About SDSS - Astro Projects
... With the aid of telescopes, however, we are able to see a lot more than just fainter stars. We can detect the remains of stars that have run out of hydrogen fuel and died – so called 'planetary nebulae' and 'supernova remnants'. We can also see 'globular clusters', collections of 100 000 or so stars ...
... With the aid of telescopes, however, we are able to see a lot more than just fainter stars. We can detect the remains of stars that have run out of hydrogen fuel and died – so called 'planetary nebulae' and 'supernova remnants'. We can also see 'globular clusters', collections of 100 000 or so stars ...
Sirius Astronomer - Orange County Astronomers
... Anza to take advantage of the situation. Maybe they were still away on spring break, or believed earlier weather forecasts that indicated that conditions wouldn’t be that good. For whatever reason, there was only one family on the Football Field, three people on Ten Pad (though Joe Busch had his sol ...
... Anza to take advantage of the situation. Maybe they were still away on spring break, or believed earlier weather forecasts that indicated that conditions wouldn’t be that good. For whatever reason, there was only one family on the Football Field, three people on Ten Pad (though Joe Busch had his sol ...
Lecture 7 Stars and Galaxies and Nebula, (Oh My!) Feb 18 2003
... They orbit in the disk of our galaxy and don't last very long, members escape the group over time. All about the same age and composition so it is likely that they formed around the same time. ...
... They orbit in the disk of our galaxy and don't last very long, members escape the group over time. All about the same age and composition so it is likely that they formed around the same time. ...
TA`s solution set
... If the universe were also infinitely old, then light would have had time to reach us along all of these sightlines! (If the universe had finite age, the light from sufficiently distant stars would not have had time to reach us and some lines of sight would appear dark.) Since the night sky is, in fa ...
... If the universe were also infinitely old, then light would have had time to reach us along all of these sightlines! (If the universe had finite age, the light from sufficiently distant stars would not have had time to reach us and some lines of sight would appear dark.) Since the night sky is, in fa ...
Solutions to Homework #4, AST 203, Spring 2009
... Of course, the supernova is at a distance of 6000 light years, and therefore we are seeing events there as they occurred 6000 years ago. It is the same 6000 year delay between different events in the history of the supernova. So the more correct way to phrase the above is that the light from the sup ...
... Of course, the supernova is at a distance of 6000 light years, and therefore we are seeing events there as they occurred 6000 years ago. It is the same 6000 year delay between different events in the history of the supernova. So the more correct way to phrase the above is that the light from the sup ...
Chapter 13 - USD Home Pages
... supernovae are “identical,” so this is a “standard candle” and its distance can be determined via the formula B = L/4πD 2 , where B is the apparent brightness. The ability to measure vast distances is crucial to understanding the universe. 23. What prevents thermonuclear fusion from occurring at the ...
... supernovae are “identical,” so this is a “standard candle” and its distance can be determined via the formula B = L/4πD 2 , where B is the apparent brightness. The ability to measure vast distances is crucial to understanding the universe. 23. What prevents thermonuclear fusion from occurring at the ...
Type Ia supernovae and the ESSENCE supernova survey
... where H0 ~ 72 km/sec/Mpc is the Hubble constant. The redshift z = (~ v/c for low redshift). Beyond a redshift of ~0.1 we must must also consider the curvature of space-time, which is related to the mass density parameter M = crit . After much grinding away, we can obtain an expression for ...
... where H0 ~ 72 km/sec/Mpc is the Hubble constant. The redshift z = (~ v/c for low redshift). Beyond a redshift of ~0.1 we must must also consider the curvature of space-time, which is related to the mass density parameter M = crit . After much grinding away, we can obtain an expression for ...
Where Do Chemical Elements Come From?
... In 1054, Chinese astronomers recorded what they called a “guest star” in the constellation of Taurus, the Bull. This star had never been seen before, and it became brighter than any star in the sky. In the American Southwest, a culture rich in astronomical tradition called the Anasazi also witnessed ...
... In 1054, Chinese astronomers recorded what they called a “guest star” in the constellation of Taurus, the Bull. This star had never been seen before, and it became brighter than any star in the sky. In the American Southwest, a culture rich in astronomical tradition called the Anasazi also witnessed ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... them very dense. The heavier the white dwarf is, then the smaller its size will be. A star like our Sun will become a white dwarf when it has run out of fuel. Near the end of its life, it will go through a red giant stage, and then lose most of its gas, until what is left settles down and becomes a ...
... them very dense. The heavier the white dwarf is, then the smaller its size will be. A star like our Sun will become a white dwarf when it has run out of fuel. Near the end of its life, it will go through a red giant stage, and then lose most of its gas, until what is left settles down and becomes a ...
Birth and Life of a Star
... them very dense. The heavier the white dwarf is, then the smaller its size will be. A star like our Sun will become a white dwarf when it has run out of fuel. Near the end of its life, it will go through a red giant stage, and then lose most of its gas, until what is left settles down and becomes a ...
... them very dense. The heavier the white dwarf is, then the smaller its size will be. A star like our Sun will become a white dwarf when it has run out of fuel. Near the end of its life, it will go through a red giant stage, and then lose most of its gas, until what is left settles down and becomes a ...
$doc.title
... Complete the pre-‐lab quiz with your team. Compile a list of resources you expect to use in the lab. Work with your team to complete the lab exercises and activities. Record your results and mar ...
... Complete the pre-‐lab quiz with your team. Compile a list of resources you expect to use in the lab. Work with your team to complete the lab exercises and activities. Record your results and mar ...
Strongly Interacting Supernovae - The National Centre for Radio
... Initial spectrum shows Type Ib and later spectrum ...
... Initial spectrum shows Type Ib and later spectrum ...
The Death of a Star
... under so much pressure at this time that fusion is no longer possible. This incredible amount of pressure is enough to force the electrons to react with the protons turning them all into neutrons. Without the outward resistance of the electrons the core collapses to about 50 km in radius. The amount ...
... under so much pressure at this time that fusion is no longer possible. This incredible amount of pressure is enough to force the electrons to react with the protons turning them all into neutrons. Without the outward resistance of the electrons the core collapses to about 50 km in radius. The amount ...
Universe ppt - Killeen ISD
... 1. A large amount of gas and dust spread out in an immense volume in the nebula 2. In the nebula gravity begins to pull some of the gas and dust together and it becomes more and more dense. 3. The contracting gas and dust become so hot that nuclear fusion starts and enormous amounts of energy are re ...
... 1. A large amount of gas and dust spread out in an immense volume in the nebula 2. In the nebula gravity begins to pull some of the gas and dust together and it becomes more and more dense. 3. The contracting gas and dust become so hot that nuclear fusion starts and enormous amounts of energy are re ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
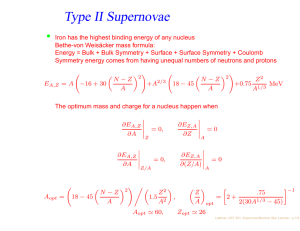
Type II Supernovae
... An observer in the orbital plane has θ = π/2 and h× = 0. The observed frequency of gravitational waves is ν = Ω/π. The intensity of gravitational waves decreases as 1/r. Consider two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars in a binary with separation of R⊙ observed from a distance of 1 kpc: P ≃ 7000 s, ν ≃ 2.9 · 10−4 ...
... An observer in the orbital plane has θ = π/2 and h× = 0. The observed frequency of gravitational waves is ν = Ω/π. The intensity of gravitational waves decreases as 1/r. Consider two 1.4 M⊙ neutron stars in a binary with separation of R⊙ observed from a distance of 1 kpc: P ≃ 7000 s, ν ≃ 2.9 · 10−4 ...
lecture19 - Stony Brook University
... that are moving away from us with huge speeds, using the observed Doppler shifts of known spectral lines. This indicates that they are very very far away (we will make this connection between recessional velocity and distance clear later – it’s called the Hubble expansion of the universe). From the ...
... that are moving away from us with huge speeds, using the observed Doppler shifts of known spectral lines. This indicates that they are very very far away (we will make this connection between recessional velocity and distance clear later – it’s called the Hubble expansion of the universe). From the ...
Neutron Stars - Otterbein University
... through the star and blows off the outer layers, including the heavy elements – a supernova • A million times brighter than a nova!! • The actual explosion takes less than a second ...
... through the star and blows off the outer layers, including the heavy elements – a supernova • A million times brighter than a nova!! • The actual explosion takes less than a second ...
Stars
... • Very useful – they’re all the ~same – 1.4 solar mass white dwarfs undergoing nuclear fusion. This turns out to mean they are… • GREAT “standard candles” – objects of known luminosity, on which we can then use simple math to determine their distance. • So, any SN I and its host galaxy, we can find ...
... • Very useful – they’re all the ~same – 1.4 solar mass white dwarfs undergoing nuclear fusion. This turns out to mean they are… • GREAT “standard candles” – objects of known luminosity, on which we can then use simple math to determine their distance. • So, any SN I and its host galaxy, we can find ...
Astronomy Universe2
... Depending on the conditions within a nebula, different types of stars can form: Red Giants = big, “cool” stars White Dwarfs = “small”, hot stars ...
... Depending on the conditions within a nebula, different types of stars can form: Red Giants = big, “cool” stars White Dwarfs = “small”, hot stars ...
Review: How does a star*s mass determine its life story?
... • As a white dwarf’s mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be more massive than 1.4MSun, the white dwarf limit (also known as the Chandrasekhar limit). ...
... • As a white dwarf’s mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be more massive than 1.4MSun, the white dwarf limit (also known as the Chandrasekhar limit). ...
Stages in the Life of a Star
... • At the bloated-out surface, the energy is spread out over a larger area so each square centimeter will be cooler giving the light a red color. • Red giants can eject a lot of mass through “winds”’. Note: A Red Giant may be large in terms of linear size, but it is less massive than the main sequenc ...
... • At the bloated-out surface, the energy is spread out over a larger area so each square centimeter will be cooler giving the light a red color. • Red giants can eject a lot of mass through “winds”’. Note: A Red Giant may be large in terms of linear size, but it is less massive than the main sequenc ...
History of supernova observation

The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 CE, when, supernova SN 185 appeared, the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by humankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since that time, with SN 1604 being the most recent supernova to be observed in this galaxy.Since the development of the telescope, the field of supernova discovery has expanded to other galaxies. These occurrences provide important information on the distances of galaxies. Successful models of supernova behavior have also been developed, and the role of supernovae in the star formation process is now increasingly understood.