In Class Overview of Chapter
... Please take some time to review state functions, the first law of thermodynamics, enthalpy and internal energy. In this chapter we will learn what determines the extent of a reaction. Thermodynamics is a powerful tool in chemistry, physics and engineering. In chapter 14, we learned about how fast re ...
... Please take some time to review state functions, the first law of thermodynamics, enthalpy and internal energy. In this chapter we will learn what determines the extent of a reaction. Thermodynamics is a powerful tool in chemistry, physics and engineering. In chapter 14, we learned about how fast re ...
AP Chemistry - Chagrin Falls Schools
... Major Projects: 5% each day; after five days, no credit will be given Everyday homework: 50% credit for a day late; after one day, no credit will be given Major Projects: 10% each day; after three days, no credit will be given Everyday homework: 50% for one day late; after the first day late, no cre ...
... Major Projects: 5% each day; after five days, no credit will be given Everyday homework: 50% credit for a day late; after one day, no credit will be given Major Projects: 10% each day; after three days, no credit will be given Everyday homework: 50% for one day late; after the first day late, no cre ...
MATTER-Ch. 3-homogeneous vs. heterogeneous, elements
... The most useful source of chemical information about the elements is a a. calculator. c. periodic table. b. table of metric equivalents. d. table of isotopes. ____ 6. A horizontal row of blocks in the periodic table is called a(n) a. group. c. family. b. period. d. octet. ____ 7. A vertical column o ...
... The most useful source of chemical information about the elements is a a. calculator. c. periodic table. b. table of metric equivalents. d. table of isotopes. ____ 6. A horizontal row of blocks in the periodic table is called a(n) a. group. c. family. b. period. d. octet. ____ 7. A vertical column o ...
Honors Chemistry I
... 1) Balance all of the chemical equations given below: a. PCl5(l) + H2O(l) H3PO4(aq) + HCl(g) b. C(s) + CaO(s) CaC2(s) + CO2(g) c. FeCO3(s) + H2CO3(aq) Fe(HCO3)2(aq) d. Fe(s) + O2(g) Fe2O3(s) e. FeO(s) + O2(g) Fe2O3 (s) f. Cr(s) + S8(s) Cr2S3(s) g. NaHCO3(s) Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) ...
... 1) Balance all of the chemical equations given below: a. PCl5(l) + H2O(l) H3PO4(aq) + HCl(g) b. C(s) + CaO(s) CaC2(s) + CO2(g) c. FeCO3(s) + H2CO3(aq) Fe(HCO3)2(aq) d. Fe(s) + O2(g) Fe2O3(s) e. FeO(s) + O2(g) Fe2O3 (s) f. Cr(s) + S8(s) Cr2S3(s) g. NaHCO3(s) Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) ...
Chpt1
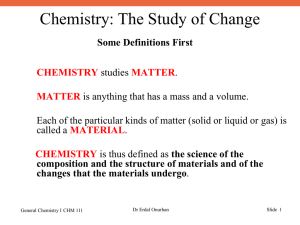
... Each of the particular kinds of matter (solid or liquid or gas) is called a MATERIAL. CHEMISTRY is thus defined as the science of the composition and the structure of materials and of the changes that the materials undergo. ...
... Each of the particular kinds of matter (solid or liquid or gas) is called a MATERIAL. CHEMISTRY is thus defined as the science of the composition and the structure of materials and of the changes that the materials undergo. ...
Chapter 6: Chemical Equilibrium
... 10. Consider the following system, which is at equilibrium, CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H2O(g). The result of removing some CH4(g) and H2O(g) from the system is that * a. more CH4(g) and H2O(g) are produced to replace that which is removed b. Kc decreases c. more CO(g) is produced d. more H2O(g) is cons ...
... 10. Consider the following system, which is at equilibrium, CO(g) + 3H2(g) CH4(g) + H2O(g). The result of removing some CH4(g) and H2O(g) from the system is that * a. more CH4(g) and H2O(g) are produced to replace that which is removed b. Kc decreases c. more CO(g) is produced d. more H2O(g) is cons ...
19a - The BOD
... “Dissolved oxygen” is there. It is a measure of how much oxygen is dissolved in a water sample. It is a measure of oxygen content. BOD is the amount of oxygen that would be consumed to completely decompose the organic matter in a water sample. It is not an indication of oxygen content. It is an indi ...
... “Dissolved oxygen” is there. It is a measure of how much oxygen is dissolved in a water sample. It is a measure of oxygen content. BOD is the amount of oxygen that would be consumed to completely decompose the organic matter in a water sample. It is not an indication of oxygen content. It is an indi ...
Thermochemistry - Ars
... Measuring heats of reaction Heats of reaction can be measured in a device called a calorimeter. This device is usually insulated to avoid heat loss or gain from outside the calorimeter during the reaction, which could introduce errors into the measurement. In a coffee cup calorimeter, the type used ...
... Measuring heats of reaction Heats of reaction can be measured in a device called a calorimeter. This device is usually insulated to avoid heat loss or gain from outside the calorimeter during the reaction, which could introduce errors into the measurement. In a coffee cup calorimeter, the type used ...
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
... Example: The compound para-aminobenzoic acid (you may have seen it listed as PABA on your bottle of sunscreen) is composed of carbon (61.31%), hydrogen (5.14%), nitrogen (10.21%), and oxygen (23.33%). Find the empirical formula of PABA. Assuming 100.00 g of para-aminobenzoic acid, ...
... Example: The compound para-aminobenzoic acid (you may have seen it listed as PABA on your bottle of sunscreen) is composed of carbon (61.31%), hydrogen (5.14%), nitrogen (10.21%), and oxygen (23.33%). Find the empirical formula of PABA. Assuming 100.00 g of para-aminobenzoic acid, ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... If 25.0 grams of carbon dioxide are used in photosynthesis how many moles of glucose (C6H12O6) could be Produced according to the following equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 ...
... If 25.0 grams of carbon dioxide are used in photosynthesis how many moles of glucose (C6H12O6) could be Produced according to the following equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 ...
Equilibrium Constant
... Internal energy (E): the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of molecules. Heat (q): energy in transit from a high temperature object to a lower temperature object. ...
... Internal energy (E): the energy associated with the random, disordered motion of molecules. Heat (q): energy in transit from a high temperature object to a lower temperature object. ...
Word Document
... 2. What is the major product seen in the free radical bromination of 2-methylpropane? Explain. 1. The reaction of cyclopentyl bromide with sodium cyanide to give cyclopentyl cyanide proceeds faster if a small amount of NaI is added. Suggest a reasonable mechanism to explain the catalytic function of ...
... 2. What is the major product seen in the free radical bromination of 2-methylpropane? Explain. 1. The reaction of cyclopentyl bromide with sodium cyanide to give cyclopentyl cyanide proceeds faster if a small amount of NaI is added. Suggest a reasonable mechanism to explain the catalytic function of ...
chemical reaction
... 3. All metal halide (halogen) compounds are soluble, except those of Ag+, Hg+ & Pb+2 4. All sulfates are soluble except: Ba+2, Sr+2, Ca+2, Pb+2,Ag+, ...
... 3. All metal halide (halogen) compounds are soluble, except those of Ag+, Hg+ & Pb+2 4. All sulfates are soluble except: Ba+2, Sr+2, Ca+2, Pb+2,Ag+, ...
Activity Series Unit
... 29. Generally speaking, what happens to these species in these reactions? They are gaining electrons from the metals. 30. When looking at electrons, what can be said about the term, reduction? Reduction means the gain of electrons. 31. In these reactions what species is causing reduction? What spec ...
... 29. Generally speaking, what happens to these species in these reactions? They are gaining electrons from the metals. 30. When looking at electrons, what can be said about the term, reduction? Reduction means the gain of electrons. 31. In these reactions what species is causing reduction? What spec ...
Types of Reactions Lab
... 1.) List the 5 types of reactions. For each type, describe them in terms of elements and compounds and describe what generally happens. 2.) A) What is bromothymol blue and how can it be used to identify an acid or a base (use your book or the internet to look this up)? B) Look up the same for univer ...
... 1.) List the 5 types of reactions. For each type, describe them in terms of elements and compounds and describe what generally happens. 2.) A) What is bromothymol blue and how can it be used to identify an acid or a base (use your book or the internet to look this up)? B) Look up the same for univer ...
c2_03_lesson
... Low demand Discuss the properties of metals and ceramics and explain what is meant by a polymer. Explain that all these materials are substances/chemicals – some pure (single substance, e.g. copper wires) others mixtures (most materials). Students should make lists of materials classifying them as ...
... Low demand Discuss the properties of metals and ceramics and explain what is meant by a polymer. Explain that all these materials are substances/chemicals – some pure (single substance, e.g. copper wires) others mixtures (most materials). Students should make lists of materials classifying them as ...
Example
... hydrate until all the water is gone. A 1.628 g sample of hydrate is heated to constant mass of 1.072 g. What is the value of X? ...
... hydrate until all the water is gone. A 1.628 g sample of hydrate is heated to constant mass of 1.072 g. What is the value of X? ...