Answers to 2017 Chemistry Exam Review Compounds and
... element gains electrons for a smaller oxidation number. In a redox reaction (and oxidation always goes with reduction), electrons move from the oxidized to the reduced element. 88. In a redox reaction, the element whose oxidation number increases is oxidized; the element whose oxidation number decre ...
... element gains electrons for a smaller oxidation number. In a redox reaction (and oxidation always goes with reduction), electrons move from the oxidized to the reduced element. 88. In a redox reaction, the element whose oxidation number increases is oxidized; the element whose oxidation number decre ...
Reactions (The Basics)
... Generally take place between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution Generally 3 things happen: ...
... Generally take place between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution Generally 3 things happen: ...
Solutions - Seattle Central
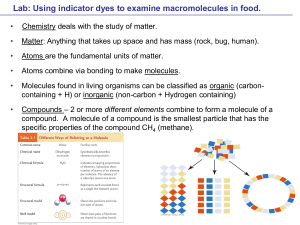
... Benedict's solution is a chemical indicator for simple sugars such as glucose: C6H12O6. Unlike some other indicators, Benedict’s solution does not work at room temperature - it must be heated first Details: ...
... Benedict's solution is a chemical indicator for simple sugars such as glucose: C6H12O6. Unlike some other indicators, Benedict’s solution does not work at room temperature - it must be heated first Details: ...
Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... • Each substance has unique physical properties • Examples – Sulfur appears as a yellow powder – The boiling point of water is 100 oC – Carbon monoxide is odorless ...
... • Each substance has unique physical properties • Examples – Sulfur appears as a yellow powder – The boiling point of water is 100 oC – Carbon monoxide is odorless ...
Final Exam Review
... A. there are two energy sublevels B. the f sublevel has 7 orbitals C. there are 3 s orbitals D. a maximum of 18 electrons are allowed ...
... A. there are two energy sublevels B. the f sublevel has 7 orbitals C. there are 3 s orbitals D. a maximum of 18 electrons are allowed ...
Review 1st Qtr KEY
... a. an s orbital. c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ...
... a. an s orbital. c. a combination of px and py orbitals. b. a px orbital. d. a combination of an s and a px orbital. ...
File - Kheriaty Chemistry
... b. What type of reaction is this? 22. a. Balance the reaction between sulfuric acid and ammonia (NH3) to yield ammonium sulfate. ...
... b. What type of reaction is this? 22. a. Balance the reaction between sulfuric acid and ammonia (NH3) to yield ammonium sulfate. ...
Notes for Types of Reactions:
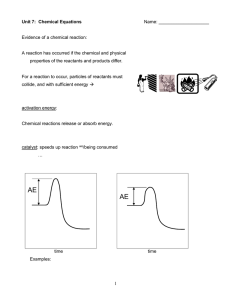
... chemical reaction = the _________ by which one or more substances are __________ into one or more _________ substances. in any chemical reaction, the _________ substances are known as the reactants and the __________ substances are known as the products. total mass of reactants = according to ...
... chemical reaction = the _________ by which one or more substances are __________ into one or more _________ substances. in any chemical reaction, the _________ substances are known as the reactants and the __________ substances are known as the products. total mass of reactants = according to ...
final exam review chapter 1-4
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
Document
... (E) none of the above 47. Lanthanide or rare earth elements have atoms or ions with partially filled: (A) s subshells (B) p subshells (C) d subshells (D) f subshells (E) g subshells 48. Which of the following liquids would make a good solvent for iodine, I2? (A) HCl (B) H2O (C) CH3OH (D) NH3 (E) CS ...
... (E) none of the above 47. Lanthanide or rare earth elements have atoms or ions with partially filled: (A) s subshells (B) p subshells (C) d subshells (D) f subshells (E) g subshells 48. Which of the following liquids would make a good solvent for iodine, I2? (A) HCl (B) H2O (C) CH3OH (D) NH3 (E) CS ...
Document
... A. the amount of product formed by a chemical reaction. B. whether or not a specific chemical reaction is possible. C. the coefficients needed to balance a chemical equation. ...
... A. the amount of product formed by a chemical reaction. B. whether or not a specific chemical reaction is possible. C. the coefficients needed to balance a chemical equation. ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... Ductile: can be pulled out into a long wire Conductivity: ability to transfer heat from one object to another ...
... Ductile: can be pulled out into a long wire Conductivity: ability to transfer heat from one object to another ...
elements of chemistry unit
... One type of chemical reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one species (species means atoms or groups of atoms) to another. REDOX REACTIONS These reactions are called oxidation reduction reactions. REDOX REACTIONS The species that loses electrons is oxidized and the species gaining electr ...
... One type of chemical reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one species (species means atoms or groups of atoms) to another. REDOX REACTIONS These reactions are called oxidation reduction reactions. REDOX REACTIONS The species that loses electrons is oxidized and the species gaining electr ...
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
... to its neighbors and the structure is very stable --> ionic compounds have a high melting point. When melted, ionic compounds can conduct electricity. ...
... to its neighbors and the structure is very stable --> ionic compounds have a high melting point. When melted, ionic compounds can conduct electricity. ...
HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... Define and predict products for combustion reactions Product testing - Know the tests for some common products such as oxygen, water, hydrogen and carbon dioxide: burning splint for oxygen, hydrogen or carbon dioxide, and lime water for carbon dioxide. Investigate mass of reactants and products in a ...
... Define and predict products for combustion reactions Product testing - Know the tests for some common products such as oxygen, water, hydrogen and carbon dioxide: burning splint for oxygen, hydrogen or carbon dioxide, and lime water for carbon dioxide. Investigate mass of reactants and products in a ...
1. What are micelles? Give two examples of micellar systems. Sol. A
... Anode reaction: 2Fe => 2Fe2+ + 4eCathode reaction: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- => 4OHThere are obviously different anodic and cathodic reactions for different alloys exposed to various environments. These half cell reactions are thought to occur (at least initially) at microscopic anodes and cathodes covering a ...
... Anode reaction: 2Fe => 2Fe2+ + 4eCathode reaction: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- => 4OHThere are obviously different anodic and cathodic reactions for different alloys exposed to various environments. These half cell reactions are thought to occur (at least initially) at microscopic anodes and cathodes covering a ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.