Slides for Earth and the Solar System Unit #1
... Before the invention of the telescope, early star-gazers knew of the only two main objects they saw in the sky. ...
... Before the invention of the telescope, early star-gazers knew of the only two main objects they saw in the sky. ...
Powerpoint slides.
... the planet is in orbit and generates a tide which will act to slow the satellite’s rotation. Because the tide raised by the planet on the satellite is large, so is the torque. This is why most satellites rotate synchronously with respect to the planet they are orbiting. F.Nimmo EART162 Spring 10 ...
... the planet is in orbit and generates a tide which will act to slow the satellite’s rotation. Because the tide raised by the planet on the satellite is large, so is the torque. This is why most satellites rotate synchronously with respect to the planet they are orbiting. F.Nimmo EART162 Spring 10 ...
Movement In Our Sky - Wallingford Public Schools
... be described by locating it relative to another object or its background. Unit Specific Enduring Understandings: • There are many objects in our sky and beyond (stars, planets, moons, asteroids, etc.) • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and stars are members of galaxies. • Our sun is a ...
... be described by locating it relative to another object or its background. Unit Specific Enduring Understandings: • There are many objects in our sky and beyond (stars, planets, moons, asteroids, etc.) • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and stars are members of galaxies. • Our sun is a ...
Looking for planets with SPHERE in planetary systems with double
... giant and cold molecular clouds that are not homogeneous structures. Therefore, by means of turbulence phenomenon, any collapsing region will possesses nonzero angular momentum. Thus disks form because particles in it have too much angular momentum to collapse directly to the star. Protoplanetary di ...
... giant and cold molecular clouds that are not homogeneous structures. Therefore, by means of turbulence phenomenon, any collapsing region will possesses nonzero angular momentum. Thus disks form because particles in it have too much angular momentum to collapse directly to the star. Protoplanetary di ...
Chapter 20
... Presumably, these stars are so young that they have not quite settled down to a steady and reliable existence on the main sequence. (T Tauri stars always have the word “stars” in their name though technically they haven’t reached the main sequence, so they are not yet fully formed stars.) In astrono ...
... Presumably, these stars are so young that they have not quite settled down to a steady and reliable existence on the main sequence. (T Tauri stars always have the word “stars” in their name though technically they haven’t reached the main sequence, so they are not yet fully formed stars.) In astrono ...
Advances in exoplanet science from Kepler
... 2014), probably because they have atmospheres with a wide range of properties. Nonetheless, theoretical models of their interiors (e.g., Fortney et al. 2007) imply that all of the planets in this class are “gas-poor”, that is, less than half — in most cases far less — of their mass consists of hydro ...
... 2014), probably because they have atmospheres with a wide range of properties. Nonetheless, theoretical models of their interiors (e.g., Fortney et al. 2007) imply that all of the planets in this class are “gas-poor”, that is, less than half — in most cases far less — of their mass consists of hydro ...
Biosignatures and Planetary Properties to be
... Earth-like planets evolving around stars of very different spectral type than the Sun, hence different spectral energy distribution, might evolve in unexpected ways (and, for K and M dwarfs, over much longer time spans than could our Earth. The ill-fated namesake of Shakespeare's play Hamlet admonis ...
... Earth-like planets evolving around stars of very different spectral type than the Sun, hence different spectral energy distribution, might evolve in unexpected ways (and, for K and M dwarfs, over much longer time spans than could our Earth. The ill-fated namesake of Shakespeare's play Hamlet admonis ...
“Breakthroughs” of the 20th Century
... elemental nuclear synthesis. Large telescopes led to a boom in astronomical spectroscopic and photometric data collection, leading to such cornerstones as the Hertzprung-Russell diagram and the mass-luminosity relationship, and to the realization that the Universe contained a multitude of galaxies a ...
... elemental nuclear synthesis. Large telescopes led to a boom in astronomical spectroscopic and photometric data collection, leading to such cornerstones as the Hertzprung-Russell diagram and the mass-luminosity relationship, and to the realization that the Universe contained a multitude of galaxies a ...
The Milky Way - UNT Department of Political Science
... Large orbital inclinations Large seasonal changes on Pluto and Charon. ...
... Large orbital inclinations Large seasonal changes on Pluto and Charon. ...
PLUTO - Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Northwestern
... has moved. It was so, that Slipher recruited Clyde Tombaugh. Clyde Tombaugh then discovered Pluto using this technique in February 18, 1930. In his own words: 8 Discovery of Pluto reminds one of UFO sighting, and especially the close encounter of the first kind, since for a while there was no other ...
... has moved. It was so, that Slipher recruited Clyde Tombaugh. Clyde Tombaugh then discovered Pluto using this technique in February 18, 1930. In his own words: 8 Discovery of Pluto reminds one of UFO sighting, and especially the close encounter of the first kind, since for a while there was no other ...
an Educator`s GuidE - Museum of Science, Boston
... Even though they are individual worlds with varying histories and circumstances, moons are vital parts of the systems they inhabit. For example, tidal forces work on a primary and its satellites at all scales. In the same way that the Moon’s gravitational pull generates Earth’s tides, the combined g ...
... Even though they are individual worlds with varying histories and circumstances, moons are vital parts of the systems they inhabit. For example, tidal forces work on a primary and its satellites at all scales. In the same way that the Moon’s gravitational pull generates Earth’s tides, the combined g ...
Astronomy - Core Knowledge Foundation
... ● Explain that the sun, moon, and stars are located in outer space ● Explain that the sun is a source of energy, light, and heat ● Classify the sun as a star ● Identify Earth as a planet and our home ● Identify the earth’s rotation, or spin, as the cause of day and night ● Explain that other pa ...
... ● Explain that the sun, moon, and stars are located in outer space ● Explain that the sun is a source of energy, light, and heat ● Classify the sun as a star ● Identify Earth as a planet and our home ● Identify the earth’s rotation, or spin, as the cause of day and night ● Explain that other pa ...
Extrasolar Cosmochemistry
... We now consider the amount of mass required in our standard model; we argue that minor planets such as asteroids are the dominant source for the pollution of white dwarf atmospheres, although there might be instances in which tidal disruption and accretion of an entire planet the size of Mars has oc ...
... We now consider the amount of mass required in our standard model; we argue that minor planets such as asteroids are the dominant source for the pollution of white dwarf atmospheres, although there might be instances in which tidal disruption and accretion of an entire planet the size of Mars has oc ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 10: 1. What are the
... 6. What proofs are there that the Earth is round, is rotating and is revolving around the sun? 7. Describe the planets Mercury, Venus and Mars, in terms of size, surface characteristics atmosphere, rotation, and temperature. 8. List the various spacecraft that have landed on Mars, and discuss their ...
... 6. What proofs are there that the Earth is round, is rotating and is revolving around the sun? 7. Describe the planets Mercury, Venus and Mars, in terms of size, surface characteristics atmosphere, rotation, and temperature. 8. List the various spacecraft that have landed on Mars, and discuss their ...
Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation
... Newton knew that the force which caused the apple's acceleration (gravity) must be dependent upon the mass of the apple. And since the force acting to cause the apple's downward acceleration also causes the earth's upward acceleration (Newton's third law), that force must also depend upon the mass o ...
... Newton knew that the force which caused the apple's acceleration (gravity) must be dependent upon the mass of the apple. And since the force acting to cause the apple's downward acceleration also causes the earth's upward acceleration (Newton's third law), that force must also depend upon the mass o ...
Assessing the Possibility of Biological Complexity on Other
... BCI values > 0. The mean BCIrel value is 0.50 (median = 0.52), which falls slightly below that for Saturn. Exoplanets for which the BCIrel > 0.50 are listed in Table 1, along with equivalently ranked Solar System bodies. The highest BCI value is for Gliese 581c, followed by Earth, followed by HD 855 ...
... BCI values > 0. The mean BCIrel value is 0.50 (median = 0.52), which falls slightly below that for Saturn. Exoplanets for which the BCIrel > 0.50 are listed in Table 1, along with equivalently ranked Solar System bodies. The highest BCI value is for Gliese 581c, followed by Earth, followed by HD 855 ...
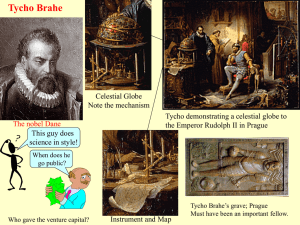
Brahe, Kepler
... ``Consecrated to the all-good, great God and Posterity. Tycho Brahe, Son of Otto, who realized that Astronomy, the oldest and most distinguished of all sciences, had indeed been studied for a long time and to a great extent, but still had not obtained sufficient firmness or had been purified of erro ...
... ``Consecrated to the all-good, great God and Posterity. Tycho Brahe, Son of Otto, who realized that Astronomy, the oldest and most distinguished of all sciences, had indeed been studied for a long time and to a great extent, but still had not obtained sufficient firmness or had been purified of erro ...
PDF Full-text
... BCI values > 0. The mean BCIrel value is 0.50 (median = 0.52), which falls slightly below that for Saturn. Exoplanets for which the BCIrel > 0.50 are listed in Table 1, along with equivalently ranked Solar System bodies. The highest BCI value is for Gliese 581c, followed by Earth, followed by HD 855 ...
... BCI values > 0. The mean BCIrel value is 0.50 (median = 0.52), which falls slightly below that for Saturn. Exoplanets for which the BCIrel > 0.50 are listed in Table 1, along with equivalently ranked Solar System bodies. The highest BCI value is for Gliese 581c, followed by Earth, followed by HD 855 ...
Question paper - Unit A183/02 - Module P7 - Higher tier
... In the late 1700s, the Titius-Bode Law was published. The law was used for calculating the distance of the planets from the Sun. The distance from the Earth to the Sun is 1AU. This is what the law says: To find the distance in AU: ...
... In the late 1700s, the Titius-Bode Law was published. The law was used for calculating the distance of the planets from the Sun. The distance from the Earth to the Sun is 1AU. This is what the law says: To find the distance in AU: ...
PTYS/ASTR 206
... categories in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. ...
... categories in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. ...
The Science of Astronomy
... Moon (see Figure 2.21) or by observing the constellations visible at a particular time (see Figure 2.14). We also trace the origins of our modern clock to ancient Egypt. Some 4000 years ago, the Egyptians divided daytime and nighttime into 12 equal parts each, which is how we got our 12 hours each o ...
... Moon (see Figure 2.21) or by observing the constellations visible at a particular time (see Figure 2.14). We also trace the origins of our modern clock to ancient Egypt. Some 4000 years ago, the Egyptians divided daytime and nighttime into 12 equal parts each, which is how we got our 12 hours each o ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.