24 Money Price Infl.tst - U of L Personal Web Sites
... B) fluctuate in value, are riskier and therefore carry a higher interest rate. C) bear a lower interest rate. D) can be sold more quickly. E) are more readily convertible to cash but take longer to sell. Topic: The Banking System 44) Which of the following statements about depository institutions is ...
... B) fluctuate in value, are riskier and therefore carry a higher interest rate. C) bear a lower interest rate. D) can be sold more quickly. E) are more readily convertible to cash but take longer to sell. Topic: The Banking System 44) Which of the following statements about depository institutions is ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES GOLD, FIAT MONEY, AND PRICE STABILITY
... gold. Gold cover for currency issue was eliminated in the United States in 1968 and the final link with gold was cut in August 1971 when President Nixon permanently closed the gold window. Gold has no monetary role anywhere in the world since the 1970s. Today’s economies use fiat money and base thei ...
... gold. Gold cover for currency issue was eliminated in the United States in 1968 and the final link with gold was cut in August 1971 when President Nixon permanently closed the gold window. Gold has no monetary role anywhere in the world since the 1970s. Today’s economies use fiat money and base thei ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES MONETARY POLICY IN THE INFORMATION ECONOMY Michael Woodford
... presumably the signal is clear only insofar as a non-trivial price movement can be caused.2 But while it is certainly true that effective signaling of government policy intentions is of great value, it would be odd to lament improvements in the timeliness of private-sector information about governme ...
... presumably the signal is clear only insofar as a non-trivial price movement can be caused.2 But while it is certainly true that effective signaling of government policy intentions is of great value, it would be odd to lament improvements in the timeliness of private-sector information about governme ...
Economic and Social Council African Union
... transactions costs when levels of intra-regional trade and investment flows are high – i.e. between countries that have close economic relationships. The main economic costs arise when countries have different economic structures (and hence are exposed to different exogenous shocks), are not well di ...
... transactions costs when levels of intra-regional trade and investment flows are high – i.e. between countries that have close economic relationships. The main economic costs arise when countries have different economic structures (and hence are exposed to different exogenous shocks), are not well di ...
Capital Controls in Brazil: Effective? by Marcos Chamon (IMF) and
... flight and help to accumulate foreign reserves. With the low rates prevailing in the US, capital started flowing in the country. So much so, that, starting in 1993, controls on capital inflows were enacted. Unlike the Chilean or Colombian capital controls, which took the form of unremunerated reserv ...
... flight and help to accumulate foreign reserves. With the low rates prevailing in the US, capital started flowing in the country. So much so, that, starting in 1993, controls on capital inflows were enacted. Unlike the Chilean or Colombian capital controls, which took the form of unremunerated reserv ...
What Has Government Done to Our Money?
... can now compare the market worth of each good to that of every other good. If a TV set exchanges for three ounces of gold, and an automobile exchanges for sixty ounces of gold, then everyone can see that one automobile is “worth” twenty TV sets on the market. These exchange-ratios are prices, and th ...
... can now compare the market worth of each good to that of every other good. If a TV set exchanges for three ounces of gold, and an automobile exchanges for sixty ounces of gold, then everyone can see that one automobile is “worth” twenty TV sets on the market. These exchange-ratios are prices, and th ...
III. Analysis of International Investment Positions
... A second notable fact is the importance of capital gains and losses in explaining the dynamics of the external position. These are primarily due to exchange rate fluctuations and changes in stock market values, which were substantial during this period. In our sample, a remarkable case is Finland, w ...
... A second notable fact is the importance of capital gains and losses in explaining the dynamics of the external position. These are primarily due to exchange rate fluctuations and changes in stock market values, which were substantial during this period. In our sample, a remarkable case is Finland, w ...
DP2004/01 Estimating a time varying neutral real interest rate for New Zealand
... and Matthew Shapiro. Remaining errors and omissions are our own. © Reserve Bank of New Zealand ...
... and Matthew Shapiro. Remaining errors and omissions are our own. © Reserve Bank of New Zealand ...
INFLATION TARGETING IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES Ferya KADIOĞLU Nilüfer ÖZDEMİR
... exchange rate of its currency to that of large, low inflation country is one of the methods to reduce inflation and keep it low. Due to its simple and easily understood framework, exchange rate targeting has gained popularity between the developed and developing countries in the past. It has several ...
... exchange rate of its currency to that of large, low inflation country is one of the methods to reduce inflation and keep it low. Due to its simple and easily understood framework, exchange rate targeting has gained popularity between the developed and developing countries in the past. It has several ...
A New Look at Pass-through
... The way the exchange rate interacts with the real economy depends critically on exchange rate passthrough, the degree to which exchange rate changes are passed through to price level changes. Our typical view of pass-through (notional pass-through) is one where the exchange rate changes for an exoge ...
... The way the exchange rate interacts with the real economy depends critically on exchange rate passthrough, the degree to which exchange rate changes are passed through to price level changes. Our typical view of pass-through (notional pass-through) is one where the exchange rate changes for an exoge ...
What Determines Government Spending Multipliers?
... exploit variation in economic conditions across space and time to gauge their impact on fiscal policy transmission. In a first step, we estimate a fiscal policy rule that is meant to describe the statistical process of government spending and provide estimates of spending shocks. The rule we conside ...
... exploit variation in economic conditions across space and time to gauge their impact on fiscal policy transmission. In a first step, we estimate a fiscal policy rule that is meant to describe the statistical process of government spending and provide estimates of spending shocks. The rule we conside ...
Monetary Policy in the Information Economy
... rate of output, both conditional upon public information at date t. The way in which output and inflation depend upon these quantities is completely independent of the extent to which any of the information available at date t may have been anticipated at earlier dates. Thus, signaling in advance th ...
... rate of output, both conditional upon public information at date t. The way in which output and inflation depend upon these quantities is completely independent of the extent to which any of the information available at date t may have been anticipated at earlier dates. Thus, signaling in advance th ...
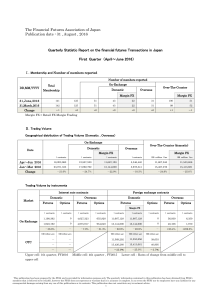
The Financial Futures Association of Japan Publication date : 31
... ・FFAJ converts the amounts of trading volume and open positions denominated in a foreign currency into JPY based on the value of each currency against the yen spot rate published by the Bank of Japan on the last day of the quarter. For currencies which do not have a yen spot rate published by the Ba ...
... ・FFAJ converts the amounts of trading volume and open positions denominated in a foreign currency into JPY based on the value of each currency against the yen spot rate published by the Bank of Japan on the last day of the quarter. For currencies which do not have a yen spot rate published by the Ba ...
... conditions of international capital mobility. A first part looks at the traditional view of inflation and payments problems as a reflection of fiscal problems and deficit finance. From there the analysis proceeds to the macro—dynamics of inflation stabilization under alternative polciy regimes. Infl ...
Digital currencies - Bank for International Settlements
... value transfers in the absence of a trusted third party. As such, various features of distributed ledger technology may have potential to improve some aspects of the efficiency of payment services and financial market infrastructures (FMIs) in general. In particular, these improvements might arise i ...
... value transfers in the absence of a trusted third party. As such, various features of distributed ledger technology may have potential to improve some aspects of the efficiency of payment services and financial market infrastructures (FMIs) in general. In particular, these improvements might arise i ...
ARREGLOS MONETARIOS EN ENTORNOS VOLÁTILES1
... hace la literatura entre regímenes de flexible inflation targeting y pure inflation targeting. Los pure inflation targeting son esencialmente los países industriales que no se preocupan por el tipo de cambio y adoptan entonces un inflation targeting puro en el sentido que no intervienen en el mercad ...
... hace la literatura entre regímenes de flexible inflation targeting y pure inflation targeting. Los pure inflation targeting son esencialmente los países industriales que no se preocupan por el tipo de cambio y adoptan entonces un inflation targeting puro en el sentido que no intervienen en el mercad ...
Effects of changes in the official interest rate in an inflation
... aggregate demand shock, the government could dampen aggregate demand by ...
... aggregate demand shock, the government could dampen aggregate demand by ...
Do Panels Help Solve the Purchasing Power Parity Puzzle?
... such as Im, Pesaran, and Shin (2003), which allow α to vary across countries. In that case, the null hypothesis is that all of the series contain a unit root and the alternative is that at least one of the series is stationary. In order to allow for contemporaneous correlation of the errors, Equati ...
... such as Im, Pesaran, and Shin (2003), which allow α to vary across countries. In that case, the null hypothesis is that all of the series contain a unit root and the alternative is that at least one of the series is stationary. In order to allow for contemporaneous correlation of the errors, Equati ...
Optimal Monetary and Fiscal Policy at the Zero Lower Bound in a
... As a response to the recent global financial crisis and its adverse consequences on output and employment, central banks of several small open economies engaged in counter cyclical policy response and lowered their conventional policy instrument, the short-term nominal interest rate. Many of these c ...
... As a response to the recent global financial crisis and its adverse consequences on output and employment, central banks of several small open economies engaged in counter cyclical policy response and lowered their conventional policy instrument, the short-term nominal interest rate. Many of these c ...
International Financial Integration* Philip R. Lane Institute for International Integration Studies
... A second notable fact is the importance of capital gains and losses in explaining the dynamics of the external position. These are primarily due to exchange rate fluctuations and changes in stock market values, which were substantial during this period. In our sample, a remarkable case is Finland, w ...
... A second notable fact is the importance of capital gains and losses in explaining the dynamics of the external position. These are primarily due to exchange rate fluctuations and changes in stock market values, which were substantial during this period. In our sample, a remarkable case is Finland, w ...
Chapter 7
... Nominal Exchange Rates--Choosing a Definition: Nominal exchange rates (E): price of foreign currency in terms of domestic currency ...
... Nominal Exchange Rates--Choosing a Definition: Nominal exchange rates (E): price of foreign currency in terms of domestic currency ...
"Foreign Reserves and International Liquidity Under the Bretton Woods System"
... put forward in his Treaty on Money (1930), the idea that monetary reserves were held for precautionary motives in order to finance temporary balance of payments deficits became widespread. The other influential theory of reserves was formulated by Gustav Cassel who emphasized the link between the gr ...
... put forward in his Treaty on Money (1930), the idea that monetary reserves were held for precautionary motives in order to finance temporary balance of payments deficits became widespread. The other influential theory of reserves was formulated by Gustav Cassel who emphasized the link between the gr ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES THE ROLE OF THE EXCHANGE RATE REGIME
... Specifically, base-country interest rates that are 1 percentage point higher lead to a 0.20 percentage point decline in annual GDP growth in pegged countries as opposed to no change in countries with floats. Turning to the channels underlying this result, we find that base rates have an impact on d ...
... Specifically, base-country interest rates that are 1 percentage point higher lead to a 0.20 percentage point decline in annual GDP growth in pegged countries as opposed to no change in countries with floats. Turning to the channels underlying this result, we find that base rates have an impact on d ...