SS5 - St. Anastasia School
... -1492: 3 ships to find a way to Asia across the Atlantic Ocean *ends up exploring the Caribbean Ocean islands -he makes multiple trips back between Spain and the islands Columbian Exchange: ...
... -1492: 3 ships to find a way to Asia across the Atlantic Ocean *ends up exploring the Caribbean Ocean islands -he makes multiple trips back between Spain and the islands Columbian Exchange: ...
Sea Floor Spreading
... proof of sea-floor spreading. The Glomar Challenger sent pipes 6 km deep in the ocean to drill hole sin the ocean floor. Scientists found that the farther away from the ridge, the older the rock sample were. ...
... proof of sea-floor spreading. The Glomar Challenger sent pipes 6 km deep in the ocean to drill hole sin the ocean floor. Scientists found that the farther away from the ridge, the older the rock sample were. ...
Uncertainty of Future Pacific Island Rainfall Explained
... international climate modeling groups, we saw that these competing mechanisms are the cause for uncertainty in the SPCZ rainfall projections.” ...
... international climate modeling groups, we saw that these competing mechanisms are the cause for uncertainty in the SPCZ rainfall projections.” ...
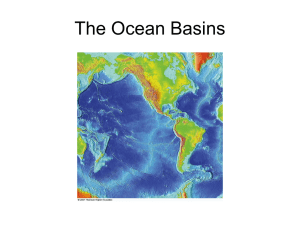
Chapter 9/10 Oceans
... 1 big ocean! • 5 ocean basins – Atlantic – Pacific – Indian – Antarctic (Southern) – Arctic (northern extension of the Atlantic) ...
... 1 big ocean! • 5 ocean basins – Atlantic – Pacific – Indian – Antarctic (Southern) – Arctic (northern extension of the Atlantic) ...
Study Guide for Oceanography Test 2016
... The bay at the mouth of a river would have the lowest salinity. The tropics or deep water in the poles will have the highest salinity content. The average salinity in the ocean is about 35 parts per thousand As you descend the water column pressure increases, temperature decreases. A current ...
... The bay at the mouth of a river would have the lowest salinity. The tropics or deep water in the poles will have the highest salinity content. The average salinity in the ocean is about 35 parts per thousand As you descend the water column pressure increases, temperature decreases. A current ...
Oceanography Notes Sheet for Presentation
... 1. ___________-largest, deepest, coldest, least salty. 2. ___________- second largest, shallow, warm, salty. 3. ___________- intermediate in depth, temperature, and salinity. The ____________Ocean near the North Pole and the _______________ Ocean near the South Pole contain vast expanses of sea ice. ...
... 1. ___________-largest, deepest, coldest, least salty. 2. ___________- second largest, shallow, warm, salty. 3. ___________- intermediate in depth, temperature, and salinity. The ____________Ocean near the North Pole and the _______________ Ocean near the South Pole contain vast expanses of sea ice. ...
Global ocean warming doubles in recent years : NBS English | News
... Global ocean warming doubles in recent years Half of the global ocean heat content increase since 1865 has occurred over the past two decades, says a new study. "In recent decades the ocean has continued to warm substantially, and with time the warming signal is reaching deeper into the ocean," said ...
... Global ocean warming doubles in recent years Half of the global ocean heat content increase since 1865 has occurred over the past two decades, says a new study. "In recent decades the ocean has continued to warm substantially, and with time the warming signal is reaching deeper into the ocean," said ...
Northeast Pacific Ocean
... • Temperature – The temp of the water is a very significant factor in the north pacific marine life, because it affects the chemical reactions that happen in the water. Most of the animals live in the top layer of the water because it is all about the same temperature, thanks to the energy from the ...
... • Temperature – The temp of the water is a very significant factor in the north pacific marine life, because it affects the chemical reactions that happen in the water. Most of the animals live in the top layer of the water because it is all about the same temperature, thanks to the energy from the ...
Unit 10 : Oceanography A. Ocean Water (salinity and density) 1
... A. Ocean Water (salinity and density) 1. Salinity – total amount of solid material dissolved in water (mainly salt) 2. ocean temperature depends on the solar radiation received and latitude 3. ocean density depends on temperature and salinity of water 4. cold water is more dense than warm water 5. d ...
... A. Ocean Water (salinity and density) 1. Salinity – total amount of solid material dissolved in water (mainly salt) 2. ocean temperature depends on the solar radiation received and latitude 3. ocean density depends on temperature and salinity of water 4. cold water is more dense than warm water 5. d ...
The Jet Stream and Ocean Currents
... In summer, the sun’s intensity is greatest over Asia. This creates a region of low pressure that rises from the land, sinks to the ocean, and brings extreme moisture in its return. In winter, insolation has its greatest intensity south of the equator. This creates a region of low pressure that rise ...
... In summer, the sun’s intensity is greatest over Asia. This creates a region of low pressure that rises from the land, sinks to the ocean, and brings extreme moisture in its return. In winter, insolation has its greatest intensity south of the equator. This creates a region of low pressure that rise ...
Ch. 16 PowerPoint
... Fa'aliga Seamount is located at 13? 4.8' S, 175? 15.8' W and is part of the Samoa Hotspot Trail on the Pacific Plate. It is 2370 m in height with the top at -1585 m and the ocean bottom at -3955 m. It is very small with a volume of 356 km3. The seamount is moderately elongated in a southeast, northw ...
... Fa'aliga Seamount is located at 13? 4.8' S, 175? 15.8' W and is part of the Samoa Hotspot Trail on the Pacific Plate. It is 2370 m in height with the top at -1585 m and the ocean bottom at -3955 m. It is very small with a volume of 356 km3. The seamount is moderately elongated in a southeast, northw ...
Do You Know Where You Are - New York Geographic Alliance
... 1. World Maps: Color the continents! North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, South America, Australia, Antarctica. Use a Wikki Stix to show the positions of the Equator and the Prime Meridian. Label the four hemispheres: Northern, Southern, Western, and Eastern. Place a sticker (star) where New York is ...
... 1. World Maps: Color the continents! North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, South America, Australia, Antarctica. Use a Wikki Stix to show the positions of the Equator and the Prime Meridian. Label the four hemispheres: Northern, Southern, Western, and Eastern. Place a sticker (star) where New York is ...
Unit 2 Vocabulary Review
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
Unit 2 Vocabulary Review
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
... a long, narrow, and deep depression on the ocean floor that forms when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another plate; trenches run parallel to volcanic island chains or to the coastlines of continents; also called a trench or a deep ocean trench ...
biome sydney 4
... OPEN OCEAN BIOME • Oceans are separated into separate zones. – Intertidal Zone is where the ocean and land meet. The pelagic zone is where one can find wales because it is very far away from the land in contrast to the intertidal zone, and tends to be very cold due to its deepness. – Next is the Be ...
... OPEN OCEAN BIOME • Oceans are separated into separate zones. – Intertidal Zone is where the ocean and land meet. The pelagic zone is where one can find wales because it is very far away from the land in contrast to the intertidal zone, and tends to be very cold due to its deepness. – Next is the Be ...
History of Oceanography
... John Ross took samples and animals in Baffin bay (Canada) Later James Ross took samples from Antarctic ocean bottom at 4.3 Miles John Ross and James Ross found that there are some bottom dwelling creatures in Baffin Bay and Antarctic Ocean. They discovered that deep Atlantic is uniformly cold. Forbe ...
... John Ross took samples and animals in Baffin bay (Canada) Later James Ross took samples from Antarctic ocean bottom at 4.3 Miles John Ross and James Ross found that there are some bottom dwelling creatures in Baffin Bay and Antarctic Ocean. They discovered that deep Atlantic is uniformly cold. Forbe ...
A gently sloping hill that connects the continental slope to the ocean
... slope to the ocean floor. This is also where sediments are deposited. ...
... slope to the ocean floor. This is also where sediments are deposited. ...
What`s Down There?
... floor plunges steeply. Marks the boundary between the oceanic crust and continental crust. Continental rise: separates the continental shelf from the ocean floor. ...
... floor plunges steeply. Marks the boundary between the oceanic crust and continental crust. Continental rise: separates the continental shelf from the ocean floor. ...
The Ocean
... • Effects on Earth’s climate: – Keep land cooler in summer (water takes time to cool off – Keep land warmer in winter (water takes time to cool down) ...
... • Effects on Earth’s climate: – Keep land cooler in summer (water takes time to cool off – Keep land warmer in winter (water takes time to cool down) ...
oceans
... World Ocean • Ocean and the origin of life – Stanley Miller’s apparatus – No oxygen (no photosynthesis!) in atmosphere ~ 4bya ...
... World Ocean • Ocean and the origin of life – Stanley Miller’s apparatus – No oxygen (no photosynthesis!) in atmosphere ~ 4bya ...
Unit 7 Chapter 23 Powerpoint
... 5 Major Oceans They are the: Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Artic and the Southern Oceans. Seas A sea is a smaller body of water that may be partially surrounded by land. Mediterranean Sea Caribbean Sea South China Sea ...
... 5 Major Oceans They are the: Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Artic and the Southern Oceans. Seas A sea is a smaller body of water that may be partially surrounded by land. Mediterranean Sea Caribbean Sea South China Sea ...
Ocean Floor
... • About 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered by oceans • Scientists study the ocean floor by using Sonar and satellites. Also use submersibles (like submarines except they can withstand lots of pressure) to collect samples of the ocean floor. Alvin is the name of one submersible. ...
... • About 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered by oceans • Scientists study the ocean floor by using Sonar and satellites. Also use submersibles (like submarines except they can withstand lots of pressure) to collect samples of the ocean floor. Alvin is the name of one submersible. ...
Pacific Ocean

The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south and is bounded by Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.At 165.25 million square kilometers (63.8 million square miles) in area, this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of the Earth's water surface and about one-third of its total surface area, making it larger than all of the Earth's land area combined. The equator subdivides it into the North Pacific Ocean and South Pacific Ocean, with two exceptions: the Galápagos and Gilbert Islands, while straddling the equator, are deemed wholly within the South Pacific. The Mariana Trench in the western North Pacific is the deepest point in the world, reaching a depth of 10,911 metres (35,797 ft).The eastern Pacific Ocean was first sighted by Europeans in the early 16th century when Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa crossed the Isthmus of Panama in 1513 and discovered the great ""southern sea"" which he named Mar del Sur. The ocean's current name was coined by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan during the Spanish circumnavigation of the world in 1521, as he encountered favourable winds on reaching the ocean. He therefore called it Mar Pacifico in Portuguese, meaning ""peaceful sea"".