Document
... 28.Al(OH)3 +3HCl-->AlCl3+3H2O, If 14g of Al(OH)3 is present, determine the theoretical yield of AlCl3 produced when the tablet reacts with HCl. 29. Zn+I2-->ZnI2 (a).Determine the theoretical yield if 1.912 mol of zinc is used. (b).Determine the percent yield is 515.6g of product is recovered. 30. Wh ...
... 28.Al(OH)3 +3HCl-->AlCl3+3H2O, If 14g of Al(OH)3 is present, determine the theoretical yield of AlCl3 produced when the tablet reacts with HCl. 29. Zn+I2-->ZnI2 (a).Determine the theoretical yield if 1.912 mol of zinc is used. (b).Determine the percent yield is 515.6g of product is recovered. 30. Wh ...
LaBrake, Fundamentals Diagnostic Questions
... These are questions to be used to help you fully prepare for 1A. While these topics will be covered in the 1ABC series, they will only be covered extremely briefly. It is expected that your chemistry background has prepared you to handle questions of this nature. Various sources can be used to help ...
... These are questions to be used to help you fully prepare for 1A. While these topics will be covered in the 1ABC series, they will only be covered extremely briefly. It is expected that your chemistry background has prepared you to handle questions of this nature. Various sources can be used to help ...
chemistry -- questions -
... __ 25. A research article indicates that researchers have used an isotope 3H to trace a certain metabolic process. 2H contains one protein, therefore, from the symbol that is given, we know this is a hydrogen isotope with a) three protons. b) three neutrons. c) three electrons. d) one proton and two ...
... __ 25. A research article indicates that researchers have used an isotope 3H to trace a certain metabolic process. 2H contains one protein, therefore, from the symbol that is given, we know this is a hydrogen isotope with a) three protons. b) three neutrons. c) three electrons. d) one proton and two ...
Document
... What two molecules are formed when H2O is added? • C2H3O2- and H3O+ What SIDE (left or right) will be favored when H3O+ is removed? • Right ...
... What two molecules are formed when H2O is added? • C2H3O2- and H3O+ What SIDE (left or right) will be favored when H3O+ is removed? • Right ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... • is a soft, silver-colored metal • melts at a temperature of 371 K • oxidizes easily in the presence of air • forms compounds with nonmetallic elements in nature • forms sodium chloride in the presence of chlorine gas 54 Identify one chemical property of sodium from this list. [1] 55 Convert the me ...
... • is a soft, silver-colored metal • melts at a temperature of 371 K • oxidizes easily in the presence of air • forms compounds with nonmetallic elements in nature • forms sodium chloride in the presence of chlorine gas 54 Identify one chemical property of sodium from this list. [1] 55 Convert the me ...
19-Oct
... The molar ratios allow us to relate the amounts of reactants and products in a chemical equation. ...
... The molar ratios allow us to relate the amounts of reactants and products in a chemical equation. ...
General Safety
... The nature of solutions and solution stoichiometry, water as a solvent, strong and weak electrolytes, concentration as expressed by molarity, stoichiometry calculations using solution concentrations, preparation of solutions from solids and by dilution from stock solutions, types of chemical reactio ...
... The nature of solutions and solution stoichiometry, water as a solvent, strong and weak electrolytes, concentration as expressed by molarity, stoichiometry calculations using solution concentrations, preparation of solutions from solids and by dilution from stock solutions, types of chemical reactio ...
Sample Exercise 19.1 Identifying Spontaneous Processes
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
The Rotational Hamiltonian
... (Note: No dipole moment) - Symmetric: Two equal moments (NH3, CH3CN) - Linear: One moment (CO2, HCl, HCN) (Note: Dipole moment depends on asymmetry) - Asymmetric: Three unequal moments (H2O) ...
... (Note: No dipole moment) - Symmetric: Two equal moments (NH3, CH3CN) - Linear: One moment (CO2, HCl, HCN) (Note: Dipole moment depends on asymmetry) - Asymmetric: Three unequal moments (H2O) ...
Section B - 8 UNO NON-WASTE CHEMICAL STORAGE
... Based on the information given in the EPA document mentioned above, eight general compatibility categories have been developed for use at UNO. Incompatibilities within those categories are broken down into classes. These compatibility classes are described below. The compatibility classes are prior ...
... Based on the information given in the EPA document mentioned above, eight general compatibility categories have been developed for use at UNO. Incompatibilities within those categories are broken down into classes. These compatibility classes are described below. The compatibility classes are prior ...
Chapter 19, part II Notes
... Equilibrium Reactions LeChatelier’s Principle Equilibrium Constants ...
... Equilibrium Reactions LeChatelier’s Principle Equilibrium Constants ...
Synthesis of monoselenanedisulfanediphosphonate by the reaction
... the amount of which is in proportion to the amount of selenite ions, was again titrated with thiosulfate. Selenium was also determined iodometrically in another way. A sample was oxidized by bromine to selenous acid, which has been determined by the reaction (8). The sample was dissolved in a mixtur ...
... the amount of which is in proportion to the amount of selenite ions, was again titrated with thiosulfate. Selenium was also determined iodometrically in another way. A sample was oxidized by bromine to selenous acid, which has been determined by the reaction (8). The sample was dissolved in a mixtur ...
Summer Assignment: Some Review / Basic Prep
... substance. This includes all of the changes of state. 2) Chemical properties describe the way a substance may change or REACT (make new bonds) to form other substances. e.g.chemical: flammability, oxidation/reduction … almost any activity that will result in a change in the electron cloud, in terms ...
... substance. This includes all of the changes of state. 2) Chemical properties describe the way a substance may change or REACT (make new bonds) to form other substances. e.g.chemical: flammability, oxidation/reduction … almost any activity that will result in a change in the electron cloud, in terms ...
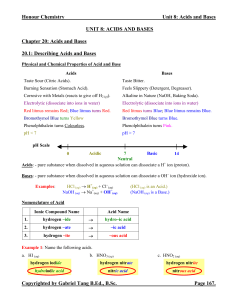
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.