Surface tension has the dimension of force per unit length, or of energy per unit area. The two are equivalent—but when referring to energy per unit of area, people use the term surface energy—which is a more general term in the sense that it applies also to solids and not just liquids.In materials science, surface tension is used for either surface stress or surface free energy.