UNIFORM PARTICLES WITH A LARGE SURFACE AREA FORMED
... Table 2 contained about 70 –90% NH4⫹ and 30 –10% H3O⫹ of monovalent cations, i.e., the jarosite formula can be written as (NH4)1⫺x(H3O⫹)xFe3(SO4)2(OH)6 with 0.7 ⬍ x ⬍ 0.9. At pH ⬃ 3 and for a large urea/Fe ratio, schwertmannite is preferred. The above-mentioned pH values typical for the formation of ...
... Table 2 contained about 70 –90% NH4⫹ and 30 –10% H3O⫹ of monovalent cations, i.e., the jarosite formula can be written as (NH4)1⫺x(H3O⫹)xFe3(SO4)2(OH)6 with 0.7 ⬍ x ⬍ 0.9. At pH ⬃ 3 and for a large urea/Fe ratio, schwertmannite is preferred. The above-mentioned pH values typical for the formation of ...
Effects of Reaction Gel Dehydration on the Synthesis of Cu(NC5H5
... 1 and 2, while only the inclusion or exclusion of water varied. Despite the strong similarities in the reactions gels, these compounds show marked differences in structure and composition. The synthesis of 1 does not require the presence of water in the reaction pouch prior to reaction but does requ ...
... 1 and 2, while only the inclusion or exclusion of water varied. Despite the strong similarities in the reactions gels, these compounds show marked differences in structure and composition. The synthesis of 1 does not require the presence of water in the reaction pouch prior to reaction but does requ ...
127 - Chimica
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
... (CO),] (compound 4), identified spectroscopically (IR and 'H NMR), which was previously synthesized'" by photochemical hydrogenation of [Re2(CO)lo].The new method parallels that recently discovered8for the transformation of [Re4H6(CO)12]2into the unsaturated [Re4H5(CO),,]-. As in that case, the proc ...
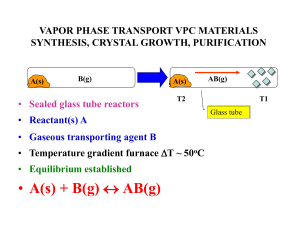
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... Self-organized <0001>oriented ZnO nanowires grown (epitaxially) on 1-3.5 nm thick Au coated sapphire substrate, dewetting makes Au nanoclusters – thickness of Au film controls diameter of Au nanocluster – ZnO nanowires grow from Au nanoclustrs - nanowire morphology related to ...
... Self-organized <0001>oriented ZnO nanowires grown (epitaxially) on 1-3.5 nm thick Au coated sapphire substrate, dewetting makes Au nanoclusters – thickness of Au film controls diameter of Au nanocluster – ZnO nanowires grow from Au nanoclustrs - nanowire morphology related to ...
Igneous rocks - Geo
... intrusive igneous rocks. That is because they intrude into the existing rocks. We would never see these rocks were it not for erosion stripping away the overlying rock. ...
... intrusive igneous rocks. That is because they intrude into the existing rocks. We would never see these rocks were it not for erosion stripping away the overlying rock. ...
Chem 1B Fa2015 FinalExam Review
... order rate law, such that: Rate = k[N2O5]. When the reaction was carried out at a certain temperature using an initial concentration [N2O5]0 = 0.100 M, the concentration of N2O5 after 5.00 minutes (300 seconds) was found to be 0.0125 M. (a) Determine the rate constant k (s–1) for the above reaction. ...
... order rate law, such that: Rate = k[N2O5]. When the reaction was carried out at a certain temperature using an initial concentration [N2O5]0 = 0.100 M, the concentration of N2O5 after 5.00 minutes (300 seconds) was found to be 0.0125 M. (a) Determine the rate constant k (s–1) for the above reaction. ...
Mineral Groups - cloudfront.net
... The roughly 1,000 silicate minerals make up over 90% of Earth’s crust. Silicates are by far the largest mineral group. Feldspar and quartz are the two most common silicate minerals. Both are extremely common rock-forming minerals. The basic building block for all silicate minerals is the silica tetr ...
... The roughly 1,000 silicate minerals make up over 90% of Earth’s crust. Silicates are by far the largest mineral group. Feldspar and quartz are the two most common silicate minerals. Both are extremely common rock-forming minerals. The basic building block for all silicate minerals is the silica tetr ...
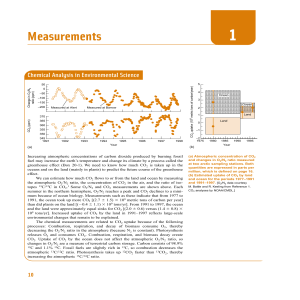
Measurements
... We can estimate how much CO2 flows to or from the land and ocean by measuring the atmospheric O2/N2 ratio, the concentration of CO2 in the air, and the ratio of isotopes 13C/12C in CO2.1 Some O2/N2 and CO2 measurements are shown above. Each summer in the northern hemisphere, O2/N2 reaches a peak and ...
... We can estimate how much CO2 flows to or from the land and ocean by measuring the atmospheric O2/N2 ratio, the concentration of CO2 in the air, and the ratio of isotopes 13C/12C in CO2.1 Some O2/N2 and CO2 measurements are shown above. Each summer in the northern hemisphere, O2/N2 reaches a peak and ...
1412_lecture_ch16 Fall_2014
... Complex-Ion Formation The formation constant, Kf, is the equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion from the aqueous metal ion and the ligands. The large value means that the complex ion is quite stable. When a large amount of NH3 is added to a solution of Ag+, you expect most of the A ...
... Complex-Ion Formation The formation constant, Kf, is the equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion from the aqueous metal ion and the ligands. The large value means that the complex ion is quite stable. When a large amount of NH3 is added to a solution of Ag+, you expect most of the A ...
Advances in Structural and Functional Analysis of Membrane
... Electron crystallography is the only electron cryomicroscopy (cryo EM) technique capable of delivering atomic resolution information for membrane proteins. Here protein structure is determined within the context of a lipid bilayer that closely mimics the native environment, and in which lipids can e ...
... Electron crystallography is the only electron cryomicroscopy (cryo EM) technique capable of delivering atomic resolution information for membrane proteins. Here protein structure is determined within the context of a lipid bilayer that closely mimics the native environment, and in which lipids can e ...
bicC-DNA manuscript
... crystallization conditions were performed using the hanging drop vapor diffusion method, equilibrating 2 l droplets against 1 ml of the reservoir solution. The optimized conditions for growing the three different crystals of GX9 (GX91, GX92 and GX93) and the AX8 crystal were as follows. For GX91, a ...
... crystallization conditions were performed using the hanging drop vapor diffusion method, equilibrating 2 l droplets against 1 ml of the reservoir solution. The optimized conditions for growing the three different crystals of GX9 (GX91, GX92 and GX93) and the AX8 crystal were as follows. For GX91, a ...
Solution
... ) will form an insoluble compound, calcium phosphate [Ca3(PO4)2], while the other product, KNO3, is soluble and remains in solution. Therefore, this is a precipitation reaction. We follow the stepwise procedure just outlined. Step 1: The balanced molecular equation for this reaction is ...
... ) will form an insoluble compound, calcium phosphate [Ca3(PO4)2], while the other product, KNO3, is soluble and remains in solution. Therefore, this is a precipitation reaction. We follow the stepwise procedure just outlined. Step 1: The balanced molecular equation for this reaction is ...
Copy of Minerals Fill in Notes
... Four Questions1. Is the substance ________ or not made from living or once living things? 2. Does the substance occur ________? It can’t be manufactured (steel). 3. Is the substance a solid in _________ form? 4. Does the substance have a consistent __________________? (ex: Fluorite has one Ca ion fo ...
... Four Questions1. Is the substance ________ or not made from living or once living things? 2. Does the substance occur ________? It can’t be manufactured (steel). 3. Is the substance a solid in _________ form? 4. Does the substance have a consistent __________________? (ex: Fluorite has one Ca ion fo ...
Name: ______KEY__________________ Date: ______ CHM 130
... 11. (6 pts) The graph to the right represents a temperature versus heat energy plot for a pure substance. Answer the following questions. a. What letter represents pure gas? _E___ b. What phase changes occur at letter B? __melting/freezing___________ c. What is the temperature of the boiling point o ...
... 11. (6 pts) The graph to the right represents a temperature versus heat energy plot for a pure substance. Answer the following questions. a. What letter represents pure gas? _E___ b. What phase changes occur at letter B? __melting/freezing___________ c. What is the temperature of the boiling point o ...
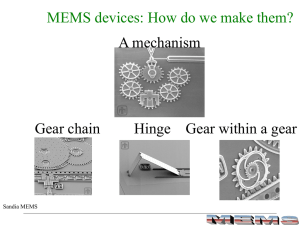
MEMS Processing
... Any MEMS device is made from the processes of deposition and removal of material e.g. a state-of-the art MEMS electric motor ...
... Any MEMS device is made from the processes of deposition and removal of material e.g. a state-of-the art MEMS electric motor ...
The Crystal Structure and Genesis of the Gold
... within several of the world’s major telluride districts. Detailed studies on the atomic structure of the gold telluride minerals began in 1935 with work on calaverite. Additional research on krennerite and sylvanite was conducted in the following years. The mineral class was then revisited in 1984, ...
... within several of the world’s major telluride districts. Detailed studies on the atomic structure of the gold telluride minerals began in 1935 with work on calaverite. Additional research on krennerite and sylvanite was conducted in the following years. The mineral class was then revisited in 1984, ...
Author`s personal copy
... pyrophosphate-dependent bacterial PFKs but does not show gene duplication typical of eukaryotes.25 A recent article describes the crystal structure of PFK from Pichia pastoris.26 The first useful crystals of ScPFK in the 12S form27 were obtained as part of this study. The 12S form is a product of th ...
... pyrophosphate-dependent bacterial PFKs but does not show gene duplication typical of eukaryotes.25 A recent article describes the crystal structure of PFK from Pichia pastoris.26 The first useful crystals of ScPFK in the 12S form27 were obtained as part of this study. The 12S form is a product of th ...
Properties of Systems in Equilibrium - Le
... salt solutions are mixed together resulting in the production of an insoluble salt. Notice that this process corresponds to a left shift of Reaction (11), and so Equation (12) can also be used to examine the conditions required for the precipitation of a solid to occur. We can denote the product [A+ ...
... salt solutions are mixed together resulting in the production of an insoluble salt. Notice that this process corresponds to a left shift of Reaction (11), and so Equation (12) can also be used to examine the conditions required for the precipitation of a solid to occur. We can denote the product [A+ ...
Minerals
... Solid substance – solids within temp ranges that are normal for Earth’s surface Crystalline structure – atoms or ions arranged in orderly & repetitive manner Definite chemical composition – most minerals are chemical compounds Generally considered inorganic – minerals generally do not come f ...
... Solid substance – solids within temp ranges that are normal for Earth’s surface Crystalline structure – atoms or ions arranged in orderly & repetitive manner Definite chemical composition – most minerals are chemical compounds Generally considered inorganic – minerals generally do not come f ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry: The Hydrosphere
... Acid-Base Reactions with Gas Formation – Some acid-base reactions produce carbon dioxide gas, CO2(g), along with water and salt. – When the base contains carbonate ion (CO32–) or hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3–), then the products of the acid-base reaction are a salt and H2CO3(aq), which breaks down ...
... Acid-Base Reactions with Gas Formation – Some acid-base reactions produce carbon dioxide gas, CO2(g), along with water and salt. – When the base contains carbonate ion (CO32–) or hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3–), then the products of the acid-base reaction are a salt and H2CO3(aq), which breaks down ...
Physical Properties of Minerals
... How do minerals form? • 1) Cooling of magma (hot, liquid rock and minerals inside the earth (from the mantle)) – Fast Cooling = No Crystals (mineraloids) – Medium Cooling = small crystals – Slow Cooling = large crystals ...
... How do minerals form? • 1) Cooling of magma (hot, liquid rock and minerals inside the earth (from the mantle)) – Fast Cooling = No Crystals (mineraloids) – Medium Cooling = small crystals – Slow Cooling = large crystals ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... Note: For all questions referring to solutions, assume that the solvent is water unless otherwise stated. Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then blacken the corre ...
... Note: For all questions referring to solutions, assume that the solvent is water unless otherwise stated. Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then blacken the corre ...
A Low-Fluorine Solution with the F/Ba Mole Ratio of 2 for the
... [5]. Such a slow process constitutes a serious barrier for industrial production. Lowering the fluorine content in the precursor solution is considered to be effective in shortening the time requirement during the pyrolysis step [7]. This idea has been realized in many groups by substituting fluorin ...
... [5]. Such a slow process constitutes a serious barrier for industrial production. Lowering the fluorine content in the precursor solution is considered to be effective in shortening the time requirement during the pyrolysis step [7]. This idea has been realized in many groups by substituting fluorin ...
Crystallization

Crystallization is the (natural or artificial) process of formation of solid crystals precipitating from a solution, melt or more rarely deposited directly from a gas. Crystallization is also a chemical solid–liquid separation technique, in which mass transfer of a solute from the liquid solution to a pure solid crystalline phase occurs. In chemical engineering crystallization occurs in a crystallizer. Crystallization is therefore an aspect of precipitation, obtained through a variation of the solubility conditions of the solute in the solvent, as compared to precipitation due to chemical reaction.