Atoms. Molecules, and Ions
... Robert Boyle (1627–1691): Provided evidence for the atoms and defined the nature of an element. ...
... Robert Boyle (1627–1691): Provided evidence for the atoms and defined the nature of an element. ...
Balanced Chemical Reaction Equations
... reacts with 5 molecules of oxygen to produce 3 molecules of carbon dioxide and 4 molecules of water. Or you could say, 1 mole of propane reacts with 5 moles of oxygen to produce 3 moles of carbon dioxide and 4 moles of water. (The scene closes as Dr. Dave rushes off to a faculty meeting, and the thr ...
... reacts with 5 molecules of oxygen to produce 3 molecules of carbon dioxide and 4 molecules of water. Or you could say, 1 mole of propane reacts with 5 moles of oxygen to produce 3 moles of carbon dioxide and 4 moles of water. (The scene closes as Dr. Dave rushes off to a faculty meeting, and the thr ...
Chemical Equations and Stoichiometry
... The Mole: Glossary of Terms to Remember • Mass: depends on the amount of matter in a substance. Unlike weight it does not depend on gravity. In chemistry we most commonly measure mass in grams. • Mole: a package of 6.02 X 1023 items, usually molecules. Technically, it is the number of atoms found in ...
... The Mole: Glossary of Terms to Remember • Mass: depends on the amount of matter in a substance. Unlike weight it does not depend on gravity. In chemistry we most commonly measure mass in grams. • Mole: a package of 6.02 X 1023 items, usually molecules. Technically, it is the number of atoms found in ...
Chapter 6 Handout
... Related to chemistry Avogadro's number = 6.02 x 1023 particles such as _________ _________________________________ and ________________ (ionic compounds) 1 mole of watermelon seeds would fit inside a watermelon slightly larger than the size of the ___________ 1 liter of water contains approximately ...
... Related to chemistry Avogadro's number = 6.02 x 1023 particles such as _________ _________________________________ and ________________ (ionic compounds) 1 mole of watermelon seeds would fit inside a watermelon slightly larger than the size of the ___________ 1 liter of water contains approximately ...
Masses of Atoms
... Element ~ smallest particle that is unique from all others Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - ...
... Element ~ smallest particle that is unique from all others Symbol ~ unique letter to represent element Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - ...
Example - Schoolwires.net
... • The standard scaled based on the carbon-12 isotope • Mass of one 12C atom = 12 amu (exactly) • Note that 12C and C-12 mean the same thing ...
... • The standard scaled based on the carbon-12 isotope • Mass of one 12C atom = 12 amu (exactly) • Note that 12C and C-12 mean the same thing ...
Unit 1 Matter Day 32 2016 Counting Atoms
... Subscripts (the little numbers) tell you how many atoms of that element are present. H2O = 2 atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen If a coefficient (big number) is written in front of a chemical formula or symbol, you have to multiply that number by all the elements in the compound. Ex. 2NaCl ( ...
... Subscripts (the little numbers) tell you how many atoms of that element are present. H2O = 2 atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen If a coefficient (big number) is written in front of a chemical formula or symbol, you have to multiply that number by all the elements in the compound. Ex. 2NaCl ( ...
Unit 4: The Nucleus
... 3. Atomic Number: The number that identifies an element, equal to an atom’s number of protons. 4. Deflect: Change in direction due to an outside force. 5. Emit: To give off something. 6. Half-life: The time it takes for half the mass of a radioactive isotope to undergo decay. Half-life is also the p ...
... 3. Atomic Number: The number that identifies an element, equal to an atom’s number of protons. 4. Deflect: Change in direction due to an outside force. 5. Emit: To give off something. 6. Half-life: The time it takes for half the mass of a radioactive isotope to undergo decay. Half-life is also the p ...
Higher Chemistry summary 3a
... Therefore, for every 0.5 moles of methane 1 mole of oxygen would be required. Looking at the quantities of reactants from step 1 there is not enough oxygen to allow all of the methane to react therefore some methane will be left over at the end. The methane is said to be in excess and the oxygen wil ...
... Therefore, for every 0.5 moles of methane 1 mole of oxygen would be required. Looking at the quantities of reactants from step 1 there is not enough oxygen to allow all of the methane to react therefore some methane will be left over at the end. The methane is said to be in excess and the oxygen wil ...
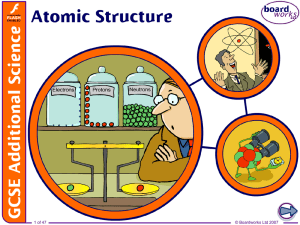
1. Atomic Structure
... positively charged because of the protons dense – it contains nearly all the mass of the atom in a tiny space. Electrons are: very small and light, and negatively charged able to be lost or gained in chemical reactions found thinly spread around the outside of the nucleus, orbiting in laye ...
... positively charged because of the protons dense – it contains nearly all the mass of the atom in a tiny space. Electrons are: very small and light, and negatively charged able to be lost or gained in chemical reactions found thinly spread around the outside of the nucleus, orbiting in laye ...
FE Exam review for Chemistry
... How do you calculate average atomic mass? Average atomic mass is a weighted average of the masses of all isotopes. Avg atomic mass = sum of all isotope (frequency)(mass) What’s the difference between an atom and an ion? Atoms are not charged because they have equal numbers of protons & e-. Ions are ...
... How do you calculate average atomic mass? Average atomic mass is a weighted average of the masses of all isotopes. Avg atomic mass = sum of all isotope (frequency)(mass) What’s the difference between an atom and an ion? Atoms are not charged because they have equal numbers of protons & e-. Ions are ...
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
... has a halflife of about 5730 years; it gradually decays away and becomes a smaller and smaller fraction of the total carbon in the plant tissue. This fraction can be measured, and tissue age deduced. Objects older than about 60,000 years cannot be dated this way – there is too little carbon1 ...
... has a halflife of about 5730 years; it gradually decays away and becomes a smaller and smaller fraction of the total carbon in the plant tissue. This fraction can be measured, and tissue age deduced. Objects older than about 60,000 years cannot be dated this way – there is too little carbon1 ...
Chemical Reactions
... You need to be able to identify the type of reaction and predict the product(s) ...
... You need to be able to identify the type of reaction and predict the product(s) ...
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
... Avogadro’s number (6.022× ×1023): number of formula units in a mole. 1 mole of hydrogen atoms = 6.022×1023 atoms of hydrogen 1 mole of water molecules = 6.022×1023 molecules of water 1 mole of Na+ ions = 6.022×1023 ions of Na+ Molar mass: is the mass of one mole of the substance expressed in grams. ...
... Avogadro’s number (6.022× ×1023): number of formula units in a mole. 1 mole of hydrogen atoms = 6.022×1023 atoms of hydrogen 1 mole of water molecules = 6.022×1023 molecules of water 1 mole of Na+ ions = 6.022×1023 ions of Na+ Molar mass: is the mass of one mole of the substance expressed in grams. ...
0 13C labeling of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and carbon conversion
... acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), energy (ATP), and reductant (NAD(P)H). To this end, the growth of key biomass components (starch, protein, and fatty acids) has been charted and intracellular metabolites involved in biochemical pathways in lesquerella have been quantified (i.e., metabolomics). The bi ...
... acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), energy (ATP), and reductant (NAD(P)H). To this end, the growth of key biomass components (starch, protein, and fatty acids) has been charted and intracellular metabolites involved in biochemical pathways in lesquerella have been quantified (i.e., metabolomics). The bi ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed
... Two atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. In nature, an element occurs as a mixture of isotopes. o For example, 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). o Most of the remaining 1% of carbon atoms have 7 neutrons (13C), while the rarest carbon isotope, ...
... Two atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. In nature, an element occurs as a mixture of isotopes. o For example, 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). o Most of the remaining 1% of carbon atoms have 7 neutrons (13C), while the rarest carbon isotope, ...
Limiting reactant - Dr. Gregory Chemistry
... Calculating Empirical Formula given % composition ›Steps 1. Change % to grams 2. Convert grams to moles 3. Divide all moles by the smallest mole 4. Write empirical formula ...
... Calculating Empirical Formula given % composition ›Steps 1. Change % to grams 2. Convert grams to moles 3. Divide all moles by the smallest mole 4. Write empirical formula ...
File
... Again, the same is true in chemistry. The reactant that runs out first will decide how much product can be made. This is called the "limiting reactant." When doing a stoichiometry problem, you must always start with the limiting reactant, because it controls when product is no longer made. Starting ...
... Again, the same is true in chemistry. The reactant that runs out first will decide how much product can be made. This is called the "limiting reactant." When doing a stoichiometry problem, you must always start with the limiting reactant, because it controls when product is no longer made. Starting ...
File - Evergreen Tutor Zone
... Whereas the mass of 1 molecule is called the relative molecular mass and the mass of 1 formula unit is called the relative formula mass, the mass of 1 mole of molecules is called the molar mass and is expressed in g∙mol-1. Consider CO2. 12 + 2(16) = 44 = mass of 1 molecule of CO2. But 44 g∙mol-1 is ...
... Whereas the mass of 1 molecule is called the relative molecular mass and the mass of 1 formula unit is called the relative formula mass, the mass of 1 mole of molecules is called the molar mass and is expressed in g∙mol-1. Consider CO2. 12 + 2(16) = 44 = mass of 1 molecule of CO2. But 44 g∙mol-1 is ...
Correlation - EngineeringDuniya.com
... a pathway ,the substrate is provided by the preceding reaction at the same rate at which it is converted to product. Thus, although the rate of the metabolite flow, the flux, may be high but the concentration of substrate, S, remains constant. ...
... a pathway ,the substrate is provided by the preceding reaction at the same rate at which it is converted to product. Thus, although the rate of the metabolite flow, the flux, may be high but the concentration of substrate, S, remains constant. ...
Supplemental Methods
... 75% ACN in PBS/CHAPS per well. The total elapsed time during the wash steps was approximately 10 min (i.e., shorter than the half off-time of the anti-peptide antibodies). Finally, the bead-antibody complex reached the elution plate where the target peptides were eluted in 13 L of 0.1% formic acid. ...
... 75% ACN in PBS/CHAPS per well. The total elapsed time during the wash steps was approximately 10 min (i.e., shorter than the half off-time of the anti-peptide antibodies). Finally, the bead-antibody complex reached the elution plate where the target peptides were eluted in 13 L of 0.1% formic acid. ...
Document
... 25. Justify why or why not we should pursue an energy program of nuclear fusion in the United States. You need to explain the differences in fission and fusion, site advantages and disadvantages of each. Fossil fuels pollute and generate CO2 (responsible for global warming) and are diminishing in a ...
... 25. Justify why or why not we should pursue an energy program of nuclear fusion in the United States. You need to explain the differences in fission and fusion, site advantages and disadvantages of each. Fossil fuels pollute and generate CO2 (responsible for global warming) and are diminishing in a ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.