Ohm`s Law and Basic Circuit Theory – Answer Sheet
... Ohm’s Law and Basic Circuit Theory – Answer Sheet Ohm’s Law: Q1) On your worksheet sketch the circuit. Set the resistance to 140 ohms. Complete the table on your worksheet. As you increase the voltage the number of batteries will increase in 1.5-volt increments. Note hat the simulation shows current ...
... Ohm’s Law and Basic Circuit Theory – Answer Sheet Ohm’s Law: Q1) On your worksheet sketch the circuit. Set the resistance to 140 ohms. Complete the table on your worksheet. As you increase the voltage the number of batteries will increase in 1.5-volt increments. Note hat the simulation shows current ...
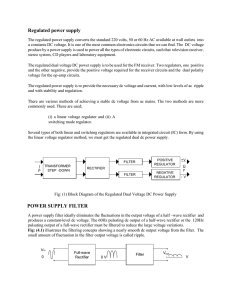
Regulated power supply
... Regulated power supply The regulated power supply converts the standard 220 volts, 50 or 60 Hz AC available at wall outlets into a constants DC voltage. It is one of the most common electronics circuits that we can find. The DC voltage produce by a power supply is used to power all the types of elec ...
... Regulated power supply The regulated power supply converts the standard 220 volts, 50 or 60 Hz AC available at wall outlets into a constants DC voltage. It is one of the most common electronics circuits that we can find. The DC voltage produce by a power supply is used to power all the types of elec ...
OSM_Al_2 Series Recloser
... Compatible with SEL-651R, Beckwith M7679 and other MRI (multi-recloser interface controls) ...
... Compatible with SEL-651R, Beckwith M7679 and other MRI (multi-recloser interface controls) ...
Document
... shown previously in (for typical CHB StatCom) that controlling the square of capacitor voltage results in a decoupled and linear cascaded control system. This paper utilizes the same concept to significantly reduce the computational power required to implement the analytic filtering scheme propose ...
... shown previously in (for typical CHB StatCom) that controlling the square of capacitor voltage results in a decoupled and linear cascaded control system. This paper utilizes the same concept to significantly reduce the computational power required to implement the analytic filtering scheme propose ...
DATASHEET: Furman AR-1220
... from problems caused by AC line voltage irregularities—sags, brownouts, or overvoltages that can cause sensitive digital equipment to malfunction, or, in extreme cases, to sustain damage. The AR-1220 is designed to provide a steady, stable 120 VAC output. It accepts input voltages from 97V to 141V a ...
... from problems caused by AC line voltage irregularities—sags, brownouts, or overvoltages that can cause sensitive digital equipment to malfunction, or, in extreme cases, to sustain damage. The AR-1220 is designed to provide a steady, stable 120 VAC output. It accepts input voltages from 97V to 141V a ...
DETERMINATION OF PLANCK`S CONSTANT USING LEDS (Rev 3
... raise the voltage. Measure in 0.2 v increments. Keep voltage < 4.5 volts. Do not exceed marked maximum currents for any LEDs. Turn off power supply. 3. Start again with zero voltage across LED. Set Protek meter to 40 ma scale. The ammeter must show all zeros. Slowly raise voltage (coarse knob) until ...
... raise the voltage. Measure in 0.2 v increments. Keep voltage < 4.5 volts. Do not exceed marked maximum currents for any LEDs. Turn off power supply. 3. Start again with zero voltage across LED. Set Protek meter to 40 ma scale. The ammeter must show all zeros. Slowly raise voltage (coarse knob) until ...
Newton`s first law of mechanics: An object moves at the same
... the charges will flow through the circuit, doing useful work and/or producing heat. A radian is a measure of angle defined as the angle subtended by and arc of length equal to the radius of the circle. Angular velocity is measured in radians per second. v = r where v is the velocity of a point on t ...
... the charges will flow through the circuit, doing useful work and/or producing heat. A radian is a measure of angle defined as the angle subtended by and arc of length equal to the radius of the circle. Angular velocity is measured in radians per second. v = r where v is the velocity of a point on t ...
1. Over voltage Damage Over voltage damage caused by spikes
... Spikes are commonly caused by the on and off switching of heavy electrical motors, such as air conditioners, electric power tools, furnace igniters, welders, office photocopiers or other large business machines and elevators. Capacitor switching by both utility and customer is also a common cause of ...
... Spikes are commonly caused by the on and off switching of heavy electrical motors, such as air conditioners, electric power tools, furnace igniters, welders, office photocopiers or other large business machines and elevators. Capacitor switching by both utility and customer is also a common cause of ...
Why led driver why not just normal dc power supply
... It seems that every thing in order right!! However driving led is not that simple The problem is that leds are tempreture sensitive if tempreture increase Each led will now ask lower forward voltage and 3vdc now is just too high ..and remember as I mentioned before forcing higher forward voltage acr ...
... It seems that every thing in order right!! However driving led is not that simple The problem is that leds are tempreture sensitive if tempreture increase Each led will now ask lower forward voltage and 3vdc now is just too high ..and remember as I mentioned before forcing higher forward voltage acr ...
DC841 - LT3477EFE Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide
... Demonstration circuit 841 is a constant LED current boost converter with input current and output voltage protection featuring the LT®3477. The board is optimized to drive 330mA LED arrays with a total LED voltage between the maximum input voltage and 36V. The high input voltage range, high-efficien ...
... Demonstration circuit 841 is a constant LED current boost converter with input current and output voltage protection featuring the LT®3477. The board is optimized to drive 330mA LED arrays with a total LED voltage between the maximum input voltage and 36V. The high input voltage range, high-efficien ...
Document
... Ohm’s Law • Voltage results in current flow • More voltage = more current • Resistance opposes current flow • More resistance = less current ...
... Ohm’s Law • Voltage results in current flow • More voltage = more current • Resistance opposes current flow • More resistance = less current ...
Test Equipment
... circuits moments after installation with ProtoLab's easy "click & drag" component placement Choose from a complete list of active and passive components Five virtual instruments allow for instant, accurate circuit analysis Pre-designed circuit library included & Low cost - only $50.00 ...
... circuits moments after installation with ProtoLab's easy "click & drag" component placement Choose from a complete list of active and passive components Five virtual instruments allow for instant, accurate circuit analysis Pre-designed circuit library included & Low cost - only $50.00 ...
High-Voltage Gain Boost Converter Based on Three
... in a Single Conversion Stage Abstract The need for renewable energy sources is on the rise because of the acute energy crisis in the world today. Renewable energy is the energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides and geothermal heat. These resources are renewable a ...
... in a Single Conversion Stage Abstract The need for renewable energy sources is on the rise because of the acute energy crisis in the world today. Renewable energy is the energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides and geothermal heat. These resources are renewable a ...
EE362L, Fall 2006
... Question – if aluminum has a higher resistivity than copper, then why do all power lines use aluminum wires instead of copper wires? (note – in power lines, “wires” are called “conductors”) Answer – larger-diameter aluminum wires make up the difference in resistance, but still have less weight per ...
... Question – if aluminum has a higher resistivity than copper, then why do all power lines use aluminum wires instead of copper wires? (note – in power lines, “wires” are called “conductors”) Answer – larger-diameter aluminum wires make up the difference in resistance, but still have less weight per ...
Surge protector

A surge protector (or surge suppressor) is an appliance/device designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold. This article primarily discusses specifications and components relevant to the type of protector that diverts (shorts) a voltage spike to ground; however, there is some coverage of other methods.The terms surge protection device (SPD), or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), are used to describe electrical devices typically installed in power distribution panels, process control systems, communications systems, and other heavy-duty industrial systems, for the purpose of protecting against electrical surges and spikes, including those caused by lightning. Scaled-down versions of these devices are sometimes installed in residential service entrance electrical panels, to protect equipment in a household from similar hazards.Many power strips have basic surge protection built in; these are typically clearly labeled as such. However, power strips that do not provide surge protection are sometimes erroneously referred to as ""surge protectors"".