Chapter 2 Water
... B. The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation The above treatment should remind you of the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation pH=pKa + log [A-]/[HA] This is the easiest equation to use when calculating buffer solution when you have a mixture of an acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A-) C. Weak acid and bases Buf ...
... B. The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation The above treatment should remind you of the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation pH=pKa + log [A-]/[HA] This is the easiest equation to use when calculating buffer solution when you have a mixture of an acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A-) C. Weak acid and bases Buf ...
Stability and Kinetics of the Acid
... The starting solutions of the complexes contained CuII and L in 2:1 molar ratio ([L]0= 3.7510-5 ...
... The starting solutions of the complexes contained CuII and L in 2:1 molar ratio ([L]0= 3.7510-5 ...
I have put this in the format of the 1984 exam
... 28. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) When the concentration of substance B in the reaction above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) the order of the reaction with respec ...
... 28. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) When the concentration of substance B in the reaction above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) the order of the reaction with respec ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... Chemical bonds are broken, atoms rearranged, and new bonds form in chemical reaction Plants use sunlight to produce sugars such as C6H12O6 glucose; the chemical energy from the sun is stored in the chemical bonds of glucose Organisms eat plants, break down the sugars, and release energy along with ...
... Chemical bonds are broken, atoms rearranged, and new bonds form in chemical reaction Plants use sunlight to produce sugars such as C6H12O6 glucose; the chemical energy from the sun is stored in the chemical bonds of glucose Organisms eat plants, break down the sugars, and release energy along with ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2016
... Predict whether the following combinations will result in a reaction. Write a balanced reaction for those reactions. Indicate you understand the specific reactions by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction. Hopefully you would have memorized the solubility rules before attempting to answer ...
... Predict whether the following combinations will result in a reaction. Write a balanced reaction for those reactions. Indicate you understand the specific reactions by writing the net ionic equation for the reaction. Hopefully you would have memorized the solubility rules before attempting to answer ...
CHM 212 - The Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta
... HF is also recycled from aluminum manufacturing processes, petroleum alkylation processes. F2 is prepared industrially by electrolytic oxidation of F- ion. (The electrolyte is a mixture of anhydrous molten KF and HF, the electrolysis cell is a steel or Cu cathode, ungraphilized carbon anode, a Mond ...
... HF is also recycled from aluminum manufacturing processes, petroleum alkylation processes. F2 is prepared industrially by electrolytic oxidation of F- ion. (The electrolyte is a mixture of anhydrous molten KF and HF, the electrolysis cell is a steel or Cu cathode, ungraphilized carbon anode, a Mond ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
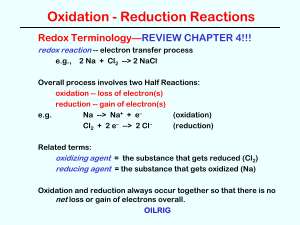
... HALF-REACTION METHOD for balancing Redox Equations 1. Write unbalanced ionic equations for the two half-reactions. (Look at oxidation numbers in the “skeleton equation.”) 2. Balance atoms other than H and O. 3. Add appropriate number of electrons. 4. Balance O with H2O. 5. Balance H with H+. 6. If ...
... HALF-REACTION METHOD for balancing Redox Equations 1. Write unbalanced ionic equations for the two half-reactions. (Look at oxidation numbers in the “skeleton equation.”) 2. Balance atoms other than H and O. 3. Add appropriate number of electrons. 4. Balance O with H2O. 5. Balance H with H+. 6. If ...
1 Q. If ΔrH is positive, what can you say about the reaction? 2 Q If
... up (and so its container would get hot) because it is releasing energy from its surroundings. ...
... up (and so its container would get hot) because it is releasing energy from its surroundings. ...
FORM 1 GEOGRAPHY REVISION GRID
... Recall the charge, mass and position of the particles found in an atom Define atomic number and mass number Draw an atom of an element (atomic numbers 1- 20) Define an Isotope Define an Ion and be able to draw the electronic structure of an ion ...
... Recall the charge, mass and position of the particles found in an atom Define atomic number and mass number Draw an atom of an element (atomic numbers 1- 20) Define an Isotope Define an Ion and be able to draw the electronic structure of an ion ...
Review Session 3 Problems
... If we have 100. g P4 and 250. g of Cl2 which will be the limiting reagent? ...
... If we have 100. g P4 and 250. g of Cl2 which will be the limiting reagent? ...
Document
... (b) Adding water to spilled acids and bases id the best way to reduce any potential harm. (c) Goggles must be worn only when dealing with chemicals. (d) If you break a piece of glassware, you should pick up all the pieces with your hands. ...
... (b) Adding water to spilled acids and bases id the best way to reduce any potential harm. (c) Goggles must be worn only when dealing with chemicals. (d) If you break a piece of glassware, you should pick up all the pieces with your hands. ...
sample paper chemistry clas xi set 3
... 3. Locate the position of element with atomic number 33. 4. Define Charles law. 5. What is the entropy change when a liquid vaporizes? 6. What is the conjugate acid of NH3? 7. Which out of the two- lithium or sodium forms nitrides? 8. What effect does branching of an alkane has on its boiling point? ...
... 3. Locate the position of element with atomic number 33. 4. Define Charles law. 5. What is the entropy change when a liquid vaporizes? 6. What is the conjugate acid of NH3? 7. Which out of the two- lithium or sodium forms nitrides? 8. What effect does branching of an alkane has on its boiling point? ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.