CAUSES OF EARTHQUAKES Ch. 3, pp. 75
... change is sudden and small (e.g., seismic waves) In ductile materials, elastic stress does not build up and earthquakes don!t happen ...
... change is sudden and small (e.g., seismic waves) In ductile materials, elastic stress does not build up and earthquakes don!t happen ...
Use of Copper-Base Shape Memory Alloys in Seismic Energy
... building collapse. This is normally accomplished by designing ductile structures, that is, structures that are capable of absorbing forces induced by earthquake motions through deformation at carefully detailed critical regions. A ductile behavior does, however, imply damage to these critical region ...
... building collapse. This is normally accomplished by designing ductile structures, that is, structures that are capable of absorbing forces induced by earthquake motions through deformation at carefully detailed critical regions. A ductile behavior does, however, imply damage to these critical region ...
DETERMINATION OF ACTIVATION ENERGY IN HOT
... laboratory casting over its height (or thickness 20 mm). Similarly the cylindrical specimens were oriented, where the areas with the as small as possible occurrence of the internal cavities were chosen, which complicated the preparation of specimens and their following hot forming. Uniaxial hot comp ...
... laboratory casting over its height (or thickness 20 mm). Similarly the cylindrical specimens were oriented, where the areas with the as small as possible occurrence of the internal cavities were chosen, which complicated the preparation of specimens and their following hot forming. Uniaxial hot comp ...
estimation of subsurface residual stress depth profiles via wideband
... altering the way that magnetic domain walls move; this results in a quantifiable change in the MBN emitted by the sample in the presence of an externally applied alternating magnetic field. The effective depth of emission of MBN for traditionally used frequency bands is very near the surface, hence ...
... altering the way that magnetic domain walls move; this results in a quantifiable change in the MBN emitted by the sample in the presence of an externally applied alternating magnetic field. The effective depth of emission of MBN for traditionally used frequency bands is very near the surface, hence ...
CTE3-Script.pdf
... Continuum Mechanics is the branch of mechanics used to investigate the deformation and flow of materials subjected to loads. Is a generalization of the classical Newtonian mechanics to macroscopic bodies. These bodies are considered formed by infinite collections of material points. As in classical ...
... Continuum Mechanics is the branch of mechanics used to investigate the deformation and flow of materials subjected to loads. Is a generalization of the classical Newtonian mechanics to macroscopic bodies. These bodies are considered formed by infinite collections of material points. As in classical ...
Chapter 12
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
Chapter 12
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
The Stillinger-Weber Potential
... Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations consists in solving the Newton’s equations for an assembly of particles interacting through an empirical potentiaL; ...
... Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations consists in solving the Newton’s equations for an assembly of particles interacting through an empirical potentiaL; ...
Chapter 9
... It is possible to change the shape or size (or both) of an object through the application of external forces When the forces are removed, the object tends to its original shape ...
... It is possible to change the shape or size (or both) of an object through the application of external forces When the forces are removed, the object tends to its original shape ...
Lecture 7 Mechanical Properties of Rocks
... on any given plane besides the principal stresses. In general, this is a three dimensional problem and can be done using mathematical tensors and vectors. In a special case where we can assume that the intermediate and minimum stresses are equal (for example below the ground surface), we can work ...
... on any given plane besides the principal stresses. In general, this is a three dimensional problem and can be done using mathematical tensors and vectors. In a special case where we can assume that the intermediate and minimum stresses are equal (for example below the ground surface), we can work ...
Strain Rate Dependent Flow Stress Characterization
... However, as the manageable stroke is very limited with the current piezoelectric press, it was imperative that the compression specimen was preloaded to a small value relative to the final loading force to ensure complete contact of the specimen with the punch. That position is set as the experiment ...
... However, as the manageable stroke is very limited with the current piezoelectric press, it was imperative that the compression specimen was preloaded to a small value relative to the final loading force to ensure complete contact of the specimen with the punch. That position is set as the experiment ...
Low Cycle Fatigue in Aluminum Foam with Notch
... Metal foams are a new material being used in industry. These materials are used in lightweight structures due to their high strength to weight and stiffness to weight ratios. However, these materials have not been fully characterized yet. This research examined Alporas, a closed cell aluminum foam, ...
... Metal foams are a new material being used in industry. These materials are used in lightweight structures due to their high strength to weight and stiffness to weight ratios. However, these materials have not been fully characterized yet. This research examined Alporas, a closed cell aluminum foam, ...
- Career Funda
... 2. The temperature of an ideal gas is directly proportional to which of the following? (A) Average translational kinetic energy of the molecules (B) Average velocity of the molecules (C) Average potential energy of the molecules (D) Average momentum of the molecules (E) None of the above Ans:A ...
... 2. The temperature of an ideal gas is directly proportional to which of the following? (A) Average translational kinetic energy of the molecules (B) Average velocity of the molecules (C) Average potential energy of the molecules (D) Average momentum of the molecules (E) None of the above Ans:A ...
Technical terms-3
... Electron volt (eV) A convenient unit of energy for atomic and subatomic systems. It is equivalent to the energy acquired by an electron when it falls through an electric potential of 1 volt. Electropositive For an atom, having a tendency to release valence electrons. Also, a term used to describe me ...
... Electron volt (eV) A convenient unit of energy for atomic and subatomic systems. It is equivalent to the energy acquired by an electron when it falls through an electric potential of 1 volt. Electropositive For an atom, having a tendency to release valence electrons. Also, a term used to describe me ...
Classes of materials
... In order to select the correct material of construction, the process environment to which the material will be exposed must be clearly defined. In addition to the main corrosive chemicals present, the following factors must be considered: 1. Temperature—affects corrosion rate and mechanical properti ...
... In order to select the correct material of construction, the process environment to which the material will be exposed must be clearly defined. In addition to the main corrosive chemicals present, the following factors must be considered: 1. Temperature—affects corrosion rate and mechanical properti ...
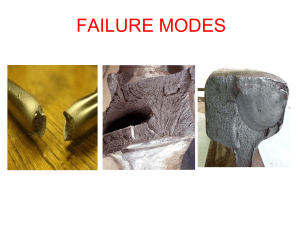
Failure Modes
... STRESS-STRAIN DIAGRAM FOR MS • The stress at which the material starts to behave in a non-elastic manner is called the elastic limit. • Between A & B, the material behaves elastically & regains the original position after removal of load. • Point ‘B’ denotes the elastic limit • As the load is incre ...
... STRESS-STRAIN DIAGRAM FOR MS • The stress at which the material starts to behave in a non-elastic manner is called the elastic limit. • Between A & B, the material behaves elastically & regains the original position after removal of load. • Point ‘B’ denotes the elastic limit • As the load is incre ...
Fang
... material after it breaks down, is it the same afterwards? • Draw the I vs. V curve for a metal vs. a semiconductor vs. an insulator. • What are the different types of defects in a material? ...
... material after it breaks down, is it the same afterwards? • Draw the I vs. V curve for a metal vs. a semiconductor vs. an insulator. • What are the different types of defects in a material? ...
Numerical Simulation of Fracture in Viscoelastic Materials Based on
... on minimization of the overall energy via the Griffith criterion. Use of the presented framework enables to study fracture behaviour of elastomers at different deformation rates. The experimental evidence from previous studies favors that the fracture toughness of non-strain-crystallising elastomers ...
... on minimization of the overall energy via the Griffith criterion. Use of the presented framework enables to study fracture behaviour of elastomers at different deformation rates. The experimental evidence from previous studies favors that the fracture toughness of non-strain-crystallising elastomers ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 23: material science and pressure
... Stress: Tells something about the force causing the deformation Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. Strain = Constant*Stress Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformati ...
... Stress: Tells something about the force causing the deformation Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. Strain = Constant*Stress Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformati ...
Presentation On MEMS Strain Sensors and Strain Engineered CMOS Professor
... Computer Engineering (ECE) and an Affiliate Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (MAE) at the University of Florida. His research interests include solid-state physical sensors and actuators, transducer noise, strained semiconductor devices, and reliability p ...
... Computer Engineering (ECE) and an Affiliate Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (MAE) at the University of Florida. His research interests include solid-state physical sensors and actuators, transducer noise, strained semiconductor devices, and reliability p ...
Mechanical Properties of Metals
... For engineering point of view: allows to predict the ability of a component or a structure to withstand the forces applied to it For science point of view: what makes materials strong → helps us to design a better new one Learn basic concepts for metals, which have the simplest behavior Return to it ...
... For engineering point of view: allows to predict the ability of a component or a structure to withstand the forces applied to it For science point of view: what makes materials strong → helps us to design a better new one Learn basic concepts for metals, which have the simplest behavior Return to it ...
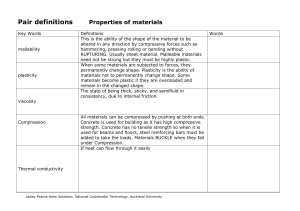
Pair definitions Properties of materials
... something such as rope, wire, or a structural beam to the point where it breaks When materials are subjected to forces they will change shape. To be elastic, the material must return to its original shape when the load is removed. Most materials are safe to use in their elastic state. A spring has t ...
... something such as rope, wire, or a structural beam to the point where it breaks When materials are subjected to forces they will change shape. To be elastic, the material must return to its original shape when the load is removed. Most materials are safe to use in their elastic state. A spring has t ...
Chapter 10 Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity continued
... Conceptual Example 8 Changing the Mass of a Simple Harmonic Oscilator The box rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The spring is stretched to x=A and released. When the box is passing through x=0, a second box of the same mass is attached to it. Discuss what happens to the (a) maximum speed ...
... Conceptual Example 8 Changing the Mass of a Simple Harmonic Oscilator The box rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The spring is stretched to x=A and released. When the box is passing through x=0, a second box of the same mass is attached to it. Discuss what happens to the (a) maximum speed ...
Viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like honey, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain when stretched and quickly return to their original state once the stress is removed. Viscoelastic materials have elements of both of these properties and, as such, exhibit time-dependent strain. Whereas elasticity is usually the result of bond stretching along crystallographic planes in an ordered solid, viscosity is the result of the diffusion of atoms or molecules inside an amorphous material.