World History Center Research Library
... World History Resource Library The World History Center works to acquire textbooks on world history from publishers. These textbooks range from survey style textbooks to textbooks devoted to a particular issue/country within a global context. The intended collection of textbooks is meant to be a res ...
... World History Resource Library The World History Center works to acquire textbooks on world history from publishers. These textbooks range from survey style textbooks to textbooks devoted to a particular issue/country within a global context. The intended collection of textbooks is meant to be a res ...
AP World History : Sample Syllabus 1
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
AP World History : Sample Syllabus 1
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
Journal of World History, vol. 2, no. 1 (1991)
... argue why and how such a world system history can and should be undertaken—even if “world history in world-system style is likely to appear. . . as downright subversive” (Allardyce 1990, 69). But then so have been all new systemic departures. The idea of a world system since 1500 has indeed gained g ...
... argue why and how such a world system history can and should be undertaken—even if “world history in world-system style is likely to appear. . . as downright subversive” (Allardyce 1990, 69). But then so have been all new systemic departures. The idea of a world system since 1500 has indeed gained g ...
AHR Forum The Problem of Interactions in World
... Parsonian sociology from the 1950s brought an analytical focus on states, bureaucracies, and economic relations.!! The revival of academic Marxism in the 1960s brought an interdisciplinary concentration on political economy.> Meanwhile, John von Neumann and Ludwig von Bertalanffy led in publicizing ...
... Parsonian sociology from the 1950s brought an analytical focus on states, bureaucracies, and economic relations.!! The revival of academic Marxism in the 1960s brought an interdisciplinary concentration on political economy.> Meanwhile, John von Neumann and Ludwig von Bertalanffy led in publicizing ...
GRADE 9 WORLD HISTORY
... technology that occurred during the Greco-Roman, Indian, Islamic, and Chinese civilizations and trace the spread of these ideas to other civilizations; C. summarize the ideas in astronomy, mathematics, and architectural engineering that developed in Mesoamerica and ...
... technology that occurred during the Greco-Roman, Indian, Islamic, and Chinese civilizations and trace the spread of these ideas to other civilizations; C. summarize the ideas in astronomy, mathematics, and architectural engineering that developed in Mesoamerica and ...
UNIT ONE: ANCIENT WORLD—CIVILIZATIONS AND RELIGIONS
... - What assumptions did medieval Europe make regarding power, authority, governance, and law? - How did roles of men/women differ in medieval society? - What role did individual citizens play in feudal society? - How were decisions made about the use of scarce resources in medieval Europe ? - What pr ...
... - What assumptions did medieval Europe make regarding power, authority, governance, and law? - How did roles of men/women differ in medieval society? - What role did individual citizens play in feudal society? - How were decisions made about the use of scarce resources in medieval Europe ? - What pr ...
World Civilizations Dr. Rick Sherrod
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
AP World History : Sample Syllabus 1
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
... Students in this course must learn to view history thematically. The AP World History course is organized around five overarching themes that serve as unifying threads throughout the course, helping students to relate what is particular about each time period or society to a “big picture” of history ...
Chapter 4: iLEAP Social Studies, Grade 6
... • Identify and interpret primary source material—e.g., quotes, literature, artifacts • Distinguish the difference between a primary and secondary source World History • Hunter-gatherer societies—e.g., wandering and nomadic lifestyle, types of food hunted, use of animals for clothing and shelter • Bu ...
... • Identify and interpret primary source material—e.g., quotes, literature, artifacts • Distinguish the difference between a primary and secondary source World History • Hunter-gatherer societies—e.g., wandering and nomadic lifestyle, types of food hunted, use of animals for clothing and shelter • Bu ...
The Impact of Islamic Civilization and Culture in Europe During the
... recapture Jerusalem by the Christians. During this time, Europeans had enough opportunity to learn about Islamic civilization and its cultural and economic benefits. Although these were ended with the political and military victory of Muslims enabling them to keep their lands, Europeans were much be ...
... recapture Jerusalem by the Christians. During this time, Europeans had enough opportunity to learn about Islamic civilization and its cultural and economic benefits. Although these were ended with the political and military victory of Muslims enabling them to keep their lands, Europeans were much be ...
Ancient Civilizations
... early agrarian societies. B. Geography, People, and the Environment 6.2.8.B.1.a- Explain the various migratory patterns of hunters/gatherers who moved from Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas, and describe the impact of migration on their lives and on the shaping of societies. 6.2.8.B.1.b ...
... early agrarian societies. B. Geography, People, and the Environment 6.2.8.B.1.a- Explain the various migratory patterns of hunters/gatherers who moved from Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas, and describe the impact of migration on their lives and on the shaping of societies. 6.2.8.B.1.b ...
HIS 101 fall 2007 sy.. - The University of Southern Mississippi
... Sept 26 Writing Workshop Turn in typed introductory paragraph containing your thesis statement, three proofs, and concluding sentence. Sept 28 Writing Workshop (cont) Block 2 Religion. One of the characteristics of civilizations is organized religion. Religious traditions give a society guidance on ...
... Sept 26 Writing Workshop Turn in typed introductory paragraph containing your thesis statement, three proofs, and concluding sentence. Sept 28 Writing Workshop (cont) Block 2 Religion. One of the characteristics of civilizations is organized religion. Religious traditions give a society guidance on ...
THE INVENTION OF THE “WEST”
... hand in hand. It was “by means of the concept of Eastern Europe” that “the narrative of Western civilization transferred onto the Slavic nations many of the stereotypes and prejudices traditionally ascribed to the Orient” and thus invented “the West” in a process which Adamovsky has described as “Eu ...
... hand in hand. It was “by means of the concept of Eastern Europe” that “the narrative of Western civilization transferred onto the Slavic nations many of the stereotypes and prejudices traditionally ascribed to the Orient” and thus invented “the West” in a process which Adamovsky has described as “Eu ...
Understanding Curriculum Maps
... to embody all seven characteristics of a civilization. 3. Ancient Egypt and the Near East: The civilization of the ancient Egyptians developed in response to its desert environment and the flooding of the Nile River. The ancient Egyptians and the near East civilizations created well-organized and co ...
... to embody all seven characteristics of a civilization. 3. Ancient Egypt and the Near East: The civilization of the ancient Egyptians developed in response to its desert environment and the flooding of the Nile River. The ancient Egyptians and the near East civilizations created well-organized and co ...
Overview of the Bronze Age World
... • The Bronze Age primarily took place between 3500 BC and 1200 BC, and is traditionally divided into the Early Bronze Age (c.3500-2000 BC), Middle Bronze Age (c.2000-1600 BC), and Late Bronze Age (c.1600-1200 BC), with progressively more sophisticated metallurgy which culminates in the discovery of ...
... • The Bronze Age primarily took place between 3500 BC and 1200 BC, and is traditionally divided into the Early Bronze Age (c.3500-2000 BC), Middle Bronze Age (c.2000-1600 BC), and Late Bronze Age (c.1600-1200 BC), with progressively more sophisticated metallurgy which culminates in the discovery of ...
chapter-16-social-studies-curriculum
... Medieval Times to Today: 3.1 South America and the Incas Medieval Times to Today: 3.2 Cultures of Middle America Tenochtitlan: Inside the Aztec Capital ...
... Medieval Times to Today: 3.1 South America and the Incas Medieval Times to Today: 3.2 Cultures of Middle America Tenochtitlan: Inside the Aztec Capital ...
6th Grade - Staff and Faculty Websites
... movement, human-environment interaction, region). compares and contrasts early world civilizations in terms of human characteristics (e.g., people, religion, language, customs, government, agriculture, industry, architecture, arts, education). traces the movement (diffusion) from one region or cente ...
... movement, human-environment interaction, region). compares and contrasts early world civilizations in terms of human characteristics (e.g., people, religion, language, customs, government, agriculture, industry, architecture, arts, education). traces the movement (diffusion) from one region or cente ...
History
... Understand the effects of scientific and technological developments. Includes identifying major scientific and technological innovations that have influenced the development of human civilizations; analyzing the factors that have encouraged or discouraged scientific discovery and technological innov ...
... Understand the effects of scientific and technological developments. Includes identifying major scientific and technological innovations that have influenced the development of human civilizations; analyzing the factors that have encouraged or discouraged scientific discovery and technological innov ...
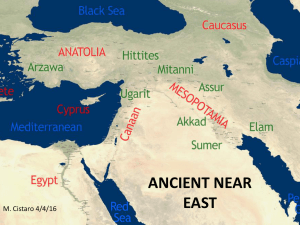
ancient near east - Mr. C at Hamilton
... • During the period states became increasingly large, until by the end the region was controlled by military empires who had conquered a number of different cultures. ...
... • During the period states became increasingly large, until by the end the region was controlled by military empires who had conquered a number of different cultures. ...
CULT STDS-11 E03
... Unit Statement: The student will use this unit to explore the rise of ancient civilizations along the Nile River Valley through discussing human environment actions and how they affect the growth of civilization in this region. Five Themes of Geography Focus: Movement and Human-Environment Interacti ...
... Unit Statement: The student will use this unit to explore the rise of ancient civilizations along the Nile River Valley through discussing human environment actions and how they affect the growth of civilization in this region. Five Themes of Geography Focus: Movement and Human-Environment Interacti ...
AP World History Syllabus
... 2. What is the importance of myth history in our understanding of early civilizations? 3. What changes were brought on by the Neolithic Revolution? 4. What are the characteristics of a civilization? 5. How did the geography and climate impact the development of early civilizations? 6. What were some ...
... 2. What is the importance of myth history in our understanding of early civilizations? 3. What changes were brought on by the Neolithic Revolution? 4. What are the characteristics of a civilization? 5. How did the geography and climate impact the development of early civilizations? 6. What were some ...
9/21/11 1 AP World History Syllabus
... is this the West and the Rest. World historians seek to understand change over time, cross cultural contact and exchange, comparative history, and regional practices that illuminate world systems. Devel ...
... is this the West and the Rest. World historians seek to understand change over time, cross cultural contact and exchange, comparative history, and regional practices that illuminate world systems. Devel ...
Sociology
... Economic: does this society employ a forced labor system? If not who does the work? What is the impact upon class and politics? What is the relationship between the economy and government? Is it a global economy? ...
... Economic: does this society employ a forced labor system? If not who does the work? What is the impact upon class and politics? What is the relationship between the economy and government? Is it a global economy? ...
Civilization

A civilization (US) or civilisation (UK) is any complex society characterized by urban development, social stratification, symbolic communication forms (typically, writing systems), and a perceived separation from and domination over the natural environment. Civilizations are intimately associated with and often further defined by other socio-politico-economic characteristics, including centralization, the domestication of both humans and other organisms, specialization of labor, culturally ingrained ideologies of progress and supremacism, monumental architecture, taxation, societal dependence upon agriculture, and expansionism.Historically, a civilization was an ""advanced"" culture in contrast to more supposedly barbarian, savage, or primitive cultures. In this broad sense, a civilization contrasts with non-centralized feudal or tribal societies, including the cultures of nomadic pastoralists or hunter-gatherers. As an uncountable noun, civilization also refers to the process of a society developing into a centralized, urbanized, stratified structure.Civilizations are organized in densely populated settlements divided into hierarchical social classes with a ruling elite and subordinate urban and rural populations, which engage in intensive agriculture, mining, small-scale manufacture and trade. Civilization concentrates power, extending human control over the rest of nature, including over other human beings.The earliest emergence of civilizations is generally associated with the final stages of the Neolithic Revolution, culminating in the relatively rapid process of state formation, a political development associated with the appearance of a governing elite. This neolithic technology and lifestyle was established first in the Middle East (for example at Göbekli Tepe, from about 9,130 BCE), and later in the Yangtze and Yellow river basins in China (for example the Pengtoushan culture from 7,500 BCE), and later spread. But similar ""revolutions"" also began independently from 7,000 BCE in such places as the Norte Chico civilization in Peru and Mesoamerica at the Balsas River. These were among the six civilizations worldwide that arose independently. The Neolithic Revolution in turn was dependent upon the development of sedentarism, the domestication of grains and animals and the development lifestyles which allowed economies of scale and the accumulation of surplus production by certain social sectors. The transition from ""complex cultures"" to ""civilisations"", while still disputed, seems to be associated with the development of state structures, in which power was further monopolised by an elite ruling class.Towards the end of the Neolithic period, various Chalcolithic civilizations began to rise in various ""cradles"" from around 3300 BCE. Chalcolithic Civilizations, as defined above, also developed in Pre-Columbian Americas and, despite an early start in Egypt, Axum and Kush, much later in Iron Age sub-Saharan Africa. The Bronze Age collapse was followed by the Iron Age around 1200 BCE, during which a number of new civilizations emerged, culminating in the Axial Age transition to Classical civilization. A major technological and cultural transition to modernity began approximately 1500 CE in western Europe, and from this beginning new approaches to science and law spread rapidly around the world.