The control of thin film deposition and recent
... time for adatoms to reach equilibrium sites. On the one hand we might consider molecular beam epitaxy (MBE), in which high substrate temperatures and low deposition rates promote the formation of high quality single crystal films whilst, on the other hand, one may use a high rate deposition source o ...
... time for adatoms to reach equilibrium sites. On the one hand we might consider molecular beam epitaxy (MBE), in which high substrate temperatures and low deposition rates promote the formation of high quality single crystal films whilst, on the other hand, one may use a high rate deposition source o ...
Physical Chemistry of Polymers: Entropy
... The importance of the surface, interfacial, and thin film properties of polymers has encouraged application of surfacesensitive or depth-profiling techniques. Some of these are familiar to the analytical chemistry communitysESCA, SIMS, reflection infrared, and ellipsometry. Others, particularly X-ra ...
... The importance of the surface, interfacial, and thin film properties of polymers has encouraged application of surfacesensitive or depth-profiling techniques. Some of these are familiar to the analytical chemistry communitysESCA, SIMS, reflection infrared, and ellipsometry. Others, particularly X-ra ...
CHAPTER 16
... molecules. The quantity of energy released as heat in this or any other reaction depends on the amounts of reactants and products. The quantity of energy as heat released during the formation of water from H2 and O2 is proportional to the quantity of water formed. Producing twice as much water vapor ...
... molecules. The quantity of energy released as heat in this or any other reaction depends on the amounts of reactants and products. The quantity of energy as heat released during the formation of water from H2 and O2 is proportional to the quantity of water formed. Producing twice as much water vapor ...
Controlled Crystal-Growth and Structures of Silicon
... the wire, see the following figure. Unlike conventional crystal growth with only two components or phases nanowires are often grown in a three phase system. The vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) growth mechanism describes such a three-phase system where the third phase is also important to the crystal growth ...
... the wire, see the following figure. Unlike conventional crystal growth with only two components or phases nanowires are often grown in a three phase system. The vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) growth mechanism describes such a three-phase system where the third phase is also important to the crystal growth ...
Ch 12 Solutions
... - Hydration is the attraction of ions for dipoles on H2O. It is the result of ion-dipole forces. The + H atom is attracted to anions (–), while the – O atom is attracted to cations (+). - Lattice energy is the attraction of oppositely charged ions to each other to form the ionic crystal. It is the ...
... - Hydration is the attraction of ions for dipoles on H2O. It is the result of ion-dipole forces. The + H atom is attracted to anions (–), while the – O atom is attracted to cations (+). - Lattice energy is the attraction of oppositely charged ions to each other to form the ionic crystal. It is the ...
Thermodynamics of Ion Association in the Saturated Solution of
... In turn, most of the theories that have been used to predict the extend of solubility of an ionic compound in a given solvent or in a mixed solvent and related ion association are based on changes in the electrostatic properties of the solvent, solute and ion solvation as well as on the ionic streng ...
... In turn, most of the theories that have been used to predict the extend of solubility of an ionic compound in a given solvent or in a mixed solvent and related ion association are based on changes in the electrostatic properties of the solvent, solute and ion solvation as well as on the ionic streng ...
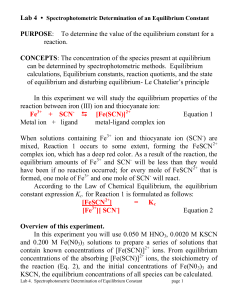
PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a
... 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How would the slope of the calibration curve (absorbance on the y-axis versus concentration of Fe(SCN)2+on the x-axis) be affected? How would this impact your Kc in Part C ...
... 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How would the slope of the calibration curve (absorbance on the y-axis versus concentration of Fe(SCN)2+on the x-axis) be affected? How would this impact your Kc in Part C ...
chemistry module p
... Making models of solids, liquids, gases using marbles or sand in a transparent container. Models help us to understand the behaviour and properties of solids, liquids and gases. The particles of a solid could be represented by gently moving the container so that the objects vibrate (rock backwards a ...
... Making models of solids, liquids, gases using marbles or sand in a transparent container. Models help us to understand the behaviour and properties of solids, liquids and gases. The particles of a solid could be represented by gently moving the container so that the objects vibrate (rock backwards a ...
1aUnit Two Handouts - Dunmore High School
... The key to writing correct net ionic equations is in knowing which substances to rewrite as ions and which substances to leave unchanged. Strong electrolytes exist in solution as ions and must always be written as ions for reactions in solution ...
... The key to writing correct net ionic equations is in knowing which substances to rewrite as ions and which substances to leave unchanged. Strong electrolytes exist in solution as ions and must always be written as ions for reactions in solution ...
Discussion Questions
... equations for the reaction, if any, that occurs when aqueous solutions of the following are mixed. a. ammonium sulfate and barium nitrate b. lead(II) nitrate and sodium chloride c. sodium phosphate and potassium nitrate d. sodium bromide and rubidium chloride e. copper(II) chloride and sod ...
... equations for the reaction, if any, that occurs when aqueous solutions of the following are mixed. a. ammonium sulfate and barium nitrate b. lead(II) nitrate and sodium chloride c. sodium phosphate and potassium nitrate d. sodium bromide and rubidium chloride e. copper(II) chloride and sod ...
Spinodal decomposition

Spinodal decomposition is a mechanism for the rapid unmixing of a mixture of liquids or solids from one thermodynamic phase, to form two coexisting phases. As an example, consider a hot mixture of water and an oil. At high temperatures the oil and the water may mix to form a single thermodynamic phase in which water molecules are surrounded by oil molecules and vice versa. The mixture is then suddenly cooled to a temperature at which thermodynamic equilibrium favours an oil-rich phase coexisting with a water-rich phase. Spinodal decomposition then occurs when the mixture is such that there is essentially no barrier to nucleation of the new oil-rich and water-rich phases. In other words, the oil and water molecules immediately start to cluster together into microscopic water-rich and oil-rich clusters throughout the liquid. These clusters then rapidly grow and coalesce until there is a single macroscopic oil-rich cluster, the oil-rich phase, and a single water-rich cluster, the water-rich phase.Spinodal decomposition can be contrasted with nucleation and growth. There the initial formation of the microscopic clusters involves a large free energy barrier, and so can be very slow, and may occur as little as once in the initial phase, not throughout the phase, as happens in spinodal decomposition.Spinodal decomposition is of interest for two primary reasons. In the first place, it is one of the few phase transformations in solids for which there is any plausible quantitative theory. The reason for this is the inherent simplicity of the reaction. Since there is no thermodynamic barrier to the reaction inside of the spinodal region, the decomposition is determined solely by diffusion. Thus, it can be treated purely as a diffusional problem, and many of the characteristics of the decomposition can be described by an approximate analytical solution to the general diffusion equation.In contrast, theories of nucleation and growth have to invoke the thermodynamics of fluctuations. And the diffusional problem involved in the growth of the nucleus is far more difficult to solve, because it is unrealistic to linearize the diffusion equation.From a more practical standpoint, spinodal decomposition provides a means of producing a very finely dispersed microstructure that can significantly enhance the physical properties of the material.