Atoms and the Particles They Contain Chemistry Packet: Honors
... Neutrons are also found in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are neutral with no charge and have a mass of 1 amu, just like the proton. Electrons are found constantly moving around the nucleus in a random fashion. For teaching purposes we say that electrons travel in electron clouds or energy levels ...
... Neutrons are also found in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are neutral with no charge and have a mass of 1 amu, just like the proton. Electrons are found constantly moving around the nucleus in a random fashion. For teaching purposes we say that electrons travel in electron clouds or energy levels ...
wahideh chemistry eportfolio hw
... 4Na(s)+O2(g)-->2Na2O(s) 100 g Na (1 mol Na/23g Na) (2mol N/4mole Na)(62 g Na2O/1mol Na2O)=134.7 g of Sodium Oxide, limsting reagent. ...
... 4Na(s)+O2(g)-->2Na2O(s) 100 g Na (1 mol Na/23g Na) (2mol N/4mole Na)(62 g Na2O/1mol Na2O)=134.7 g of Sodium Oxide, limsting reagent. ...
Document
... (a) It is possible to identify the sulfite ion without memorizing all the ions in Table 2.4. If you remember the name and formula of one of the sulfur–oxygen polyatomic anions, you should be able to deduce the names of others. Suppose you remember that sulfate is SO42–. The -ite anion has one fewer ...
... (a) It is possible to identify the sulfite ion without memorizing all the ions in Table 2.4. If you remember the name and formula of one of the sulfur–oxygen polyatomic anions, you should be able to deduce the names of others. Suppose you remember that sulfate is SO42–. The -ite anion has one fewer ...
Assignment # 6 Atomic Structure Drill
... The atomic mass values listed on the periodic table are what are known as “weighted” averages of the naturally occurring masses of the isotopes. You are somewhat familiar with the notion of a weighted average. Many of your course grades are determined this way. If your teacher says to you “tests are ...
... The atomic mass values listed on the periodic table are what are known as “weighted” averages of the naturally occurring masses of the isotopes. You are somewhat familiar with the notion of a weighted average. Many of your course grades are determined this way. If your teacher says to you “tests are ...
Essential Standard: 8.P.1 Understand the properties of matter and
... Elements are pure substances that cannot be changed into simpler substances. Elements are composed of one kind of atom. Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more types of elements that are chemically combined. Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements ...
... Elements are pure substances that cannot be changed into simpler substances. Elements are composed of one kind of atom. Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more types of elements that are chemically combined. Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements ...
powerpoint
... How to identify the type of reaction! Follow this series of questions. When you can answer "yes" to a question, then stop! 1) Does your reaction have oxygen as one of its reactants and carbon dioxide and water as products? If yes, then it's a combustion reaction 2) Does your reaction have two (or m ...
... How to identify the type of reaction! Follow this series of questions. When you can answer "yes" to a question, then stop! 1) Does your reaction have oxygen as one of its reactants and carbon dioxide and water as products? If yes, then it's a combustion reaction 2) Does your reaction have two (or m ...
Early Atomic History
... chemical composition of many compounds. He found that a given compound always contains the exact same proportion of elements by mass. This is known as the law of definite proportion. For example, all samples of water contain 88.8% oxygen by mass, and 11.2% hydrogen by mass. ...
... chemical composition of many compounds. He found that a given compound always contains the exact same proportion of elements by mass. This is known as the law of definite proportion. For example, all samples of water contain 88.8% oxygen by mass, and 11.2% hydrogen by mass. ...
Early Ideas of Atoms
... 2 grams of hydrogen will react with 9.4 grams of nitrogen. Can you guess how much nitrogen would react with 3 grams of hydrogen? Scientists studied reaction after reaction, but every time the result was the same. The reactants for a given chemical reaction always reacted in the same proportions. At ...
... 2 grams of hydrogen will react with 9.4 grams of nitrogen. Can you guess how much nitrogen would react with 3 grams of hydrogen? Scientists studied reaction after reaction, but every time the result was the same. The reactants for a given chemical reaction always reacted in the same proportions. At ...
Full Text
... of Phe as the source of both the tropone moiety and the aromatic side chain in roseobacticide B as well as those of Tyr and Trp in generating the other roseobacticide analogs. Given that amino acids serve as roseobacticide precursors, we wondered whether this knowledge could be used to generate new ...
... of Phe as the source of both the tropone moiety and the aromatic side chain in roseobacticide B as well as those of Tyr and Trp in generating the other roseobacticide analogs. Given that amino acids serve as roseobacticide precursors, we wondered whether this knowledge could be used to generate new ...
atomic mass - Belle Vernon Area School District
... • Thomson believed that these particles were therefore the ultimate building blocks of matter “We have in the cathode rays matter in a new state, a state in which the subdivision of matter is carried very much further . . . a state in which all matter . . . is of one and the same kind; this matter ...
... • Thomson believed that these particles were therefore the ultimate building blocks of matter “We have in the cathode rays matter in a new state, a state in which the subdivision of matter is carried very much further . . . a state in which all matter . . . is of one and the same kind; this matter ...
atom
... add protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons and Atomic Number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number of that atom. All atoms of an element have the same atomic number. ...
... add protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons and Atomic Number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number of that atom. All atoms of an element have the same atomic number. ...
CHEM 20 FINAL EXAM: STUDY HEADINGS Jan 2012
... early theories of atomic structure; properties of subatomic particles: proton, neutron, electron atomic number and average atomic mass; isotope symbols; Dalton, Thomson and Rutherford atomic models The Bohr atomic model; energy levels; emission and absorption spectra ...
... early theories of atomic structure; properties of subatomic particles: proton, neutron, electron atomic number and average atomic mass; isotope symbols; Dalton, Thomson and Rutherford atomic models The Bohr atomic model; energy levels; emission and absorption spectra ...
Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
... crushed alka seltzer tablets will react faster than a solid tablet with water. Catalyst: a substance that helps increase the reaction rate by lowering the amount of energy needed to make the reaction occur. Catalysts are present with the reactants but are not consumed in the reaction. e.g., enzyme ...
... crushed alka seltzer tablets will react faster than a solid tablet with water. Catalyst: a substance that helps increase the reaction rate by lowering the amount of energy needed to make the reaction occur. Catalysts are present with the reactants but are not consumed in the reaction. e.g., enzyme ...
Chemical Equations
... Reaction Types: Synthesis or Composition • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compound. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction ...
... Reaction Types: Synthesis or Composition • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compound. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction ...
CHEMISTRY
... (4) CH3COONa and Excess HCI 4. Ammonia gas dissolves in water to form NH4OH. In this reaction water acts as: ...
... (4) CH3COONa and Excess HCI 4. Ammonia gas dissolves in water to form NH4OH. In this reaction water acts as: ...
Stoichiometry …like a beautiful sunset on a serene lake – NOT!
... • CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • In a chemical reaction, atoms have been rearranged but have NOT been created or destroyed. This is why we have to balance every chemical reaction/equation. Java-Balancing! • Balance CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • Balance HCl + NaHCO3 → CO2 + H2O + NaCl • When balancing equations, t ...
... • CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • In a chemical reaction, atoms have been rearranged but have NOT been created or destroyed. This is why we have to balance every chemical reaction/equation. Java-Balancing! • Balance CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O • Balance HCl + NaHCO3 → CO2 + H2O + NaCl • When balancing equations, t ...
Products for Solid State NMR - Sigma
... example relate to larger membrane proteins14,15. In addition, block labeling16,17 as well as reverse18 labeling strategies have successfully been used in ssNMR. In these experiments, a dedicated set of amino-acid precursors or amino acids is used during expression. The combination of such measures w ...
... example relate to larger membrane proteins14,15. In addition, block labeling16,17 as well as reverse18 labeling strategies have successfully been used in ssNMR. In these experiments, a dedicated set of amino-acid precursors or amino acids is used during expression. The combination of such measures w ...
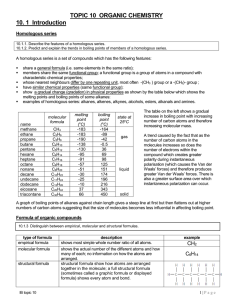
organic chemistry - Peoria Public Schools
... Conditions: catalyst + heat + high pressure (each polymerization has own conditions) The monomer, which is the small alkene molecule, is the repeating subunit. The reaction can also be applied to alkenes which have a hydrogen substituted usually by a halogen (chloroalkenes). This gives a wide variet ...
... Conditions: catalyst + heat + high pressure (each polymerization has own conditions) The monomer, which is the small alkene molecule, is the repeating subunit. The reaction can also be applied to alkenes which have a hydrogen substituted usually by a halogen (chloroalkenes). This gives a wide variet ...
L24_Krebs
... oxaloacetate prochiral • Citrate can leave the mitochondria or be oxidised – Depending on whether the cell is doing lipogenesis or needs energy ...
... oxaloacetate prochiral • Citrate can leave the mitochondria or be oxidised – Depending on whether the cell is doing lipogenesis or needs energy ...
111 Review Outline TRO
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride are produced from ...
... Key: You must have a balanced equation!! How many grams of chromic chloride are produced from ...
Chemical Reactions Chapter 11
... Writing chemical Equations • In chemical reactions one or more reactants change into one or more products. • Chemists use a chemical equations to convey a s much information as possible about what happens in a chemical reaction. • The reactants are written on the left and the products on the right ...
... Writing chemical Equations • In chemical reactions one or more reactants change into one or more products. • Chemists use a chemical equations to convey a s much information as possible about what happens in a chemical reaction. • The reactants are written on the left and the products on the right ...
Year 9 Chemical Sciences Program Term 3 Course 2 2017
... recognising that the conservation of mass in a chemical reaction can be demonstrated by simple chemical equations ...
... recognising that the conservation of mass in a chemical reaction can be demonstrated by simple chemical equations ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.