Name
... As a part of their training before going into orbit, astronauts ride in an airliner that is flown along the parabolic trajectory as a freely falling projectile. Explain why this gives the same apparent weightlessness as being in orbit. ...
... As a part of their training before going into orbit, astronauts ride in an airliner that is flown along the parabolic trajectory as a freely falling projectile. Explain why this gives the same apparent weightlessness as being in orbit. ...
CALIFORNIA WRITING STANDARDS
... mass of the two objects and the distance between them. Objects in the solar system are held in their predictable paths by the inward-pulling gravitational attraction of the very massive sun. 2. The Earth and other planets move through space in two ways: rotation on an axis and revolution around the ...
... mass of the two objects and the distance between them. Objects in the solar system are held in their predictable paths by the inward-pulling gravitational attraction of the very massive sun. 2. The Earth and other planets move through space in two ways: rotation on an axis and revolution around the ...
PILEO GRADO 8° The Earth, Sun and Moon On most day the sun
... cannot tell that earth carries you with it as a moves . The earth spins -or rotates- as a basketball spin son the tip of a player’s finger. The earth makes one rotation when it spins around once. The time for each rotation is 24 hours –what we call a day. The earth rotates around an imaginary line t ...
... cannot tell that earth carries you with it as a moves . The earth spins -or rotates- as a basketball spin son the tip of a player’s finger. The earth makes one rotation when it spins around once. The time for each rotation is 24 hours –what we call a day. The earth rotates around an imaginary line t ...
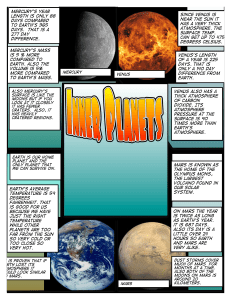
Mercury`s year length is only 88 days compared to
... surface is 90 times more than Earth's atmosphere. ...
... surface is 90 times more than Earth's atmosphere. ...
A Short Look at Earth History
... • Objects kilometers across hold together by gravity • As planets get bigger, gravity gets stronger, impacts get more violent • Big impacts throw out sediment/rocks, trap heat • Magma ocean • Formation of core early in earth history as iron sinks ...
... • Objects kilometers across hold together by gravity • As planets get bigger, gravity gets stronger, impacts get more violent • Big impacts throw out sediment/rocks, trap heat • Magma ocean • Formation of core early in earth history as iron sinks ...
Dawn of Astronomy - University of Toledo
... Benchmark A: Describe how the positions and motions of the objects in the universe cause predictable and cyclic events. Benchmark B: Explain that the universe is composed of vast amounts of matter, most of which is at incomprehensible distances and held together by a gravitational force. Describe ho ...
... Benchmark A: Describe how the positions and motions of the objects in the universe cause predictable and cyclic events. Benchmark B: Explain that the universe is composed of vast amounts of matter, most of which is at incomprehensible distances and held together by a gravitational force. Describe ho ...
Solar_System_handout
... - protoplanetary disc: the revolving ring of excess material that, over time, accumulated together to form the planets, moons, and asteroids *During the protostar’s transition into our current sun, the center of the cloud was incredibly hot, and only rocky non-gaseous materials could withstand the h ...
... - protoplanetary disc: the revolving ring of excess material that, over time, accumulated together to form the planets, moons, and asteroids *During the protostar’s transition into our current sun, the center of the cloud was incredibly hot, and only rocky non-gaseous materials could withstand the h ...
The Formation of the Solar System
... - protoplanetary disc: the revolving ring of excess material that, over time, accumulated together to form the planets, moons, and asteroids *During the protostar’s transition into our current sun, the center of the cloud was incredibly hot, and only rocky non-gaseous materials could withstand the h ...
... - protoplanetary disc: the revolving ring of excess material that, over time, accumulated together to form the planets, moons, and asteroids *During the protostar’s transition into our current sun, the center of the cloud was incredibly hot, and only rocky non-gaseous materials could withstand the h ...
Astronomy Introduction
... • Planets, sun, moons all have mass and gravity • Without gravity, the planets would move through space through their inertia ...
... • Planets, sun, moons all have mass and gravity • Without gravity, the planets would move through space through their inertia ...
Tutorial 6
... suppose it got stronger. If that fictitious law were true, would it be possible for bodies such as the planets to orbit the Sun? Hint: assume that a planet could still execute uniform circular motion. a) Yes, just as they presently do ...
... suppose it got stronger. If that fictitious law were true, would it be possible for bodies such as the planets to orbit the Sun? Hint: assume that a planet could still execute uniform circular motion. a) Yes, just as they presently do ...
Definition - SchoolNotes
... geographer, and astronomer, who lived almost 2,000 years ago, was the first scientist to formulate this idea. In the Ptolemaic system, or geocentric view of the universe, Ptolemy described the planets and stars are revolving around the Earth in perfect circular orbits. Definition: an early model of ...
... geographer, and astronomer, who lived almost 2,000 years ago, was the first scientist to formulate this idea. In the Ptolemaic system, or geocentric view of the universe, Ptolemy described the planets and stars are revolving around the Earth in perfect circular orbits. Definition: an early model of ...
Earth`s rotation?
... What shape is the Earth’s orbit? • The Earth’s orbit around the sun is shaped like an ellipse. • An ellipse is a slightly flattened circle. • Mars has a very elliptical orbit. Because of this, the difference between its closest and most distant point along its orbit vary by 19%. This extreme differ ...
... What shape is the Earth’s orbit? • The Earth’s orbit around the sun is shaped like an ellipse. • An ellipse is a slightly flattened circle. • Mars has a very elliptical orbit. Because of this, the difference between its closest and most distant point along its orbit vary by 19%. This extreme differ ...
EARTH AS A PLANET TEST REVIEW
... 19. What is the main contributor of our seasonal changes? Why is this so? Add a diagram to clarify. ...
... 19. What is the main contributor of our seasonal changes? Why is this so? Add a diagram to clarify. ...
File
... Ceres has recently been promoted to the status of dwarf planet (like Pluto). Some asteroids even have their own moon. Meteoroids, Meteors, Meteorites Meteoroids are pieces of rock moving through space. Astronomers think that meteoroids are rocky chunks that have broken off asteroids and planets. Whe ...
... Ceres has recently been promoted to the status of dwarf planet (like Pluto). Some asteroids even have their own moon. Meteoroids, Meteors, Meteorites Meteoroids are pieces of rock moving through space. Astronomers think that meteoroids are rocky chunks that have broken off asteroids and planets. Whe ...
Same and Different - Passport to Knowledge
... For example, do all three objects have a core? Yes. Is that core solid? Yes, for Earth. No, for the Sun, though pressure at its center is so great that the plasma of ions and electrons is 13 times denser than lead. Does that make it solid? No. As for Jupiter, we don’t know, but researchers think the ...
... For example, do all three objects have a core? Yes. Is that core solid? Yes, for Earth. No, for the Sun, though pressure at its center is so great that the plasma of ions and electrons is 13 times denser than lead. Does that make it solid? No. As for Jupiter, we don’t know, but researchers think the ...
8th grade Physical Science
... Various gaseous elements emit different spectra of light. These spectra are indicative of the types of gasses present. Using a spectroscope and a spectral tube, students can break down this light in order to analyze its components. This method is similar to that used by scientists to determine the t ...
... Various gaseous elements emit different spectra of light. These spectra are indicative of the types of gasses present. Using a spectroscope and a spectral tube, students can break down this light in order to analyze its components. This method is similar to that used by scientists to determine the t ...
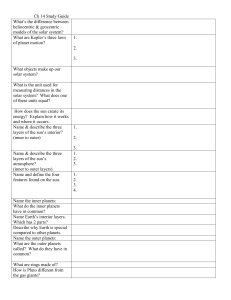
Ch 14 Study Guide What`s the difference between heliocentric
... What’s the difference between heliocentric & geocentric models of the solar system? What are Kepler’s three laws of planet motion? ...
... What’s the difference between heliocentric & geocentric models of the solar system? What are Kepler’s three laws of planet motion? ...
msess1
... Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the analysis of data from Earth-based instruments, space-based telescopes, and spacecraft to determine similarities and differences among solar system objects. Examples o ...
... Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the analysis of data from Earth-based instruments, space-based telescopes, and spacecraft to determine similarities and differences among solar system objects. Examples o ...
Benchmark Number:
... A celestial body that appears as a fuzzy head usually surrounding a bright nucleus, that has a usually highly eccentric orbit, that consists primarily of ice and dust, and that often develops one or more long tails when near the sun. ...
... A celestial body that appears as a fuzzy head usually surrounding a bright nucleus, that has a usually highly eccentric orbit, that consists primarily of ice and dust, and that often develops one or more long tails when near the sun. ...
Use only g, π, the moon`s period and earth`s radius to calculate the
... Using the last equation we had for g but from the point of the sun we obtain: ...
... Using the last equation we had for g but from the point of the sun we obtain: ...
Earth's rotation

Earth's rotation is the rotation of the planet Earth around its own axis. The Earth rotates from the west towards east. As viewed from North Star or polestar Polaris, the Earth turns counter-clockwise.The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from the Earth's North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is the other point where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica.The Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the sun and once every 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to the stars (see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tidal effects the Moon has on Earth's rotation. Atomic clocks show that a modern-day is longer by about 1.7 milliseconds than a century ago, slowly increasing the rate at which UTC is adjusted by leap seconds.