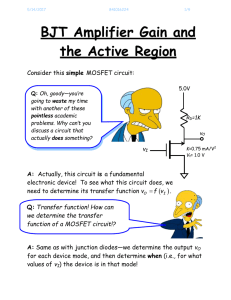
1. A simple series circuit contains a resistance R and an ideal
... 1. A simple series circuit contains a resistance R and an ideal battery. If a second resistor is connected in parallel to R (a) the current through R will decrease (b) the voltage across R will decrease (c) the total current in the circuit will increase (d) the rate of heat production in R will incr ...
... 1. A simple series circuit contains a resistance R and an ideal battery. If a second resistor is connected in parallel to R (a) the current through R will decrease (b) the voltage across R will decrease (c) the total current in the circuit will increase (d) the rate of heat production in R will incr ...
L6920 - STMicroelectronics
... Usually, inductors ranging between 5µH to 40µH satisfy most of the applications. Small value inductors have smaller physical size and guarantee a faster response to load transient but in steady state condition a bigger ripple on output voltage is generated. In fact the output ripple voltage is given ...
... Usually, inductors ranging between 5µH to 40µH satisfy most of the applications. Small value inductors have smaller physical size and guarantee a faster response to load transient but in steady state condition a bigger ripple on output voltage is generated. In fact the output ripple voltage is given ...
3Jain-Agarwal
... three-phase shunt active power filter. It is used to improve power quality by compensating harmonics and reactive power requirement of non-linear loads. The compensation process proposed is simple, which is based on sensing line currents and regulating the dc link voltage. It operates without sensin ...
... three-phase shunt active power filter. It is used to improve power quality by compensating harmonics and reactive power requirement of non-linear loads. The compensation process proposed is simple, which is based on sensing line currents and regulating the dc link voltage. It operates without sensin ...
PHY252 Fall 2015 Practical Lab #1: Ohm’s Law Objectives Apparatus
... One important question is whether your results agree with what is expected. Let’s denote the result by r and the expected value by e. The ideal situation would be r = e or r - e = 0. We often use Δ (pronounced “Delta”) to denote the difference between two quantities: Δ =r-e ...
... One important question is whether your results agree with what is expected. Let’s denote the result by r and the expected value by e. The ideal situation would be r = e or r - e = 0. We often use Δ (pronounced “Delta”) to denote the difference between two quantities: Δ =r-e ...
FUNCTION GENERATOR NOTES
... Freq: Frequency in repetitions per second. In the case of a pulse, this parameter corresponds to the frequency at which repeated pulses are sent. Ampl: Amplitude (peak-to-peak), defined as the distance between the highest and lowest voltage points of a waveform. Offset: DC voltage offset. The time-v ...
... Freq: Frequency in repetitions per second. In the case of a pulse, this parameter corresponds to the frequency at which repeated pulses are sent. Ampl: Amplitude (peak-to-peak), defined as the distance between the highest and lowest voltage points of a waveform. Offset: DC voltage offset. The time-v ...
Design of a Modified Cockcroft Walton Generator
... voltage multiplier (CWVM) failed to continually raise the value of output voltage when the number of stages increase or when the operating frequency and capacitance are not sufficiently high to avoid voltage drop in coupling capacitors at each stage. Complete understanding of the working principle ...
... voltage multiplier (CWVM) failed to continually raise the value of output voltage when the number of stages increase or when the operating frequency and capacitance are not sufficiently high to avoid voltage drop in coupling capacitors at each stage. Complete understanding of the working principle ...
Example Report
... turned out to be closer to 40.0 Ω each. This makes sense because a parallel circuit has the same voltage across each path and ends up drawing more current towards them overall, and as a direct result, more power is dissipated. This can be seen in the forms of light (brighter) and heat (increases res ...
... turned out to be closer to 40.0 Ω each. This makes sense because a parallel circuit has the same voltage across each path and ends up drawing more current towards them overall, and as a direct result, more power is dissipated. This can be seen in the forms of light (brighter) and heat (increases res ...
Capacitance Level Sensor for two levels V-25
... The pin configuration is to be strictly adhered to. The device is only to be operated with the voltage entered on the rating plane. Screened cables are to be used as connecting cables. The screening is to be singly earthed. The connecting cable is not to be laid parallel to the driving cables. Opera ...
... The pin configuration is to be strictly adhered to. The device is only to be operated with the voltage entered on the rating plane. Screened cables are to be used as connecting cables. The screening is to be singly earthed. The connecting cable is not to be laid parallel to the driving cables. Opera ...
FSL106MR Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™) Features
... noise nearby switching frequency and allows the use of a cost-effective inductor instead of an AC input line filter to satisfy the world-wide EMI requirements. ...
... noise nearby switching frequency and allows the use of a cost-effective inductor instead of an AC input line filter to satisfy the world-wide EMI requirements. ...
ASCO Model 350 Guide Specifications
... 1200 Volts for 120, 120/208, or 120/240 Volt systems 1200 Volts for 208, 240, 277, 220/380, 240/415 or 277/480 Volt systems 1800 Volts for 480 Volt systems 1.7.4 ANSI/UL 1449 Nominal Discharge Current: The ANSI/UL 1449 Nominal Discharge Current Rating shall be a minimum of 20kA. ...
... 1200 Volts for 120, 120/208, or 120/240 Volt systems 1200 Volts for 208, 240, 277, 220/380, 240/415 or 277/480 Volt systems 1800 Volts for 480 Volt systems 1.7.4 ANSI/UL 1449 Nominal Discharge Current: The ANSI/UL 1449 Nominal Discharge Current Rating shall be a minimum of 20kA. ...
AN1637: Level Shifting Between 1.8V and 3.3V Using I2C
... Level Shifting Between 1.8V and 3.3V Using I2C Buffers As the trend in low voltage microcontrollers migrates to 1.8V logic levels, I2C bus systems will need logic level shifting to communicate with 3.3V I2C slave devices. Without level shifting, the output logic levels of mixed voltage devices are n ...
... Level Shifting Between 1.8V and 3.3V Using I2C Buffers As the trend in low voltage microcontrollers migrates to 1.8V logic levels, I2C bus systems will need logic level shifting to communicate with 3.3V I2C slave devices. Without level shifting, the output logic levels of mixed voltage devices are n ...
Resistors in Series and Parallel
... Ammeters are used to measure current. An ammeter is connected in series with the circuit so that all the current being measured flows through the ammeter. Therefore, ammeters need to have very small resistance in order not to alter the current in the circuit. Voltmeters are used to measure voltages. ...
... Ammeters are used to measure current. An ammeter is connected in series with the circuit so that all the current being measured flows through the ammeter. Therefore, ammeters need to have very small resistance in order not to alter the current in the circuit. Voltmeters are used to measure voltages. ...
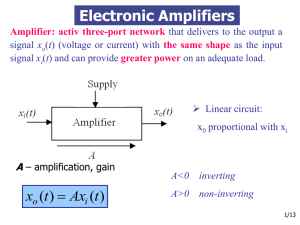
Amplificatoare electronice
... the decrease of the gain to low frequency – coupling / decoupling capacitors (usual fractions – tens of F) ...
... the decrease of the gain to low frequency – coupling / decoupling capacitors (usual fractions – tens of F) ...
AC - UniMAP Portal
... Determine the total voltages and currents that have DC and AC components. Apply Ohm’s Law, KCL, and KVL to analyze a simple AC circuit. Write the time domain equation for any sinusoidal waveform with a DC component. ...
... Determine the total voltages and currents that have DC and AC components. Apply Ohm’s Law, KCL, and KVL to analyze a simple AC circuit. Write the time domain equation for any sinusoidal waveform with a DC component. ...
PHYS 222 Worksheet 24 More AC Circuits
... 2) You have a 200-Ω resistor, a 0.400-H inductor, a 6.00-μF capacitor and a voltage source that has a voltage amplitude of 30.0 V and an angular frequency of 250 rad/s. The resistor, inductor, capacitor, and voltage source are connected to form an L-R-C series circuit. The current is given by I = I ...
... 2) You have a 200-Ω resistor, a 0.400-H inductor, a 6.00-μF capacitor and a voltage source that has a voltage amplitude of 30.0 V and an angular frequency of 250 rad/s. The resistor, inductor, capacitor, and voltage source are connected to form an L-R-C series circuit. The current is given by I = I ...
Circuits PPT - sections 4 and 5
... Identify all the junctions in the circuit. Find the current into and out of each junction. How does the current into a junction compare to the current out of the junction? How might you express this mathematically? ...
... Identify all the junctions in the circuit. Find the current into and out of each junction. How does the current into a junction compare to the current out of the junction? How might you express this mathematically? ...
Equation 1
... 6. Measure the magnitude of the voltages across the inductor, capacitor and the resistor for the frequencies chosen in Table 1. For all of these measurements adjust the Volts/Div until there is no DC offset to the waveforms and until you can clearly see each sinusoidal waveform (if the sinusoidal wa ...
... 6. Measure the magnitude of the voltages across the inductor, capacitor and the resistor for the frequencies chosen in Table 1. For all of these measurements adjust the Volts/Div until there is no DC offset to the waveforms and until you can clearly see each sinusoidal waveform (if the sinusoidal wa ...
Surge protector

A surge protector (or surge suppressor) is an appliance/device designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold. This article primarily discusses specifications and components relevant to the type of protector that diverts (shorts) a voltage spike to ground; however, there is some coverage of other methods.The terms surge protection device (SPD), or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), are used to describe electrical devices typically installed in power distribution panels, process control systems, communications systems, and other heavy-duty industrial systems, for the purpose of protecting against electrical surges and spikes, including those caused by lightning. Scaled-down versions of these devices are sometimes installed in residential service entrance electrical panels, to protect equipment in a household from similar hazards.Many power strips have basic surge protection built in; these are typically clearly labeled as such. However, power strips that do not provide surge protection are sometimes erroneously referred to as ""surge protectors"".