Natural Science 9: Test Review-Space Answers 1. pg 434 #2 a – i a
... Orbital period – the period of time required for an orbiting object to complete one revolution Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an or ...
... Orbital period – the period of time required for an orbiting object to complete one revolution Constellations – a group of stars that forms shapes or patterns Probe – an unmanned space craft sent into space to obtain data and complete research Satellite – a large natural object that travels in an or ...
Planets - Britannica Encyclopedia Online
... traveled very far in their orbit. A different part of the planet is then facing the sun. Therefore their day is not yet complete. It takes much longer for the same part of the planet to face the sun again. ...
... traveled very far in their orbit. A different part of the planet is then facing the sun. Therefore their day is not yet complete. It takes much longer for the same part of the planet to face the sun again. ...
Document
... inside of stars. 2. Movement of planets, dwarf planets, and satellites that orbit the sun a. The sun is the center of the solar system (show diagram/basketball) b. System is flat (show side view) c. Each planet has its own orbit it follows around the sun Mercury has an inclined orbit. The Dwarf plan ...
... inside of stars. 2. Movement of planets, dwarf planets, and satellites that orbit the sun a. The sun is the center of the solar system (show diagram/basketball) b. System is flat (show side view) c. Each planet has its own orbit it follows around the sun Mercury has an inclined orbit. The Dwarf plan ...
Slide 1
... There are hundreds of billions of estimated Galaxies but over the years technology (having bigger and better equipment )has changed and now they are finding lots more of them. There are three types of Galaxies- Spiral-Elliptical-Irregular The only difference in these Galaxies are the size . The sma ...
... There are hundreds of billions of estimated Galaxies but over the years technology (having bigger and better equipment )has changed and now they are finding lots more of them. There are three types of Galaxies- Spiral-Elliptical-Irregular The only difference in these Galaxies are the size . The sma ...
Solar Nebula
... • Example: An object is 4 AU far from the Sun and its mass is 1/10th the Sun's. Calculate its orbital period? (≈ 7.6 years) • Example: Calculate the orbital period of the Earth. (m⊕ = 5.97x1027 ...
... • Example: An object is 4 AU far from the Sun and its mass is 1/10th the Sun's. Calculate its orbital period? (≈ 7.6 years) • Example: Calculate the orbital period of the Earth. (m⊕ = 5.97x1027 ...
The solar system
... objects in space that orbit (go around) it. The Sun is orbited by planets, moons, asteroids, comets and other things. ...
... objects in space that orbit (go around) it. The Sun is orbited by planets, moons, asteroids, comets and other things. ...
Planets and Moons - Fraser Heights Chess Club
... THE PLANETS The path each planet travels around the Sun is called orbit. The planets are kept in their orbits due to the pulling force of the Sun’s gravity. The time a planet makes one trip around the Sun is called a Year. Each planet spins around itself and around the Sun. The face of the ...
... THE PLANETS The path each planet travels around the Sun is called orbit. The planets are kept in their orbits due to the pulling force of the Sun’s gravity. The time a planet makes one trip around the Sun is called a Year. Each planet spins around itself and around the Sun. The face of the ...
Lesson Power Point
... the rest of the objects in the solar system put together. The next largest object is the planet Jupiter. ...
... the rest of the objects in the solar system put together. The next largest object is the planet Jupiter. ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... both planets occur because their axes tilt slightly. Earth is inclined 23.5 degrees. Neptune is tipped at an even greater angle: 29 degrees. As both planets circle the Sun, one hemisphere is always tipped toward the Sun; the other is tilted away from the Sun. When the southern hemisphere tips toward ...
... both planets occur because their axes tilt slightly. Earth is inclined 23.5 degrees. Neptune is tipped at an even greater angle: 29 degrees. As both planets circle the Sun, one hemisphere is always tipped toward the Sun; the other is tilted away from the Sun. When the southern hemisphere tips toward ...
the solar system
... 2) Origin of asteroid belt (a) a planet formed and Jupiter pulled it apart (b) Jupiter’s gravity kept the pieces from forming in the first place (c) a planet formed but then a large object hit it and broke it into pieces C) meteoroids—small rocks in space 1) made of broken asteroids or 2) broken com ...
... 2) Origin of asteroid belt (a) a planet formed and Jupiter pulled it apart (b) Jupiter’s gravity kept the pieces from forming in the first place (c) a planet formed but then a large object hit it and broke it into pieces C) meteoroids—small rocks in space 1) made of broken asteroids or 2) broken com ...
How Math, And Not A Telescope, May Have Found A New Planet
... In the early 20th century, astronomer Percival Lowell calculated a discrepancy in the orbit of Neptune that he attributed to an unseen Planet X. Lowell hired Clyde Tombaugh to look for Planet X, and lo and behold, Tombaugh found Pluto. In 1930, Pluto was thought to be a big planet — considerably mor ...
... In the early 20th century, astronomer Percival Lowell calculated a discrepancy in the orbit of Neptune that he attributed to an unseen Planet X. Lowell hired Clyde Tombaugh to look for Planet X, and lo and behold, Tombaugh found Pluto. In 1930, Pluto was thought to be a big planet — considerably mor ...
Solar System Scale Activity
... your strip so that the Sun is at the top and Pluto is on the bottom. 2. Fold the strip in half and open the strip. a. What is the middle of our Solar System? Is there a planet there? b. What are the planets of our Solar System? 3. Write the name of the object in the crease, if there is one? 4. Write ...
... your strip so that the Sun is at the top and Pluto is on the bottom. 2. Fold the strip in half and open the strip. a. What is the middle of our Solar System? Is there a planet there? b. What are the planets of our Solar System? 3. Write the name of the object in the crease, if there is one? 4. Write ...
Pluto_Ceres_ASP
... neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, (c) has not cleared the neighbourhood around its ...
... neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, (c) has not cleared the neighbourhood around its ...
120409_Gravity LP
... 7. What holds the planets in orbit around the Sun? d. gravity 8. What four planets would experience the greatest pull of gravity from the Sun? Why? Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars (they are closest to the sun) Too easy? Try some tenth grade questions. (Look up at the board for hints!) ***Have definition ...
... 7. What holds the planets in orbit around the Sun? d. gravity 8. What four planets would experience the greatest pull of gravity from the Sun? Why? Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars (they are closest to the sun) Too easy? Try some tenth grade questions. (Look up at the board for hints!) ***Have definition ...
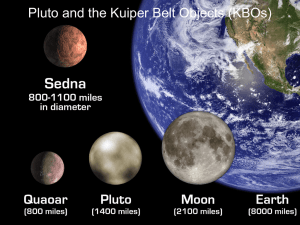
Pluto and the Kuiper Belt Objects
... The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other bodies, except satellites, in our Solar System be defined into three distinct categories in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body f ...
... The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other bodies, except satellites, in our Solar System be defined into three distinct categories in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body f ...
Inner Planets - Spokane Public Schools
... and outer planets. The inner planets are closest to the sun. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. These planets are also called the terrestrial planets because they are most similar to Earth. Mercury is a small planet which is the closest to the Sun. Since it is between the Sun and Earth, it is ...
... and outer planets. The inner planets are closest to the sun. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. These planets are also called the terrestrial planets because they are most similar to Earth. Mercury is a small planet which is the closest to the Sun. Since it is between the Sun and Earth, it is ...
Goal: To understand what the Kuiper Belt is, and why it is
... • Has an orbital resonance (3:2) with Neptune. • Shares an orbit with millions to hundreds of millions of other Plutinos. • Pluto is considered a dwarf planet, Plutino, and a TNO. ...
... • Has an orbital resonance (3:2) with Neptune. • Shares an orbit with millions to hundreds of millions of other Plutinos. • Pluto is considered a dwarf planet, Plutino, and a TNO. ...
earth
... possess a number of thin, breathing tubes on their arms allowing Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System at two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn, Ura ...
... possess a number of thin, breathing tubes on their arms allowing Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System at two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn, Ura ...
Our Solar System
... Ancient observers believed that the Sun and all the other celestial bodies revolved around Earth. But astronomers gradually realized that the Earth-centered model did not account for the motions of the planets. In the early 17th century, Galileo Galilei’s discoveries using the recently invented tele ...
... Ancient observers believed that the Sun and all the other celestial bodies revolved around Earth. But astronomers gradually realized that the Earth-centered model did not account for the motions of the planets. In the early 17th century, Galileo Galilei’s discoveries using the recently invented tele ...
3 The Outer Planets
... Which Planet Is Next? Some astronomers predicted that there was a planet beyond Uranus before the planet was observed. Uranus did not move in its orbit exactly as they expected. The force of gravity due to another large object was affecting it. Using predictions of its effect on Uranus, astronomers ...
... Which Planet Is Next? Some astronomers predicted that there was a planet beyond Uranus before the planet was observed. Uranus did not move in its orbit exactly as they expected. The force of gravity due to another large object was affecting it. Using predictions of its effect on Uranus, astronomers ...
Why are planets round?
... Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Some planets are much larger than others, and some are surrounded by rings or moons. But all planets have three things in common. They orbit the sun, they are massive enough that their gravity controls all the objects in the area around them, and th ...
... Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Some planets are much larger than others, and some are surrounded by rings or moons. But all planets have three things in common. They orbit the sun, they are massive enough that their gravity controls all the objects in the area around them, and th ...
Planets beyond Neptune

Following the discovery of the planet Neptune in 1846, there was considerable speculation that another planet might exist beyond its orbit. The search began in the mid-19th century and culminated at the start of the 20th with Percival Lowell's quest for Planet X. Lowell proposed the Planet X hypothesis to explain apparent discrepancies in the orbits of the giant planets, particularly Uranus and Neptune, speculating that the gravity of a large unseen ninth planet could have perturbed Uranus enough to account for the irregularities.Clyde Tombaugh's discovery of Pluto in 1930 appeared to validate Lowell's hypothesis, and Pluto was officially named the ninth planet. In 1978, Pluto was conclusively determined to be too small for its gravity to affect the giant planets, resulting in a brief search for a tenth planet. The search was largely abandoned in the early 1990s, when a study of measurements made by the Voyager 2 spacecraft found that the irregularities observed in Uranus's orbit were due to a slight overestimation of Neptune's mass. After 1992, the discovery of numerous small icy objects with similar or even wider orbits than Pluto led to a debate over whether Pluto should remain a planet, or whether it and its neighbours should, like the asteroids, be given their own separate classification. Although a number of the larger members of this group were initially described as planets, in 2006 the International Astronomical Union reclassified Pluto and its largest neighbours as dwarf planets, leaving Neptune the farthest known planet in the Solar System.Today, the astronomical community widely agrees that Planet X, as originally envisioned, does not exist, but the concept of Planet X has been revived by a number of astronomers to explain other anomalies observed in the outer Solar System. In popular culture, and even among some astronomers, Planet X has become a stand-in term for any undiscovered planet in the outer Solar System, regardless of its relationship to Lowell's hypothesis. Other trans-Neptunian planets have also been suggested, based on different evidence. As of March 2014, observations with the WISE telescope have ruled out the possibility of a Saturn-sized object out to 10,000 AU, and a Jupiter-sized or larger object out to 26,000 AU.