26 - Cabrillo College
... Why do electric power companies reduce voltage during times of heavy demand? What is being saved? Explain. The textbook states that good thermal conductors are also good electrical conductors. If so, why don’t the cords used to connect toasters, irons, and similar heat-producing appliances get h ...
... Why do electric power companies reduce voltage during times of heavy demand? What is being saved? Explain. The textbook states that good thermal conductors are also good electrical conductors. If so, why don’t the cords used to connect toasters, irons, and similar heat-producing appliances get h ...
t6_transformers
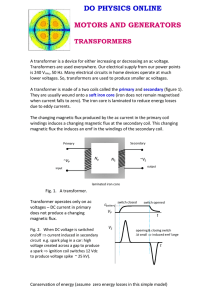
... TRANSFORMERS A transformer is a device for either increasing or decreasing an ac voltage. Transformers are used everywhere. Our electrical supply from our power points is 240 Vrms, 50 Hz. Many electrical circuits in home devices operate at much lower voltages. So, transformers are used to produce sm ...
... TRANSFORMERS A transformer is a device for either increasing or decreasing an ac voltage. Transformers are used everywhere. Our electrical supply from our power points is 240 Vrms, 50 Hz. Many electrical circuits in home devices operate at much lower voltages. So, transformers are used to produce sm ...
SS8050 NPN Epitaxial Silicon Transistor
... 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life the body, or (b) support or sus ...
... 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life the body, or (b) support or sus ...
1500 Watt SMC Transient Voltage Suppressor, 10 V Unidir
... current to full current) and lead inductance. This inductive effect produces an overshoot in the voltage across the equipment or component being protected as shown in Figure 6. Minimizing this overshoot is very important in the application, since the main purpose for adding a transient suppressor is ...
... current to full current) and lead inductance. This inductive effect produces an overshoot in the voltage across the equipment or component being protected as shown in Figure 6. Minimizing this overshoot is very important in the application, since the main purpose for adding a transient suppressor is ...
Product profile No. 3213
... Type 1 UL® 1449 3rd Edition Listed for easy specification and installation on the loadside or lineside of the service entrance overcurrent protective device. ...
... Type 1 UL® 1449 3rd Edition Listed for easy specification and installation on the loadside or lineside of the service entrance overcurrent protective device. ...
RPI-1133
... Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants contained herein are shown as examples of standard use and operation. Please pay careful attention to the peripheral conditions when designing circuits and deciding upon circuit constants in the set. Any data, including, but not limited to applicati ...
... Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants contained herein are shown as examples of standard use and operation. Please pay careful attention to the peripheral conditions when designing circuits and deciding upon circuit constants in the set. Any data, including, but not limited to applicati ...
LB11851MC
... of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent-Marking.pdf. SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no wa ...
... of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent-Marking.pdf. SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no wa ...
File - BCS-2C
... AC provides a means for us to distribute electrical power, but most devices actually want DC – bulbs, toasters, heaters, fans don’t care: plug straight in – sophisticated devices care because they have diodes and transistors that require a certain polarity rather than oscillating polarity derived fr ...
... AC provides a means for us to distribute electrical power, but most devices actually want DC – bulbs, toasters, heaters, fans don’t care: plug straight in – sophisticated devices care because they have diodes and transistors that require a certain polarity rather than oscillating polarity derived fr ...
AP_Physics_C_-_Kirchhoffs_Law_Lab
... between each element to that the current can be easily measured. Obtain the instructors initials before proceeding. ___________________________ On the figure above, DRAW and LABEL the CURRENT(Example: I1, I2….) as it moves through each resistor As you can see in the schematic above there are TWO loo ...
... between each element to that the current can be easily measured. Obtain the instructors initials before proceeding. ___________________________ On the figure above, DRAW and LABEL the CURRENT(Example: I1, I2….) as it moves through each resistor As you can see in the schematic above there are TWO loo ...
1 - School-Portal.co.uk
... Current (symbol I, measured in amperes, A) is the rate of flow of electrical charges (symbol Q) or electrons i.e. The number of charges per second. Current is the amount of charges (measured in Coulombs) that flow every second, it is represented by the equation: Current (Ampere, A) = Charge (Coulom ...
... Current (symbol I, measured in amperes, A) is the rate of flow of electrical charges (symbol Q) or electrons i.e. The number of charges per second. Current is the amount of charges (measured in Coulombs) that flow every second, it is represented by the equation: Current (Ampere, A) = Charge (Coulom ...
Lab Guide - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu - University of California, Berkeley
... 2. In the following set of questions, you will be measuring the threshold voltage of the diode of the circuit you built above. To do this, measure the voltage difference the input and output signal. a. Measure VT when the input is Frequency = 1KHz, Vpp = 5V, Offset = 0. b. What happens when you lowe ...
... 2. In the following set of questions, you will be measuring the threshold voltage of the diode of the circuit you built above. To do this, measure the voltage difference the input and output signal. a. Measure VT when the input is Frequency = 1KHz, Vpp = 5V, Offset = 0. b. What happens when you lowe ...
open saved file with Word to simulate
... 0 volts and off. Set the volt meter (XMM1) to the 20 volts range. Set the amp meter (ammeter) (XMM2) to the 200 mA range. Prepare to record the voltage across the resistor and the resulting current through the resistor as the voltage source is set to various values. The set of recorded values will b ...
... 0 volts and off. Set the volt meter (XMM1) to the 20 volts range. Set the amp meter (ammeter) (XMM2) to the 200 mA range. Prepare to record the voltage across the resistor and the resulting current through the resistor as the voltage source is set to various values. The set of recorded values will b ...
Resistors
... To measure the voltage across a resistor, the voltmeter is placed in parallel with it To measure the current through a resistor, the ammeter is placed in series with it To measure the resistance of a resistor, the resistor is removed from the circuit and each end is connected to an end of the ...
... To measure the voltage across a resistor, the voltmeter is placed in parallel with it To measure the current through a resistor, the ammeter is placed in series with it To measure the resistance of a resistor, the resistor is removed from the circuit and each end is connected to an end of the ...
Consequences of Harmonic Currents and Voltages Generated by
... impedance differences. Utility transformers are frequently rated to carry the total plant load. DG Sets are often only sized to carry emergency or critical loads. Thus DG Sets may have 5 to 100 times greater subtransient reactance than normal source transformers. Consequently, nonlinear loads may wo ...
... impedance differences. Utility transformers are frequently rated to carry the total plant load. DG Sets are often only sized to carry emergency or critical loads. Thus DG Sets may have 5 to 100 times greater subtransient reactance than normal source transformers. Consequently, nonlinear loads may wo ...
Impedance
... is the measure of the opposition that a circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current (AC) circuit ...
... is the measure of the opposition that a circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current (AC) circuit ...
Surge protector

A surge protector (or surge suppressor) is an appliance/device designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold. This article primarily discusses specifications and components relevant to the type of protector that diverts (shorts) a voltage spike to ground; however, there is some coverage of other methods.The terms surge protection device (SPD), or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), are used to describe electrical devices typically installed in power distribution panels, process control systems, communications systems, and other heavy-duty industrial systems, for the purpose of protecting against electrical surges and spikes, including those caused by lightning. Scaled-down versions of these devices are sometimes installed in residential service entrance electrical panels, to protect equipment in a household from similar hazards.Many power strips have basic surge protection built in; these are typically clearly labeled as such. However, power strips that do not provide surge protection are sometimes erroneously referred to as ""surge protectors"".