Chemistry 134 Problem Set Introduction
... 14.74 (a) List each of the elements in the nitrogen family and classify it as a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal. (b) Which member of the nitrogen family is the most abundant element in the Earth's atmosphere? (c) List the highest and lowest oxidation state for each member of the nitrogen family. 14.75 ...
... 14.74 (a) List each of the elements in the nitrogen family and classify it as a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal. (b) Which member of the nitrogen family is the most abundant element in the Earth's atmosphere? (c) List the highest and lowest oxidation state for each member of the nitrogen family. 14.75 ...
June Exam Review Material World
... 9. Which of the following is true about the periodic table? a) The period indicates the number of neutrons that an atom has b) The Group number indicates the number of electrons that an atom has c) The period indicates the number of protons that an atom has d) The Group number indicates the number o ...
... 9. Which of the following is true about the periodic table? a) The period indicates the number of neutrons that an atom has b) The Group number indicates the number of electrons that an atom has c) The period indicates the number of protons that an atom has d) The Group number indicates the number o ...
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the
... of Formation. The evolution of the size of the largest cluster for all BS is shown in Figure 2. It reveals a systematic increase of the aggregates’ size with time. Only for CH and TDCH a larger cluster dissociates temporarily to a smaller one (a pentamer to a tetramer) but is restored in ca. 20 ns. ...
... of Formation. The evolution of the size of the largest cluster for all BS is shown in Figure 2. It reveals a systematic increase of the aggregates’ size with time. Only for CH and TDCH a larger cluster dissociates temporarily to a smaller one (a pentamer to a tetramer) but is restored in ca. 20 ns. ...
1.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... Most chemical reactions and virtually all biological processes take place not between pure solids, liquids or gases, but rather among ions and molecules dissolved in water or other solvents (i.e. in solution). In this module we will therefore examine the various types of solutions and their properti ...
... Most chemical reactions and virtually all biological processes take place not between pure solids, liquids or gases, but rather among ions and molecules dissolved in water or other solvents (i.e. in solution). In this module we will therefore examine the various types of solutions and their properti ...
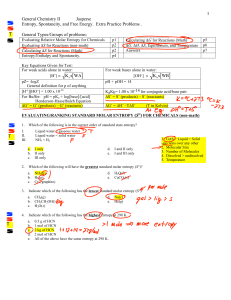
1 General Chemistry II Jasperse Entropy, Spontaneity, and Free
... 25. Hydrogen reacts with nitrogen to form ammonia (NH3) according to the reaction 3H2(g) + N2(g) D 2NH3(g) ...
... 25. Hydrogen reacts with nitrogen to form ammonia (NH3) according to the reaction 3H2(g) + N2(g) D 2NH3(g) ...
File
... aluminum oxide (Al2O3) forms on its surface. This layer prevents further reaction between Al and O2, and it is why Al does not corrode. ...
... aluminum oxide (Al2O3) forms on its surface. This layer prevents further reaction between Al and O2, and it is why Al does not corrode. ...
Experiment 1 - Melting Points - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... a physical property that can be used for its identification. It is a measure of the amount of kinetic energy (heat) that must be supplied to the particles of the substance in order to overcome the intermolecular forces (such as Van der Waals, dipole-dipole, and Hbonding) that confine them to the sol ...
... a physical property that can be used for its identification. It is a measure of the amount of kinetic energy (heat) that must be supplied to the particles of the substance in order to overcome the intermolecular forces (such as Van der Waals, dipole-dipole, and Hbonding) that confine them to the sol ...
Escaping the no man`s land: recent experiments on metastable
... and Angell noticed that many properties of stable and supercooled water (such as αP , or the isothermal compressibility κT , the heat capacity at constant pressure CP , etc. . . ) could be fitted by power laws which extrapolated to a common temperature of divergence of 228 K at atmospheric pressure, ...
... and Angell noticed that many properties of stable and supercooled water (such as αP , or the isothermal compressibility κT , the heat capacity at constant pressure CP , etc. . . ) could be fitted by power laws which extrapolated to a common temperature of divergence of 228 K at atmospheric pressure, ...
Stoichiometery
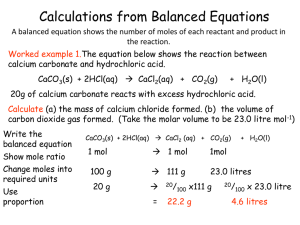
... A chemical equation is a recipe for making a molecule. This can be written in “shopping list” format: H2 + O2 → H2O But this doesn’t help with specific amounts ...
... A chemical equation is a recipe for making a molecule. This can be written in “shopping list” format: H2 + O2 → H2O But this doesn’t help with specific amounts ...
Core_Class_Science_Chemistry_for_the_web 838.3 KB
... Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes that give off radiation are called radioactive isotopes. A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elem ...
... Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes that give off radiation are called radioactive isotopes. A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elem ...
CHE 1402 Lab Manual
... molecules changes? 4. Write the ideal-gas equation and give the units for each term when R = 0.0821 L-atm /mol-K. 5. Show by mathematical equations how one can determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid by measurement of the pressure, volume, temperature, and weight of the liquid. 6. If 0.75 g of ...
... molecules changes? 4. Write the ideal-gas equation and give the units for each term when R = 0.0821 L-atm /mol-K. 5. Show by mathematical equations how one can determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid by measurement of the pressure, volume, temperature, and weight of the liquid. 6. If 0.75 g of ...
Modeling the Solubility of Nitrogen Dioxide in Water Using
... water provides an estimate of the number of proton-acceptor sites to be between 2 and 3, corresponding to molecular and ionic structures, respectively. We choose the average value of 2.5 for this number, which is quite unusual being a noninteger, but justifiable as it turns out to represent the binar ...
... water provides an estimate of the number of proton-acceptor sites to be between 2 and 3, corresponding to molecular and ionic structures, respectively. We choose the average value of 2.5 for this number, which is quite unusual being a noninteger, but justifiable as it turns out to represent the binar ...
Answer
... • In the spaces provided, explain the meanings of the following terms. You may use an equation or diagram where appropriate. (a) hydrogen bonding An unusually strong dipole-dipole interaction that forms when a hydrogen atom is bonded to one of the very electronegative atoms F, O or N. ...
... • In the spaces provided, explain the meanings of the following terms. You may use an equation or diagram where appropriate. (a) hydrogen bonding An unusually strong dipole-dipole interaction that forms when a hydrogen atom is bonded to one of the very electronegative atoms F, O or N. ...
IX Chemistry Chapter 02
... 1. Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter under goes changes. However, it has been found that in all chemical changes, there is no change in the mass of the substances being changed. For example, in iron (Fe) increase in weight on rusting is because of its combination with oxygen from the air and the i ...
... 1. Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter under goes changes. However, it has been found that in all chemical changes, there is no change in the mass of the substances being changed. For example, in iron (Fe) increase in weight on rusting is because of its combination with oxygen from the air and the i ...
2008 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For
... (e) In aqueous solution near-neutral pH, most of Glycine exists as a zwitterion as a result of an internal proton transfer. The very small K b arises from protonation of the carboxylate anion of the zwitterions, rather than the amine group, which is already protonated. ...
... (e) In aqueous solution near-neutral pH, most of Glycine exists as a zwitterion as a result of an internal proton transfer. The very small K b arises from protonation of the carboxylate anion of the zwitterions, rather than the amine group, which is already protonated. ...
Topic 1 - Coral Gables Senior High
... theory. This proposed the existence of a fire-like element that was released during these processes. The theory seemed to explain some of the observations of its time, although these were purely qualitative. It could not explain later quantitative data showing that substances actually gain rather th ...
... theory. This proposed the existence of a fire-like element that was released during these processes. The theory seemed to explain some of the observations of its time, although these were purely qualitative. It could not explain later quantitative data showing that substances actually gain rather th ...
Answer
... Under these conditions, calculate the energy per mole that is available from the splitting of ATP. With these concentrations, the reaction quotient, Q, is: ...
... Under these conditions, calculate the energy per mole that is available from the splitting of ATP. With these concentrations, the reaction quotient, Q, is: ...
Amount of substance
... a) reaction of hydrochloric acid (aq) with potassium hydroxide (aq) b) precipitation of silver iodide from reaction between silver nitrate (aq) and potassium iodide (aq) c) reaction of potassium carbonate (aq) with nitric acid (aq) d) precipitation of calcium hydroxide from reaction between sodium h ...
... a) reaction of hydrochloric acid (aq) with potassium hydroxide (aq) b) precipitation of silver iodide from reaction between silver nitrate (aq) and potassium iodide (aq) c) reaction of potassium carbonate (aq) with nitric acid (aq) d) precipitation of calcium hydroxide from reaction between sodium h ...
Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to an electric current being passed through the water.This technique can be used to make hydrogen fuel (hydrogen gas) and breathable oxygen; though currently most industrial methods make hydrogen fuel from natural gas instead.