View PDF
... Position & Motion of Objects in the sky Big Ideas: The sun is the central and largest body in the solar system. The sun’s warming of the Earth and tilt of the Earth on its axis have an importan t connection to the seasons. Earth’s motion is the basis for measuring time. Objects in the sky move in re ...
... Position & Motion of Objects in the sky Big Ideas: The sun is the central and largest body in the solar system. The sun’s warming of the Earth and tilt of the Earth on its axis have an importan t connection to the seasons. Earth’s motion is the basis for measuring time. Objects in the sky move in re ...
DAILY LESSON PLAN FORMAT
... the universe. Key concepts include a) cosmology including the Big Bang theory; and b) the origin and evolution of stars, star systems, and galaxies. Essential knowledge or skills to be taught: Describe the development of exploration of the Moon Identify the relative positions and motions of Eart ...
... the universe. Key concepts include a) cosmology including the Big Bang theory; and b) the origin and evolution of stars, star systems, and galaxies. Essential knowledge or skills to be taught: Describe the development of exploration of the Moon Identify the relative positions and motions of Eart ...
File
... The other planets take different amounts of time to complete one revolution (Mercury – 88 days; Neptune – 164 years) ...
... The other planets take different amounts of time to complete one revolution (Mercury – 88 days; Neptune – 164 years) ...
Page 577 - ClassZone
... For thousands of years, the predominant model of the universe stated that Earth stood still at the center of the universe. Such a model of the universe is called a geocentric (JEE-oh-SEN-trihk), or Earth-centered, model. As long as 6000 years ago, astronomers were recording the movements of the star ...
... For thousands of years, the predominant model of the universe stated that Earth stood still at the center of the universe. Such a model of the universe is called a geocentric (JEE-oh-SEN-trihk), or Earth-centered, model. As long as 6000 years ago, astronomers were recording the movements of the star ...
Find the Planet Facts column for each of the planets: Mercury: Venus
... Why do you think there isn’t much of a temperature range on Venus? ___Greenhouse effect from all the clouds that cover Venus. The heat from the sun can’t escape. ___The people who live on Venus have the whole planet under climate control so it never varies more than 10oC ___It’s too close to the sun ...
... Why do you think there isn’t much of a temperature range on Venus? ___Greenhouse effect from all the clouds that cover Venus. The heat from the sun can’t escape. ___The people who live on Venus have the whole planet under climate control so it never varies more than 10oC ___It’s too close to the sun ...
Review Questions on the Solar System
... 10. True or False: All planets have at least one moon. (If the answer is false, correct the statement above) False, Mercury + Venus have no moons. 11. Why is a full day on Earth 24 hours? It takes 23h 56 min for the Earth to rotate on its axis. 12. Which planet has the longest rotation period? Venus ...
... 10. True or False: All planets have at least one moon. (If the answer is false, correct the statement above) False, Mercury + Venus have no moons. 11. Why is a full day on Earth 24 hours? It takes 23h 56 min for the Earth to rotate on its axis. 12. Which planet has the longest rotation period? Venus ...
Formation of the solar system notes
... We know that stars, in life and death create new elements. We can also see stars forming from the nebula of stars that have died before them. (think recycling!) ...
... We know that stars, in life and death create new elements. We can also see stars forming from the nebula of stars that have died before them. (think recycling!) ...
Planets - Classifying
... high densities, slow rotation and solid surfaces Jovian – Gas planets composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Tend to have low densities, rapid rotation and deep atmospheres. Pluto belongs to neither group. It is mainly composed of ice. ...
... high densities, slow rotation and solid surfaces Jovian – Gas planets composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Tend to have low densities, rapid rotation and deep atmospheres. Pluto belongs to neither group. It is mainly composed of ice. ...
Solar system rotation curves: student activity
... Activity: Rotation curves for the solar system. ...
... Activity: Rotation curves for the solar system. ...
Other objects in space guided notes
... • When the comet gets close to the sun the ice evaporates and creates an atmosphere called an _______________ • Radiation from the sun push some of the gas and dust away creating a _______________________ • Can only see be seen if they have a tail, so they only appear near the Sun • ________________ ...
... • When the comet gets close to the sun the ice evaporates and creates an atmosphere called an _______________ • Radiation from the sun push some of the gas and dust away creating a _______________________ • Can only see be seen if they have a tail, so they only appear near the Sun • ________________ ...
solar eclipse
... eclipses were caused by a giant dragon eating the sun. The Emperor ordered that to frighten the dragon away, loud drums were to be beaten and arrows fired into the air. After the few minutes, the loud noises and weapons scared off the dragon, and the sun returned. ...
... eclipses were caused by a giant dragon eating the sun. The Emperor ordered that to frighten the dragon away, loud drums were to be beaten and arrows fired into the air. After the few minutes, the loud noises and weapons scared off the dragon, and the sun returned. ...
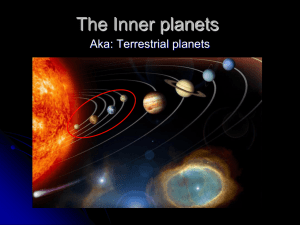
The Inner planets
... Seen from earth just after sunset in the west. Also known as the evening star. So close to the size of the earth that it is called “Earth’s Twin” Venus rotates on its axis so slowly its day is longer than a its year Very hostile atmosphere. The atmosphere pressure is 90 times greater than ours. Venu ...
... Seen from earth just after sunset in the west. Also known as the evening star. So close to the size of the earth that it is called “Earth’s Twin” Venus rotates on its axis so slowly its day is longer than a its year Very hostile atmosphere. The atmosphere pressure is 90 times greater than ours. Venu ...
Our Solar System
... • Neptune has visual belts of clouds • It has a system of 5 rings and at least 13 moons • Orbit Period 165 years • Rotation Period 16 hours ...
... • Neptune has visual belts of clouds • It has a system of 5 rings and at least 13 moons • Orbit Period 165 years • Rotation Period 16 hours ...
MERCURY VENUS MARS JUPITER
... 88 days, which is the same as four complete journeys around the Sun every year. If people moved to Mercury, they would be four times older than their Earth age! It moves so quickly that it can only be seen from Earth six times a year. ...
... 88 days, which is the same as four complete journeys around the Sun every year. If people moved to Mercury, they would be four times older than their Earth age! It moves so quickly that it can only be seen from Earth six times a year. ...
The Inner Planets of Our Solar System
... The Inner Planets of Our Solar System Why are they called the Inner planets? • They are closer together and closer to the sun Mercury l Closest planet to our sun l Smallest planet in the solar system l Planet with the longest day l Fastest orbiting planet l Caloris Basin is the largest impact c ...
... The Inner Planets of Our Solar System Why are they called the Inner planets? • They are closer together and closer to the sun Mercury l Closest planet to our sun l Smallest planet in the solar system l Planet with the longest day l Fastest orbiting planet l Caloris Basin is the largest impact c ...
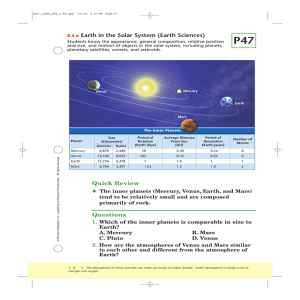
Quick Review Questions 8.4.e Earth in the Solar System (Earth
... Students know the appearance, general composition, relative position and size, and motion of objects in the solar system, including planets, planetary satellites, comets, and asteroids. ...
... Students know the appearance, general composition, relative position and size, and motion of objects in the solar system, including planets, planetary satellites, comets, and asteroids. ...
Astronomy Guided Reading
... d. the same mass as all of the other planets and moons combined _________are pieces of rocky and metallic materials held together by frozen gases. One of Jupiter’s moons,______________, is one of only three volcanically active bodies in the solar system. A(n)___________________________ , or display ...
... d. the same mass as all of the other planets and moons combined _________are pieces of rocky and metallic materials held together by frozen gases. One of Jupiter’s moons,______________, is one of only three volcanically active bodies in the solar system. A(n)___________________________ , or display ...
física y química – 4.º eso – everest primer trimestre – evaluación
... a) The satellite has a period of rotation, T=1 year. b) The speed of the satellite around the Earth is 10,000 ms-1. c) In this case, the centripetal force is the gravitational force and has a value of 1.12 x 103 N. d) The gravitational acceleration at the height of the satellite is bigger than on th ...
... a) The satellite has a period of rotation, T=1 year. b) The speed of the satellite around the Earth is 10,000 ms-1. c) In this case, the centripetal force is the gravitational force and has a value of 1.12 x 103 N. d) The gravitational acceleration at the height of the satellite is bigger than on th ...
in which direction would the ball fly off?
... speed to win it all. a. What limits the speed at which he can negotiate the curve? b. If he goes into a curve of 200 m radius with a speed of 100 m/s, what centripetal acceleration does he experience? ...
... speed to win it all. a. What limits the speed at which he can negotiate the curve? b. If he goes into a curve of 200 m radius with a speed of 100 m/s, what centripetal acceleration does he experience? ...
Study Guide: Astronomy Test
... a. diameter of the Milky Way________ b. distance from the sun to Earth_______ c. distance from Earth to Neptune_______ d. distance from the sun to the nearest star______ e. distance from the Milky Way to the closest galaxy?_______ f. distance from the center of the Milky Way to the solar system?____ ...
... a. diameter of the Milky Way________ b. distance from the sun to Earth_______ c. distance from Earth to Neptune_______ d. distance from the sun to the nearest star______ e. distance from the Milky Way to the closest galaxy?_______ f. distance from the center of the Milky Way to the solar system?____ ...
miracleplanetnotes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... N- gaseous, no solid core U- rings, same size as N S- ice crystal rings J- 1000x earth size, ammonia hydrogen atmos. M- fastest orbit, barren surface V- hot, poisonous atmos. MER- red, hostile, desolate 3) SPACE TRAVEL PIECES TOGETHER… details of earth’s origin 4) IMPORTANCE OF MOON’S CRATORSthese t ...
... N- gaseous, no solid core U- rings, same size as N S- ice crystal rings J- 1000x earth size, ammonia hydrogen atmos. M- fastest orbit, barren surface V- hot, poisonous atmos. MER- red, hostile, desolate 3) SPACE TRAVEL PIECES TOGETHER… details of earth’s origin 4) IMPORTANCE OF MOON’S CRATORSthese t ...
A Quick Tour of the Solar System
... and the Oort cloud toward the sun in an elliptical orbit. We see the tail, or cloud of dust and gas surrounding the comet’s core, as it is blown by the solar wind. ...
... and the Oort cloud toward the sun in an elliptical orbit. We see the tail, or cloud of dust and gas surrounding the comet’s core, as it is blown by the solar wind. ...
Earth's rotation

Earth's rotation is the rotation of the planet Earth around its own axis. The Earth rotates from the west towards east. As viewed from North Star or polestar Polaris, the Earth turns counter-clockwise.The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from the Earth's North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is the other point where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica.The Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the sun and once every 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to the stars (see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tidal effects the Moon has on Earth's rotation. Atomic clocks show that a modern-day is longer by about 1.7 milliseconds than a century ago, slowly increasing the rate at which UTC is adjusted by leap seconds.