Document
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
Black hole theory
... ★ Based off of Einstein’s Theory of Relativity ★ Black Hole defined: a region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation can escape. ★ Escape Velocity defined: lowest velocity that a body must have in order to escape the gravitational attraction of a particular plan ...
... ★ Based off of Einstein’s Theory of Relativity ★ Black Hole defined: a region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation can escape. ★ Escape Velocity defined: lowest velocity that a body must have in order to escape the gravitational attraction of a particular plan ...
$doc.title
... • Want to use the plethora of observational data to measure the key parameters and unravel the uncertain amount of mixing induced during shock traversals Maybe one case we fully understand! ...
... • Want to use the plethora of observational data to measure the key parameters and unravel the uncertain amount of mixing induced during shock traversals Maybe one case we fully understand! ...
Test 1 - Brock physics
... (a) yellow, because they emit a significant amount of yellow electromagnetic radiation. (b) blue, because they emit a significant amount of blue and ultraviolet electromagnetic radiation. (c) red, because electrons recombine with protons and then make transitions to lower energy levels, emitting red ...
... (a) yellow, because they emit a significant amount of yellow electromagnetic radiation. (b) blue, because they emit a significant amount of blue and ultraviolet electromagnetic radiation. (c) red, because electrons recombine with protons and then make transitions to lower energy levels, emitting red ...
Life Cycle of a Star - Intervention Worksheet
... 3. Nebula can form either an _________ star that is about the size of our Sun or a ___________ star which can be over three times as big as our Sun! These stars stay in this period for most of their lives and they convert hydrogen to helium while generating lots of heat and light. ...
... 3. Nebula can form either an _________ star that is about the size of our Sun or a ___________ star which can be over three times as big as our Sun! These stars stay in this period for most of their lives and they convert hydrogen to helium while generating lots of heat and light. ...
Astronomy 10 - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... When the helium core is first formed, the core is not hot enough fuse the helium into heavier elements. Only once the red giant phase occurs, and the core contracts and heats up to a temperature of around 108 K is the core hot enough to start burning helium. (11) page 321, question 6 When a star she ...
... When the helium core is first formed, the core is not hot enough fuse the helium into heavier elements. Only once the red giant phase occurs, and the core contracts and heats up to a temperature of around 108 K is the core hot enough to start burning helium. (11) page 321, question 6 When a star she ...
zaneposter
... Highly magnetized neutron stars (aka “magnetars”) recently underwent a phase of renewed interest in high-energy astrophysics. These extreme objects comprise the Anomalous X-ray Pulsars (AXPs) and the Soft Gamma-ray Repeaters (SGRs), two classes of sources observationally very similar in many respect ...
... Highly magnetized neutron stars (aka “magnetars”) recently underwent a phase of renewed interest in high-energy astrophysics. These extreme objects comprise the Anomalous X-ray Pulsars (AXPs) and the Soft Gamma-ray Repeaters (SGRs), two classes of sources observationally very similar in many respect ...
The Triple-Ring Nebula: Fingerprint of a Binary Merger
... to decrease, just as an ice-skater starts to spin more slowly when extending her arms at the end of a pirouette. ...
... to decrease, just as an ice-skater starts to spin more slowly when extending her arms at the end of a pirouette. ...
Slide 1
... Principle of Equivalence “ A uniform gravitational field in some direction is indistinguishable from a uniform acceleration in the opposite direction.” Note: if you are in an accelerating reference frame pseudo-forces appear in the direction opposite to the true acceleration. Example 1. Car brakes ...
... Principle of Equivalence “ A uniform gravitational field in some direction is indistinguishable from a uniform acceleration in the opposite direction.” Note: if you are in an accelerating reference frame pseudo-forces appear in the direction opposite to the true acceleration. Example 1. Car brakes ...
Theoretical Problem 3
... the ratio of mass M to radius R is the same and depends only on physical constants. Find the equation for the ratio M / R for stars fusing hydrogen. ...
... the ratio of mass M to radius R is the same and depends only on physical constants. Find the equation for the ratio M / R for stars fusing hydrogen. ...
Lecture 24 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
... from apparent brightness and distance (d). Apparent magnitude (old way). We can see about 1,000 stars in Northern Hemisphere with naked eye. Hipparchus rated them from 1 to 6. A '1' is 2.52 x brighter than a '2', etc. Range in brightness from the sun at '-26' magnitude to the faintest objects seen a ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... continues contracting, but no pressure to stop it – Temperature increases so much the Iron nuclei start to break apart – Collapse pushes electrons into protons, creating bulk of neutrons at nuclear density – Rapid implosion causes material to “bounce” ...
... continues contracting, but no pressure to stop it – Temperature increases so much the Iron nuclei start to break apart – Collapse pushes electrons into protons, creating bulk of neutrons at nuclear density – Rapid implosion causes material to “bounce” ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 2
... During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as our Sun could emit over its life span. The explosion expels much or all of the star’s material and causes a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. The interstellar medium is the gas and dust that exists between the s ...
... During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as our Sun could emit over its life span. The explosion expels much or all of the star’s material and causes a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. The interstellar medium is the gas and dust that exists between the s ...
Document
... than the rate of decrease of the energy of pulsations by the excitation of shortwavelength acoustic waves. The dissipation of the vibrational energy by the last process is the main source of heating of matter.Convective motion in the presence of an Urca shell is considered, and equations generalizin ...
... than the rate of decrease of the energy of pulsations by the excitation of shortwavelength acoustic waves. The dissipation of the vibrational energy by the last process is the main source of heating of matter.Convective motion in the presence of an Urca shell is considered, and equations generalizin ...
Structure of Neutron Stars
... Being hot, lepton rich they have much higher limit: about 0.7 solar mass. Stellar evolution does not produce NSs with baryonic mass less than about 1.2-1.4 solar mass. Fragmentation of a core due to rapid rotation potentially can lead to smaller masses, but not as small as the limit for cold NSs. ...
... Being hot, lepton rich they have much higher limit: about 0.7 solar mass. Stellar evolution does not produce NSs with baryonic mass less than about 1.2-1.4 solar mass. Fragmentation of a core due to rapid rotation potentially can lead to smaller masses, but not as small as the limit for cold NSs. ...
PowerPoint
... balance point (center of mass) for a teeter-totter. Archimedes discovered that the balance point (center of mass) for a board with masses m1 and m2 at each end satisfies m1r1=m2r2 (Law of the Lever). ...
... balance point (center of mass) for a teeter-totter. Archimedes discovered that the balance point (center of mass) for a board with masses m1 and m2 at each end satisfies m1r1=m2r2 (Law of the Lever). ...
star
... or black hole). These pairs of stars produce X-rays if the stars are close enough together that material is pulled off the normal star by the gravity of the dense, collapsed star. The X-rays come from the area around the collapsed star where the material that is falling toward it is heated to very h ...
... or black hole). These pairs of stars produce X-rays if the stars are close enough together that material is pulled off the normal star by the gravity of the dense, collapsed star. The X-rays come from the area around the collapsed star where the material that is falling toward it is heated to very h ...
Chapter 15 part 1
... Our next nearest neighbor to the Sun beyond the Alpha Centauri system is called Barnard’s Star. Its parallax is 0.55'', so it lies at a distance of 1.8 pc, or 6.0 light-years. ...
... Our next nearest neighbor to the Sun beyond the Alpha Centauri system is called Barnard’s Star. Its parallax is 0.55'', so it lies at a distance of 1.8 pc, or 6.0 light-years. ...
slide-show source file - Bartol Research Institute
... The high temperature causes the corona to emit X-rays. Images made by orbiting X-ray telescopes show the solar corona has a high degree of spatial structure, organized by magnetic fields. Within closed field coronal loops, these effectively hold back the coronal expansion. But along radially ori ...
... The high temperature causes the corona to emit X-rays. Images made by orbiting X-ray telescopes show the solar corona has a high degree of spatial structure, organized by magnetic fields. Within closed field coronal loops, these effectively hold back the coronal expansion. But along radially ori ...
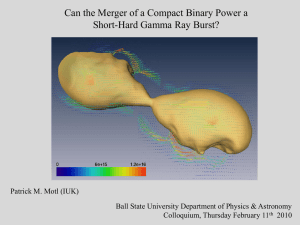
motl_bsu_021210
... horizon*, to escape from the event horizon you must have a velocity equal to the speed of light (impossible for any material body). The region inside the event horizon is fundamentally isolated (causally disconnected) from the outside Universe From a certain point of view, astrophysical black holes ...
... horizon*, to escape from the event horizon you must have a velocity equal to the speed of light (impossible for any material body). The region inside the event horizon is fundamentally isolated (causally disconnected) from the outside Universe From a certain point of view, astrophysical black holes ...
Lecture 26 Pre-Main Sequence Evolution
... Embedded stars - seen only at NIR or longer wavelengths, usually presumed to be very young Revealed stars - seen at optical wavelengths or shorter, usually presumed to be older What makes young stars particularly interesting is Circumstellar gas and dust – both flowing in as well as out, e.g., jets, ...
... Embedded stars - seen only at NIR or longer wavelengths, usually presumed to be very young Revealed stars - seen at optical wavelengths or shorter, usually presumed to be older What makes young stars particularly interesting is Circumstellar gas and dust – both flowing in as well as out, e.g., jets, ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.