hp calculators
... determining another number of different events that can be observed. The permutation formula shown in figure 2 below indicates the ordered permutations of n items taken r at a time. ...
... determining another number of different events that can be observed. The permutation formula shown in figure 2 below indicates the ordered permutations of n items taken r at a time. ...
Big-O examples
... Consider sorting. When the collection of data that we are sorting is large, it is very important that an efficient algorithm is used, since we would otherwise spend more time than necessary sorting. The algorithms discussed can be applied to any type of objects, including integers, floating point ...
... Consider sorting. When the collection of data that we are sorting is large, it is very important that an efficient algorithm is used, since we would otherwise spend more time than necessary sorting. The algorithms discussed can be applied to any type of objects, including integers, floating point ...
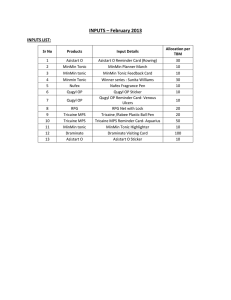
INPUTS – February 2013
... In patients with venous ulcers, reports state that 30% of the total number of isolates are anaerobes, where plain povidone-iodine offers incomplete treatment. In such cases, combination with Ornidazole is beneficial as it is effective against anaerobes, when applied topically. Sir, introducing Qugyl ...
... In patients with venous ulcers, reports state that 30% of the total number of isolates are anaerobes, where plain povidone-iodine offers incomplete treatment. In such cases, combination with Ornidazole is beneficial as it is effective against anaerobes, when applied topically. Sir, introducing Qugyl ...
slides
... We’d like to say “Algorithm A never takes more than f(n) steps for an input of size n” “Big-O” Notation gives worst-case, i.e., maximum, running times. A correct algorithm is a constructive upper bound on the complexity of the problem that it solves. ...
... We’d like to say “Algorithm A never takes more than f(n) steps for an input of size n” “Big-O” Notation gives worst-case, i.e., maximum, running times. A correct algorithm is a constructive upper bound on the complexity of the problem that it solves. ...
Percent Composition and empirical Formula
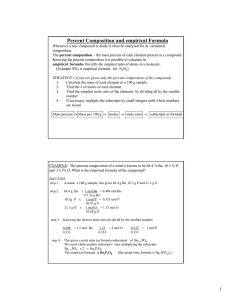
... 1. From grams of H2O and CO2 produced, perform a gram to mole conversion to find molar amounts of C in CO2 and H in H2O 2. Carry out mole to mass conversion to find the grams of C and H in the original sample 3. Subtract the sum of the masses of C and H from the original sample and determine the gra ...
... 1. From grams of H2O and CO2 produced, perform a gram to mole conversion to find molar amounts of C in CO2 and H in H2O 2. Carry out mole to mass conversion to find the grams of C and H in the original sample 3. Subtract the sum of the masses of C and H from the original sample and determine the gra ...
A Genetic Algorithm Approach to Solve for Multiple Solutions of
... Mutation operations, finds the individuals that have the best fitness values and combines them to produce individuals that offer better fitness values than their parents. This process continues until the population converges around the single individual that have the best fitness value. However, in a la ...
... Mutation operations, finds the individuals that have the best fitness values and combines them to produce individuals that offer better fitness values than their parents. This process continues until the population converges around the single individual that have the best fitness value. However, in a la ...
Humans, Computer, and Computational Complexity
... considered a kind of improvement. It is not difficult to see that for any type of computational problem there is at least one elegant program because in LISP, the value of a LISP expression is itself a LISP expression. There is a set of programs that give the same outputs, and while it would not mak ...
... considered a kind of improvement. It is not difficult to see that for any type of computational problem there is at least one elegant program because in LISP, the value of a LISP expression is itself a LISP expression. There is a set of programs that give the same outputs, and while it would not mak ...
Knapsack problem
The knapsack problem or rucksack problem is a problem in combinatorial optimization: Given a set of items, each with a mass and a value, determine the number of each item to include in a collection so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit and the total value is as large as possible. It derives its name from the problem faced by someone who is constrained by a fixed-size knapsack and must fill it with the most valuable items.The problem often arises in resource allocation where there are financial constraints and is studied in fields such as combinatorics, computer science, complexity theory, cryptography and applied mathematics.The knapsack problem has been studied for more than a century, with early works dating as far back as 1897. It is not known how the name ""knapsack problem"" originated, though the problem was referred to as such in the early works of mathematician Tobias Dantzig (1884–1956), suggesting that the name could have existed in folklore before a mathematical problem had been fully defined.