Cadmium zinc telluride and its use as a nuclear radiation detector
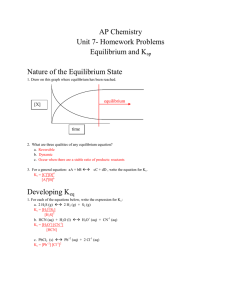
... incomplete hole collection, which results in less than full charge collection and a reduced current pulse. This in turn broadens the photopeak in the pulse height spectrum to the low energy side and thereby decreases the resolution of the spectrometer. 5. High-purity, homogeneous, defect-free materi ...
... incomplete hole collection, which results in less than full charge collection and a reduced current pulse. This in turn broadens the photopeak in the pulse height spectrum to the low energy side and thereby decreases the resolution of the spectrometer. 5. High-purity, homogeneous, defect-free materi ...
Chapter 2 1.Certain gases in the 293K and 9.97 × 104Pa when the
... radius of the small, Cs as the first Vice-group elements, the electronic structure of 6s1, After the loss of an electron into a stable structure 5s25p6 Rn> At At the halogens, while the Rn for eight electronic structure of inert gas, it is difficult to lose the outermost electron, and so the first i ...
... radius of the small, Cs as the first Vice-group elements, the electronic structure of 6s1, After the loss of an electron into a stable structure 5s25p6 Rn> At At the halogens, while the Rn for eight electronic structure of inert gas, it is difficult to lose the outermost electron, and so the first i ...
Solidification kinetics in undercooled pure iron and iron
... general, dendritic solidification in undercooled melts is mainly governed by nucleation and crystal growth. Namely the interfacial energy, the interfacial mobility and the crystal anisotropy are key factors for dendrite growth kinetics and dendritic morphology which will be investigated in the prese ...
... general, dendritic solidification in undercooled melts is mainly governed by nucleation and crystal growth. Namely the interfacial energy, the interfacial mobility and the crystal anisotropy are key factors for dendrite growth kinetics and dendritic morphology which will be investigated in the prese ...
Chemistry 143 Experiment #11 AcidBase Titration Dr. Caddell
... Because you will weigh out the KHP, knowing the molar mass of KHP allows you to calculate the moles of KHP. Because the mole to mole ratio between NaOH and KHP is 1:1, at the endpoint (when the solution first turns pink) the moles of KHP = moles of NaOH, so you know how many moles of NaOH you a ...
... Because you will weigh out the KHP, knowing the molar mass of KHP allows you to calculate the moles of KHP. Because the mole to mole ratio between NaOH and KHP is 1:1, at the endpoint (when the solution first turns pink) the moles of KHP = moles of NaOH, so you know how many moles of NaOH you a ...
Experimental Chemistry I
... which the volume of titrant added (with a given concentration) is exactly that required to neutralize the analyte (based on the stoichiometric relation between titrant and analyte). Procedure: Clean 50mL burette with deionized water and 1. rinse burette with calibration solution (1.000M) NaOH and fi ...
... which the volume of titrant added (with a given concentration) is exactly that required to neutralize the analyte (based on the stoichiometric relation between titrant and analyte). Procedure: Clean 50mL burette with deionized water and 1. rinse burette with calibration solution (1.000M) NaOH and fi ...
Numerical solution methods for shock and detonation jump
... Function PostShock fr: Demos - Matlab: demo PSfr.m Python: demo PSfr.py 2. Reactive shock wave. The region sufficiently far downstream from the shock wave is considered in thermodynamic equilibrium. Thermodynamics can be used to determine the chemical composition, but this is coupled to the conserva ...
... Function PostShock fr: Demos - Matlab: demo PSfr.m Python: demo PSfr.py 2. Reactive shock wave. The region sufficiently far downstream from the shock wave is considered in thermodynamic equilibrium. Thermodynamics can be used to determine the chemical composition, but this is coupled to the conserva ...
Spinodal decomposition

Spinodal decomposition is a mechanism for the rapid unmixing of a mixture of liquids or solids from one thermodynamic phase, to form two coexisting phases. As an example, consider a hot mixture of water and an oil. At high temperatures the oil and the water may mix to form a single thermodynamic phase in which water molecules are surrounded by oil molecules and vice versa. The mixture is then suddenly cooled to a temperature at which thermodynamic equilibrium favours an oil-rich phase coexisting with a water-rich phase. Spinodal decomposition then occurs when the mixture is such that there is essentially no barrier to nucleation of the new oil-rich and water-rich phases. In other words, the oil and water molecules immediately start to cluster together into microscopic water-rich and oil-rich clusters throughout the liquid. These clusters then rapidly grow and coalesce until there is a single macroscopic oil-rich cluster, the oil-rich phase, and a single water-rich cluster, the water-rich phase.Spinodal decomposition can be contrasted with nucleation and growth. There the initial formation of the microscopic clusters involves a large free energy barrier, and so can be very slow, and may occur as little as once in the initial phase, not throughout the phase, as happens in spinodal decomposition.Spinodal decomposition is of interest for two primary reasons. In the first place, it is one of the few phase transformations in solids for which there is any plausible quantitative theory. The reason for this is the inherent simplicity of the reaction. Since there is no thermodynamic barrier to the reaction inside of the spinodal region, the decomposition is determined solely by diffusion. Thus, it can be treated purely as a diffusional problem, and many of the characteristics of the decomposition can be described by an approximate analytical solution to the general diffusion equation.In contrast, theories of nucleation and growth have to invoke the thermodynamics of fluctuations. And the diffusional problem involved in the growth of the nucleus is far more difficult to solve, because it is unrealistic to linearize the diffusion equation.From a more practical standpoint, spinodal decomposition provides a means of producing a very finely dispersed microstructure that can significantly enhance the physical properties of the material.