Page 1 Neuropharmacology of Traumatic Brain Injury
... • Up to 25% of delirious medical patients die during hospitalization and 37% within 1-3 months of onset • Can lead to self-injurious behavior, decreased selfmanagement, caregiver management problems • Associated with increased length of hospital stay and increased risk of institutional placement • O ...
... • Up to 25% of delirious medical patients die during hospitalization and 37% within 1-3 months of onset • Can lead to self-injurious behavior, decreased selfmanagement, caregiver management problems • Associated with increased length of hospital stay and increased risk of institutional placement • O ...
Symptoms
... secondary health problems, such as cirrhosis of the liver, heart problems (in part, the result of being overweight), and various forms of cancer, as well as severe and persistent forms of dementia and memory impairment or amnestic disorders, such as Korsakoff’s syndrome • Alcoholism is also associat ...
... secondary health problems, such as cirrhosis of the liver, heart problems (in part, the result of being overweight), and various forms of cancer, as well as severe and persistent forms of dementia and memory impairment or amnestic disorders, such as Korsakoff’s syndrome • Alcoholism is also associat ...
biopsychosocial_dim - Multi
... Treatment. Medications can be used to help reestablish normal brain function and to prevent relapse and diminish cravings. Currently, we have medications for opioids (heroin, morphine), tobacco (nicotine), and alcohol addiction and are developing others for treating stimulant (cocaine, methamphetami ...
... Treatment. Medications can be used to help reestablish normal brain function and to prevent relapse and diminish cravings. Currently, we have medications for opioids (heroin, morphine), tobacco (nicotine), and alcohol addiction and are developing others for treating stimulant (cocaine, methamphetami ...
Unrecognised Facts about Modern Psychiatric Practice
... inspired by a few interesting discoveries related to what are now know as the organic brain diseases. Perhaps the best-known example is Huntington’s disease. This is caused by a gene carried on chromosome 4 that destroys brain cells on the frontal lobes, leading to impairments in cognitive functioni ...
... inspired by a few interesting discoveries related to what are now know as the organic brain diseases. Perhaps the best-known example is Huntington’s disease. This is caused by a gene carried on chromosome 4 that destroys brain cells on the frontal lobes, leading to impairments in cognitive functioni ...
PSYCHOSIS Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital What is Psychosis?
... Research indicates that relapse of symptoms is much less likely for people who comply with medication. The main type of medications prescribed for psychotic conditions are the antipsychotics. The newer style oral antipsychotics (‘atypicals’) are used widely as they cause far fewer side effects than ...
... Research indicates that relapse of symptoms is much less likely for people who comply with medication. The main type of medications prescribed for psychotic conditions are the antipsychotics. The newer style oral antipsychotics (‘atypicals’) are used widely as they cause far fewer side effects than ...
Development of Diagnostic Variables
... Criteria for Major Depressive Episode A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. Note: Do not include symp ...
... Criteria for Major Depressive Episode A. Five (or more) of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2-week period and represent a change from previous functioning; at least one of the symptoms is either (1) depressed mood or (2) loss of interest or pleasure. Note: Do not include symp ...
The Subjective Experience of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Pediatric
... long from school as those patients who recovery within the typical timeframe (Grubenhoff, Deakyne, Comstock, Kirkwood, & Bajaj, 2015). Studies have also suggested that mood symptoms are comorbid with concussion recovery (Luis & Mittenberg, 2002). Further, pediatric concussion patients who suffer fro ...
... long from school as those patients who recovery within the typical timeframe (Grubenhoff, Deakyne, Comstock, Kirkwood, & Bajaj, 2015). Studies have also suggested that mood symptoms are comorbid with concussion recovery (Luis & Mittenberg, 2002). Further, pediatric concussion patients who suffer fro ...
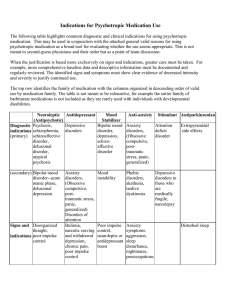
Indications for Psychotropic Medication Use
... This is perhaps the most contentious and challenging rationale. The risk of it being used as a “garbage can” to justify medication for a variety of unpleasant, obnoxious, even hurtful behaviors that serve clear functional means for an individual is inherent. This rationale should be accompanied by a ...
... This is perhaps the most contentious and challenging rationale. The risk of it being used as a “garbage can” to justify medication for a variety of unpleasant, obnoxious, even hurtful behaviors that serve clear functional means for an individual is inherent. This rationale should be accompanied by a ...
Slide Deck
... – Note: there was no difference in hippocampal size between those who never had PTSD and those who had recovered from PTSD • Interpretations? ...
... – Note: there was no difference in hippocampal size between those who never had PTSD and those who had recovered from PTSD • Interpretations? ...
Tourette Syndrome - Canadian Psychological Association
... presentations is therefore an extremely important component of initial care; in fact, a thorough demystification can even diminish any further need for treatment at all. Psychology can also help with neurodevelopmental conditions commonly comorbid with TS. For example, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder ...
... presentations is therefore an extremely important component of initial care; in fact, a thorough demystification can even diminish any further need for treatment at all. Psychology can also help with neurodevelopmental conditions commonly comorbid with TS. For example, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder ...
inhalants - Family Drug Support Australia
... tried. Detoxification from inhalants takes much longer than from alcohol; short-term detoxification requires from two weeks to 30 days. By this time, mental function starts to return to normal and participation in conventional treatment programs and counselling may become possible. A gradual longer ...
... tried. Detoxification from inhalants takes much longer than from alcohol; short-term detoxification requires from two weeks to 30 days. By this time, mental function starts to return to normal and participation in conventional treatment programs and counselling may become possible. A gradual longer ...
Epidemiology of Psychoses
... use (more than 15 x) increased risk of schizophrenia 6 x Cannabis associated psychosis associated with FH schizophrenia Also some interest in LSD and other hallucinogens role in initiation ...
... use (more than 15 x) increased risk of schizophrenia 6 x Cannabis associated psychosis associated with FH schizophrenia Also some interest in LSD and other hallucinogens role in initiation ...
Final Recommendations
... cutoff scores. It is important to note that individuals do not typically endorse a self-harm item exclusively or independent of other symptom; rather, it occurs with several other symptom endorsements. Thus, it is the patient’s endorsement of multiple symptoms that will define the need for services ...
... cutoff scores. It is important to note that individuals do not typically endorse a self-harm item exclusively or independent of other symptom; rather, it occurs with several other symptom endorsements. Thus, it is the patient’s endorsement of multiple symptoms that will define the need for services ...
Psychiatric drug-induced Chronic Brain Impairment (CBI
... or terminate drug treatment. CBI is the most frequent reason families become concerned about taking a family member off psychiatric drugs. CBI also leads individual patients to seek psychiatric help for themselves, but often they do not attribute their worsening condition to drug effects. Instead, t ...
... or terminate drug treatment. CBI is the most frequent reason families become concerned about taking a family member off psychiatric drugs. CBI also leads individual patients to seek psychiatric help for themselves, but often they do not attribute their worsening condition to drug effects. Instead, t ...
Insomnia - Heal Naturally
... Insomnia is defined as the persistent difficulty or the inability to fall and/or stay asleep. This condition may have no apparent etiology, but is often a symptom of an underlying medical or psychological condition. Insomnia is generally not considered a disease, but rather a symptom of other pathol ...
... Insomnia is defined as the persistent difficulty or the inability to fall and/or stay asleep. This condition may have no apparent etiology, but is often a symptom of an underlying medical or psychological condition. Insomnia is generally not considered a disease, but rather a symptom of other pathol ...
Schizophrenia
... be done very carefully, because introspection and selfdisclosure may cause intense emotions and even a psychotic episode What seems best is practical advice and support, helping the client to distinguish reality from illusion, and setting specific goals Group therapy can be helpful for it provid ...
... be done very carefully, because introspection and selfdisclosure may cause intense emotions and even a psychotic episode What seems best is practical advice and support, helping the client to distinguish reality from illusion, and setting specific goals Group therapy can be helpful for it provid ...
Dimensional Assessment for Co
... Dimension 6 Assessment Considerations • Do any family members, significant others, living situations, or school or work situations pose a threat to the person’s safety or engagement in treatment • Are there supportive family, friendships, financial resources, or educational/vocational resources • A ...
... Dimension 6 Assessment Considerations • Do any family members, significant others, living situations, or school or work situations pose a threat to the person’s safety or engagement in treatment • Are there supportive family, friendships, financial resources, or educational/vocational resources • A ...
The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders
... for the substance; or use of the same (or a closely related) substance with the intention of relieving or avoiding withdrawal symptoms; (d) evidence of tolerance, such that increased doses of the psychoactive substances are required in order to achieve effects originally produced by lower doses (cle ...
... for the substance; or use of the same (or a closely related) substance with the intention of relieving or avoiding withdrawal symptoms; (d) evidence of tolerance, such that increased doses of the psychoactive substances are required in order to achieve effects originally produced by lower doses (cle ...
Mental Health and Environmental Exposures
... shoes, equipment, tools, and even skin and hair. Careful removal of take-home exposures is especially important when children are involved, for they are often more sensitive to exposures than adults. This fact sheet does not discuss the level of exposure that can lead to mental health symptoms, in p ...
... shoes, equipment, tools, and even skin and hair. Careful removal of take-home exposures is especially important when children are involved, for they are often more sensitive to exposures than adults. This fact sheet does not discuss the level of exposure that can lead to mental health symptoms, in p ...
Panic Disorder
... primary care intervention. Studies suggest that virtually all placebo patients who sampled alcohol relapsed, while only half the naltrexone patients who sampled alcohol relapsed. ...
... primary care intervention. Studies suggest that virtually all placebo patients who sampled alcohol relapsed, while only half the naltrexone patients who sampled alcohol relapsed. ...
Continuous, categorical and mixture models of DSM
... analysis (CFA) using community and treatment centre samples. With this sample they found a two-factor solution no better than the one-factor solution; but when they ‘trimmed’ the data of extreme respondents (those who responded ‘no’ to all criteria or ‘yes’ to 10 or 11 criteria) they found the two-f ...
... analysis (CFA) using community and treatment centre samples. With this sample they found a two-factor solution no better than the one-factor solution; but when they ‘trimmed’ the data of extreme respondents (those who responded ‘no’ to all criteria or ‘yes’ to 10 or 11 criteria) they found the two-f ...
Definitions, Terms, and Self-Assessment
... overdose. Alcohol and other drug addiction can cause serious medical problems in one’s brain, liver, heart, and many other organs. Alcohol and other drug use has a strong role in suicides, homicides, motor vehicle crashes, and other traumatic events. Addiction involves poor control over use. Poor co ...
... overdose. Alcohol and other drug addiction can cause serious medical problems in one’s brain, liver, heart, and many other organs. Alcohol and other drug use has a strong role in suicides, homicides, motor vehicle crashes, and other traumatic events. Addiction involves poor control over use. Poor co ...
Amphetamines Addiction
... To diagnose amphetamine dependence, your doctor may : • ask you questions to find out how much and long you have been using amphetamines • take blood tests to detect amphetamines in your system • perform a physical exam and order any necessary tests to detect health problems caused by your amphetamin ...
... To diagnose amphetamine dependence, your doctor may : • ask you questions to find out how much and long you have been using amphetamines • take blood tests to detect amphetamines in your system • perform a physical exam and order any necessary tests to detect health problems caused by your amphetamin ...
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome is a set of symptoms that can occur when an individual reduces or stops alcoholic consumption after long periods of use. Prolonged and excessive use of alcohol leads to tolerance and physical dependence. The withdrawal syndrome is largely a hyper-excitable response of the central nervous system due to lack of alcohol. Symptoms typical of withdrawal include agitation, seizures, and delirium tremens.Sedative-hypnotics, such as alcohol, are well known for their ability to cause physiological dependence. This dependence is due to alcohol-induced neuro-adaptation. Withdrawal is characterized by neuropsychiatric excitability and autonomic disturbances. Dependence on other sedative-hypnotics can increase the severity of the withdrawal syndrome.About half of people with alcoholism will develop withdrawal symptoms upon reducing their use. Of these, about three to five percent develop DTs or have seizures.