Document
... A brown dwarf is a substellar object below the sustained hydrogenburning limit of about 7.5% to 8.0% solar masses, and forms in a manner similar to stars by fragmentation of collapsing gas clouds. An extra-solar giant planet is a giant planet like Jupiter in orbit around a star other than the sun, a ...
... A brown dwarf is a substellar object below the sustained hydrogenburning limit of about 7.5% to 8.0% solar masses, and forms in a manner similar to stars by fragmentation of collapsing gas clouds. An extra-solar giant planet is a giant planet like Jupiter in orbit around a star other than the sun, a ...
C472 Continuous Assessment: Essay #2
... of the prevalence of communicating intelligent life in the Universe for the first SETI conference. The now famous Drake Equation considers, amongst others, the factors discussed by Wallace, as a series of diminishing probabilities in an attempt to quantify the number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy ...
... of the prevalence of communicating intelligent life in the Universe for the first SETI conference. The now famous Drake Equation considers, amongst others, the factors discussed by Wallace, as a series of diminishing probabilities in an attempt to quantify the number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy ...
Planets and Moons
... Phobos and Deimos Phobos and Deimos are Mars‘ companions. Phobos means “fear“, Deimos means “panic“. Mars itself has been named for the Roman God of War. They are quite small (<15km) and look rather like potatoes than like moons. ...
... Phobos and Deimos Phobos and Deimos are Mars‘ companions. Phobos means “fear“, Deimos means “panic“. Mars itself has been named for the Roman God of War. They are quite small (<15km) and look rather like potatoes than like moons. ...
Part 2: Solar System Formation
... • In the outer parts of the Solar Nebula the planets become large enough to have a significant gravitational pull and collect gas around them. – Ice is ten times more abundant than silicates and iron compounds, therefore there is more planet building material in the outer solar system. • Planets in ...
... • In the outer parts of the Solar Nebula the planets become large enough to have a significant gravitational pull and collect gas around them. – Ice is ten times more abundant than silicates and iron compounds, therefore there is more planet building material in the outer solar system. • Planets in ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants - Hutchison
... Answers will vary. [Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars all have masses below 100 ×1023 kg, radii below 10,000 km, and densities greater than 3.0 g/cm3. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune all have masses above 800 ×1023 kg, radii above 20,000 km, and densities less than 2.0 g/cm3. Pluto has characteri ...
... Answers will vary. [Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars all have masses below 100 ×1023 kg, radii below 10,000 km, and densities greater than 3.0 g/cm3. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune all have masses above 800 ×1023 kg, radii above 20,000 km, and densities less than 2.0 g/cm3. Pluto has characteri ...
lec03_30sep2011
... Disk-star- and protoplanet interactions lead to migration while the gas is present. Coreaccretion? 1 AU at 140 pc subtends 0.’’007. ...
... Disk-star- and protoplanet interactions lead to migration while the gas is present. Coreaccretion? 1 AU at 140 pc subtends 0.’’007. ...
A105 Stars and Galaxies
... A planet orbits the star e Eridani at a radius of 3.2 A.U. e Eridani is similar to our Sun e Eridani is only 10.5 light years away The planet is similar to Jupiter The planet orbits e Eridani in 7 years e Eridani has at least one more planet ...
... A planet orbits the star e Eridani at a radius of 3.2 A.U. e Eridani is similar to our Sun e Eridani is only 10.5 light years away The planet is similar to Jupiter The planet orbits e Eridani in 7 years e Eridani has at least one more planet ...
Activity: Planets and Scale - GK-12
... are also many comets, asteroids, satellites of the planets, and background dust in the solar system. The Sun contains 99.85% of all the matter in the Solar System. The planets, which condensed out of the same disk of material that formed the Sun, contain only 0.135% of the mass of the solar system. ...
... are also many comets, asteroids, satellites of the planets, and background dust in the solar system. The Sun contains 99.85% of all the matter in the Solar System. The planets, which condensed out of the same disk of material that formed the Sun, contain only 0.135% of the mass of the solar system. ...
Workbook II - Mr. Hill`s Science Website
... Find your answer on the pages shown in the book icon next to each question. 1. Which of these is not one of the criteria the group of astronomers used to identify an object in space as a planet? a. Its gravity squishes it into a round ball. b. It must orbit the Sun. c. It must have at least one moon ...
... Find your answer on the pages shown in the book icon next to each question. 1. Which of these is not one of the criteria the group of astronomers used to identify an object in space as a planet? a. Its gravity squishes it into a round ball. b. It must orbit the Sun. c. It must have at least one moon ...
Pocket Solar System - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... There are two reasons why no planet formed at the distance of the asteroid belt. First, even though there are many asteroids, most are very small. All of the asteroids added together have only 0.4% the mass of the Earth (or 4% the mass of the Moon)! Second, both Jupiter and Mars ...
... There are two reasons why no planet formed at the distance of the asteroid belt. First, even though there are many asteroids, most are very small. All of the asteroids added together have only 0.4% the mass of the Earth (or 4% the mass of the Moon)! Second, both Jupiter and Mars ...
The Planets in our Solar System Solar System Basics
... substances within the evolving solar system. • Eventually, the condensing material merged to form large bodies hundreds of kilometers in diameter. ...
... substances within the evolving solar system. • Eventually, the condensing material merged to form large bodies hundreds of kilometers in diameter. ...
Meet the Jovians` Hot Siblings DONT ERASE
... Jovians. Hundreds of these strange new planets have been found around stars the same size or smaller than our own we call the sun. The majority of these planets have been filed under the category of “Hot jupiters”. ...
... Jovians. Hundreds of these strange new planets have been found around stars the same size or smaller than our own we call the sun. The majority of these planets have been filed under the category of “Hot jupiters”. ...
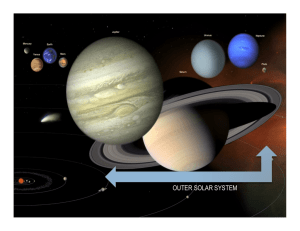
the outer solar system
... • Uranus is the seventh planet from the sun at a distance of about 2.9 billion km (1.8 billion miles) or 19.19 AU. • One day on Uranus takes about 17 hours (the time it takes for Uranus to rotate or spin once). Uranus makes a complete orbit around the sun (a year in Uranian time) in about 84 Earth ...
... • Uranus is the seventh planet from the sun at a distance of about 2.9 billion km (1.8 billion miles) or 19.19 AU. • One day on Uranus takes about 17 hours (the time it takes for Uranus to rotate or spin once). Uranus makes a complete orbit around the sun (a year in Uranian time) in about 84 Earth ...
File
... Launched in 1989, the Galileo Spacecraft, on its way to Jupiter, captured close-up images of asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Launched in 1996, the Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker (NEAR Shoemaker), passed near asteroid 253 Mathilde and established orbit around 433 Eros. In 2001, NEAR Shoemaker “ ...
... Launched in 1989, the Galileo Spacecraft, on its way to Jupiter, captured close-up images of asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Launched in 1996, the Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker (NEAR Shoemaker), passed near asteroid 253 Mathilde and established orbit around 433 Eros. In 2001, NEAR Shoemaker “ ...
INTRODUCTION
... forces. However, Venus is covered with a dense atmosphere that is mostly carbon dioxide, and has very high surface pressure (90 atm) and temperatures (462°C). ...
... forces. However, Venus is covered with a dense atmosphere that is mostly carbon dioxide, and has very high surface pressure (90 atm) and temperatures (462°C). ...
What makes a planet habitable?
... to finding a world similar to Earth. MIDDLE: The habitable zone. BOTTOM: Light from exoplanets, if passed through a prism, can be spread out into a rainbow of colors called a spectrum. Different colors correspond to different wavelengths of light. Missing colors show up as black lines, indicating spe ...
... to finding a world similar to Earth. MIDDLE: The habitable zone. BOTTOM: Light from exoplanets, if passed through a prism, can be spread out into a rainbow of colors called a spectrum. Different colors correspond to different wavelengths of light. Missing colors show up as black lines, indicating spe ...
Solar System Study Guide Questions
... 7. What are rings and how do they form? What planet or planets have rings? 8. Why is Titan and Triton interesting places? 9. Why are Uranus & Neptune blue in color? 10. How is a planet different than a dwarf planet and small solar system body? 11. Explain the entire life cycle of a comet. ...
... 7. What are rings and how do they form? What planet or planets have rings? 8. Why is Titan and Triton interesting places? 9. Why are Uranus & Neptune blue in color? 10. How is a planet different than a dwarf planet and small solar system body? 11. Explain the entire life cycle of a comet. ...
File - Mrs. Ratzlaff
... – The four larger planets having thick atmospheres and no solid surface. ...
... – The four larger planets having thick atmospheres and no solid surface. ...
Solar System Orbit Lab
... note the date at the top right of the screen) for the planets your group was assigned. Then calculate the quantity P2/D3 for each of your planets, and write it on the board in the table. (You do not need to be exact – limit yourself to two or three significant digits – but try to make your measureme ...
... note the date at the top right of the screen) for the planets your group was assigned. Then calculate the quantity P2/D3 for each of your planets, and write it on the board in the table. (You do not need to be exact – limit yourself to two or three significant digits – but try to make your measureme ...
Solar System Orbit Lab
... the quantity P /D for each of your planets, and write it on the board in the table. (You do not need to be exact – limit yourself to two or three significant digits – but try to make your measurements as accurate as you can.) Mercury ...
... the quantity P /D for each of your planets, and write it on the board in the table. (You do not need to be exact – limit yourself to two or three significant digits – but try to make your measurements as accurate as you can.) Mercury ...
Chapter 6 Our Solar System and Its Origin
... 2. able to explain all (at least most) the observable facts with reasonable accuracy, and 3. able to explain other planetary systems. ...
... 2. able to explain all (at least most) the observable facts with reasonable accuracy, and 3. able to explain other planetary systems. ...
Chapter 6 Our Solar System and Its Origin
... 2. able to explain all (at least most) the observable facts with reasonable accuracy, and 3. able to explain other planetary systems. ...
... 2. able to explain all (at least most) the observable facts with reasonable accuracy, and 3. able to explain other planetary systems. ...
The solar system
... • Numerous large volcanoes – largest is Mons Olympus • Less-abundant impact craters • Tectonically dead • Several canyons • Some larger than Grand Canyon ...
... • Numerous large volcanoes – largest is Mons Olympus • Less-abundant impact craters • Tectonically dead • Several canyons • Some larger than Grand Canyon ...
Dwarf planet

A dwarf planet is a planetary-mass object that is neither a planet nor a natural satellite. That is, it is in direct orbit of the Sun, and is massive enough for its shape to be in hydrostatic equilibrium under its own gravity, but has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit.The term dwarf planet was adopted in 2006 as part of a three-way categorization of bodies orbiting the Sun, brought about by an increase in discoveries of objects farther away from the Sun than Neptune that rivaled Pluto in size, and finally precipitated by the discovery of an even more massive object, Eris. The exclusion of dwarf planets from the roster of planets by the IAU has been both praised and criticized; it was said to be the ""right decision"" by astronomer Mike Brown, who discovered Eris and other new dwarf planets, but has been rejected by Alan Stern, who had coined the term dwarf planet in 1990.The International Astronomical Union (IAU) currently recognizes five dwarf planets: Ceres, Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris. Brown criticizes this official recognition: ""A reasonable person might think that this means that there are five known objects in the solar system which fit the IAU definition of dwarf planet, but this reasonable person would be nowhere close to correct.""It is suspected that another hundred or so known objects in the Solar System are dwarf planets. Estimates are that up to 200 dwarf planets may be found when the entire region known as the Kuiper belt is explored, and that the number may exceed 10,000 when objects scattered outside the Kuiper belt are considered. Individual astronomers recognize several of these, and in August 2011 Mike Brown published a list of 390 candidate objects, ranging from ""nearly certain"" to ""possible"" dwarf planets. Brown currently identifies eleven known objects – the five accepted by the IAU plus 2007 OR10, Quaoar, Sedna, Orcus, 2002 MS4 and Salacia – as ""virtually certain"", with another dozen highly likely. Stern states that there are more than a dozen known dwarf planets.However, only two of these bodies, Ceres and Pluto, have been observed in enough detail to demonstrate that they actually fit the IAU's definition. The IAU accepted Eris as a dwarf planet because it is more massive than Pluto. They subsequently decided that unnamed trans-Neptunian objects with an absolute magnitude brighter than +1 (and hence a diameter of ≥838 km assuming a geometric albedo of ≤1) are to be named under the assumption that they are dwarf planets. The only two such objects known at the time, Makemake and Haumea, went through this naming procedure and were declared to be dwarf planets. The question of whether other likely objects are dwarf planets has never been addressed by the IAU. The classification of bodies in other planetary systems with the characteristics of dwarf planets has not been addressed.