Full answers
... on an octahedron with the lone pairs located opposite to one another to minimise repulsion between them. The geometry of the actual molecule is therefore square planar. • Explain briefly, in terms of intermolecular forces, why an analogue of DNA could not be made with phosphorus atoms replacing some ...
... on an octahedron with the lone pairs located opposite to one another to minimise repulsion between them. The geometry of the actual molecule is therefore square planar. • Explain briefly, in terms of intermolecular forces, why an analogue of DNA could not be made with phosphorus atoms replacing some ...
Nickel(II) cis- and trans-Dimethyl Complexes of
... Isolation of 1 results in effect from the incomplete substitution of PMe3 by tBuCCmeth, and therefore, an alternative Ni(II) dimethyl complex containing ligands considered more likely to undergo substitution was sought. Reaction between tBuCCeth and [Ni(bipy)Me2]17 at -78 °C gives the target compoun ...
... Isolation of 1 results in effect from the incomplete substitution of PMe3 by tBuCCmeth, and therefore, an alternative Ni(II) dimethyl complex containing ligands considered more likely to undergo substitution was sought. Reaction between tBuCCeth and [Ni(bipy)Me2]17 at -78 °C gives the target compoun ...
IV. Relating Mass to Numbers of Atoms
... mole is the amount of a substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of ______________________. 2. Avogadro’s Number-the number of particles in exactly one mole of a pure substance. This number was determined experimentally and its value is 6.022 X 1023, which mea ...
... mole is the amount of a substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of ______________________. 2. Avogadro’s Number-the number of particles in exactly one mole of a pure substance. This number was determined experimentally and its value is 6.022 X 1023, which mea ...
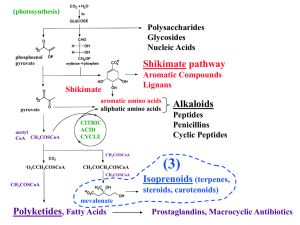
Lecture 03, NEW - terpenes + polyketides
... - often present in moldy grain consumed by cattle or people Winter 1942: thousands of Russians died after eating grains left in the field over winter, due to the war; grain was infected with the trichothecene-producing fungus 1981: USA accused Russia of spraying fungal spores in Vietnam, resulting i ...
... - often present in moldy grain consumed by cattle or people Winter 1942: thousands of Russians died after eating grains left in the field over winter, due to the war; grain was infected with the trichothecene-producing fungus 1981: USA accused Russia of spraying fungal spores in Vietnam, resulting i ...
Is That a Fact!
... Each element has a limited number of isotopes that are found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apar ...
... Each element has a limited number of isotopes that are found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apar ...
Chapter 3 Lecture Notes
... Determing formula weights in either grams or amu’s are done in an identical manner. The difference is that if we are talking about the formula weight of an individual atom or molecule, then that mass unit is the amu. However, it is much more common, to be more concerned with a larger quantity of mat ...
... Determing formula weights in either grams or amu’s are done in an identical manner. The difference is that if we are talking about the formula weight of an individual atom or molecule, then that mass unit is the amu. However, it is much more common, to be more concerned with a larger quantity of mat ...
IB Definitions
... An exothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall negative enthalpy change (heat is evolved) An endothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall postive enthalpy change (heat is absorbed) The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change when one mole of reactants is ...
... An exothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall negative enthalpy change (heat is evolved) An endothermic reaction is one in which there is an overall postive enthalpy change (heat is absorbed) The standard enthalpy change of a reaction is the enthalpy change when one mole of reactants is ...
The Atom
... Each element has a limited number of isotopes that are found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apar ...
... Each element has a limited number of isotopes that are found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apar ...
Chapter 2
... Nuclear Stability There are many factors that determine whether a particular nucleus will radioactively decay (is unstable) or not. Based on observations, the following has been observed: 1) Nuclei with an even number of both protons and neutrons are generally more stable than those with an odd num ...
... Nuclear Stability There are many factors that determine whether a particular nucleus will radioactively decay (is unstable) or not. Based on observations, the following has been observed: 1) Nuclei with an even number of both protons and neutrons are generally more stable than those with an odd num ...
Atomic Structure - Mr Andrews` Science Space!
... Many elements are a mixture of isotopes. The RAM given in the periodic table takes account of this. To calculate the RAM of a mixture of isotopes, multiply the percentage of each isotope by its atomic mass and add them together. For example, chlorine exists as two isotopes: chlorine-35 (75%) and chl ...
... Many elements are a mixture of isotopes. The RAM given in the periodic table takes account of this. To calculate the RAM of a mixture of isotopes, multiply the percentage of each isotope by its atomic mass and add them together. For example, chlorine exists as two isotopes: chlorine-35 (75%) and chl ...
Introduction to Metabolism
... Anaerobes – Live in the absence of oxygen. Catabolize nutrients without molecular oxygen. Obligate anaerobes- are poisoned by oxygen. Facultative – Some organisms can live in either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. They are called faculatives. Examples are yeast and E. coli. III. Nitrogen All living ...
... Anaerobes – Live in the absence of oxygen. Catabolize nutrients without molecular oxygen. Obligate anaerobes- are poisoned by oxygen. Facultative – Some organisms can live in either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. They are called faculatives. Examples are yeast and E. coli. III. Nitrogen All living ...
Meeting no
... elements and the formula. To make the calculation easy (i.e., let the percentages convert directly to grams), let's assume we have 100 g of vitamin C. If you are given mass percentages, always work with a hypothetical 100 gram sample. In a 100 gram sample, there are 40.9 g C, 4.58 g H, and 54.5 g O. ...
... elements and the formula. To make the calculation easy (i.e., let the percentages convert directly to grams), let's assume we have 100 g of vitamin C. If you are given mass percentages, always work with a hypothetical 100 gram sample. In a 100 gram sample, there are 40.9 g C, 4.58 g H, and 54.5 g O. ...
AS Chemistry - Crawshaw Academy
... (d) use calculators to find and use power, exponential and logarithmic functions. ...
... (d) use calculators to find and use power, exponential and logarithmic functions. ...
Application of stable isotopes and mass isotopomer distribution
... glucose catabolism. By contrast, if radioactive [U-14C] glucose had been given, measurement of the wholemolecule 14C-specific activity of pyruvate would have led to an overestimation of pyruvate flux from glucose. Further, valuable metabolic information on the rate of and sources for gluconeogenesis ...
... glucose catabolism. By contrast, if radioactive [U-14C] glucose had been given, measurement of the wholemolecule 14C-specific activity of pyruvate would have led to an overestimation of pyruvate flux from glucose. Further, valuable metabolic information on the rate of and sources for gluconeogenesis ...
Chapter 3 Reading
... A mixture of 1.50 mol of Al and 3.00 mol of Cl2 is •Often, one or more reactants is present in excess. allowed to react. (a) Which is the limiting reactant? •Therefore, at the end of reaction those reactants present in excess will (b) How many moles of AlCl3 are formed? still be in the reaction mixt ...
... A mixture of 1.50 mol of Al and 3.00 mol of Cl2 is •Often, one or more reactants is present in excess. allowed to react. (a) Which is the limiting reactant? •Therefore, at the end of reaction those reactants present in excess will (b) How many moles of AlCl3 are formed? still be in the reaction mixt ...
2 - My CCSD
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
People asked the question – for thousands of years: What is matter
... produce tiny oil droplets. Very fine oil droplets were sprayed into a chamber and then were allowed to fall between two charged plates where they were then observed, visually. The air inside the chamber was exposed to x-rays, which displace electrons from air molecules resulting in both negatively c ...
... produce tiny oil droplets. Very fine oil droplets were sprayed into a chamber and then were allowed to fall between two charged plates where they were then observed, visually. The air inside the chamber was exposed to x-rays, which displace electrons from air molecules resulting in both negatively c ...
Chapter 7
... but that also makes me have 2 copper atoms as products. I then have to add a 2 in front of copper. Now 2 copper in and out and 2 oxygen in and out. ...
... but that also makes me have 2 copper atoms as products. I then have to add a 2 in front of copper. Now 2 copper in and out and 2 oxygen in and out. ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
... at the basic principles of chemistry as they apply to life processes. In fact, it is almost impossible to speak of either the components or the processes of living things without using the biochemist's terms. For example, 96% of the human body is made up of just four major elements. Chemical reactio ...
... at the basic principles of chemistry as they apply to life processes. In fact, it is almost impossible to speak of either the components or the processes of living things without using the biochemist's terms. For example, 96% of the human body is made up of just four major elements. Chemical reactio ...
Chemistry 4021/8021 Computational Chemistry 3/4 Credits Spring
... b. To what electronic transitions do the two peaks in the UV spectrum correspond (show pictures of the orbitals)? Based on the nature of these transitions, how might you expect the geometries of the first and second excited states to differ from the ground state (don’t do an excited-state geometry ...
... b. To what electronic transitions do the two peaks in the UV spectrum correspond (show pictures of the orbitals)? Based on the nature of these transitions, how might you expect the geometries of the first and second excited states to differ from the ground state (don’t do an excited-state geometry ...
Atomic Structure
... 1.What is the mass of a proton? Neutron? Electron? 2.A neutral atom has 14 protons and 18 neutrons. Write the correct nuclear (isotope) symbol. 3.Which of the following pairs show two atoms with the same number of neutrons? ...
... 1.What is the mass of a proton? Neutron? Electron? 2.A neutral atom has 14 protons and 18 neutrons. Write the correct nuclear (isotope) symbol. 3.Which of the following pairs show two atoms with the same number of neutrons? ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry
... Solution: Since carbon has as an atomic mass of 12 amu, the element must have an atomic mass of about 48 amu, Ti atomic mass is 47.90 amu. 2. Germanium (Ge) is about six times heavier than carbon. What is its approximate atomic mass? _______________ ...
... Solution: Since carbon has as an atomic mass of 12 amu, the element must have an atomic mass of about 48 amu, Ti atomic mass is 47.90 amu. 2. Germanium (Ge) is about six times heavier than carbon. What is its approximate atomic mass? _______________ ...
The Structure of the Atom
... Atomic Theory of Matter 1. All matter is made of . . . 2. Atoms cannot be . . . 3. Atoms of a given element . . . ...
... Atomic Theory of Matter 1. All matter is made of . . . 2. Atoms cannot be . . . 3. Atoms of a given element . . . ...
copyrighted material
... represented by chemical symbols of one or two letters, such as C (carbon), Ca (calcium), H (hydrogen), O (oxygen), N (nitrogen), and P (phosphorus). The smallest quantity of an element that still possesses the characteristics of that element is an atom. Atoms chemically bond together to form molecul ...
... represented by chemical symbols of one or two letters, such as C (carbon), Ca (calcium), H (hydrogen), O (oxygen), N (nitrogen), and P (phosphorus). The smallest quantity of an element that still possesses the characteristics of that element is an atom. Atoms chemically bond together to form molecul ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.