Today`s Powerpoint
... Ionized helium. Requires extreme UV photons. Only hottest stars produce many of these. ...
... Ionized helium. Requires extreme UV photons. Only hottest stars produce many of these. ...
APS Centenary Poster - Bartol Research Institute
... But massive stars show the strongest winds, with speeds sometimes exceeding 3000 km/s, and mass loss rates up to a billion times the solar wind, i.e. ~ 10-5 MO/yr ! This is large enough that, during the course of their relatively brief (~107 yr) evolutionary lifetime, such massive stars can be str ...
... But massive stars show the strongest winds, with speeds sometimes exceeding 3000 km/s, and mass loss rates up to a billion times the solar wind, i.e. ~ 10-5 MO/yr ! This is large enough that, during the course of their relatively brief (~107 yr) evolutionary lifetime, such massive stars can be str ...
Unit 3 - Section 8.9 Life of Stars
... If the remnants of the explosion are between1.4 to 3 times as massive as our Sun, it will become a Neutron Star. After the Supernova explosion, the centre of the star collapses so that protons and electrons combine to form neutrons (...thus, Neutron Star). A Neutron Star is very, very dense (e.g., ...
... If the remnants of the explosion are between1.4 to 3 times as massive as our Sun, it will become a Neutron Star. After the Supernova explosion, the centre of the star collapses so that protons and electrons combine to form neutrons (...thus, Neutron Star). A Neutron Star is very, very dense (e.g., ...
Slide 1
... To summarize this – the only way to get elements heavier than iron is through a supernova. Gold comes from exploded stars! ...
... To summarize this – the only way to get elements heavier than iron is through a supernova. Gold comes from exploded stars! ...
AGN Workshop
... What is clustering of mergers? • LRG/QSO clustering on small scales looks similar (in shape) on all scales • Can you rule out fueling mechanisms from this? ...
... What is clustering of mergers? • LRG/QSO clustering on small scales looks similar (in shape) on all scales • Can you rule out fueling mechanisms from this? ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... What happens to a star after the main sequence phase? Old age and death! How long it takes for a star to die depends upon its initial mass. Larger stars have more fuel, but they have to burn (fuse) it faster in order to maintain equilibrium. Because thermonuclear fusion occurs at a faster rate in ma ...
... What happens to a star after the main sequence phase? Old age and death! How long it takes for a star to die depends upon its initial mass. Larger stars have more fuel, but they have to burn (fuse) it faster in order to maintain equilibrium. Because thermonuclear fusion occurs at a faster rate in ma ...
4. Massive Stars and HII Regions
... if rare in numbers, have a profound impact on their environment. They are the fundamental producers of heavy elements, generate huge amounts of high energy radiation, trigger star formation. Their lifetime on the main sequence is rather short: ...
... if rare in numbers, have a profound impact on their environment. They are the fundamental producers of heavy elements, generate huge amounts of high energy radiation, trigger star formation. Their lifetime on the main sequence is rather short: ...
Neutron stars, pulsars
... Spin up of neutron star If the Sun (spin rate 1/25 days, radius 7× 108 m) were to collapse to a neutron star with a radius of 12 km, how fast would it be spinning? ...
... Spin up of neutron star If the Sun (spin rate 1/25 days, radius 7× 108 m) were to collapse to a neutron star with a radius of 12 km, how fast would it be spinning? ...
Document
... • Roche Lobe: 3-D boundary where the gravity of 2 stars is equal; if a star expands beyond this boundary some of its matter accretes onto the other star • Matter that transfers from one star to another spirals onto the other star through an accretion disk • As the matter gets closer to the object, i ...
... • Roche Lobe: 3-D boundary where the gravity of 2 stars is equal; if a star expands beyond this boundary some of its matter accretes onto the other star • Matter that transfers from one star to another spirals onto the other star through an accretion disk • As the matter gets closer to the object, i ...
Fitting X-ray Spectra with Imperfect Models
... EUV/X-ray Line Ratios from Chandra LETG spectrum of Capella Predicted X-ray fluxes are too low for all the X-ray ...
... EUV/X-ray Line Ratios from Chandra LETG spectrum of Capella Predicted X-ray fluxes are too low for all the X-ray ...
Document
... • Kepler needs asteroseismology to determine the absolute sizes of any potentially habitable Earthlike planets that may be discovered. • The mission will yield a variety of data to calibrate dynamo models, sampling many different sets of physical conditions and evolutionary phases. ...
... • Kepler needs asteroseismology to determine the absolute sizes of any potentially habitable Earthlike planets that may be discovered. • The mission will yield a variety of data to calibrate dynamo models, sampling many different sets of physical conditions and evolutionary phases. ...
Soal Short
... 8. Gravitational forces of the Sun and the Moon lead to raising and lowering of sea water surfaces. Let be the difference in longitude between points A and B, where both points are at the equator and A is on the sea surface. Derive the horizontal acceleration of sea water at position A due to Moon ...
... 8. Gravitational forces of the Sun and the Moon lead to raising and lowering of sea water surfaces. Let be the difference in longitude between points A and B, where both points are at the equator and A is on the sea surface. Derive the horizontal acceleration of sea water at position A due to Moon ...
Brock physics - Brock University
... (c) the radius of the region around a neutron star within which X-ray bursts occur. (d) * the radius of the region around a black hole within which not even light can escape. ...
... (c) the radius of the region around a neutron star within which X-ray bursts occur. (d) * the radius of the region around a black hole within which not even light can escape. ...
Picture Match Words Valence Nebula Supernova Pulsar Attract
... 1. Some of the debris from past collisions (objects hitting the Earth) were _________by the planet’s gravity and became part of Earth crust and inner core. 2. Large clouds of gas and dust, mostly made up of hydrogen, are ...
... 1. Some of the debris from past collisions (objects hitting the Earth) were _________by the planet’s gravity and became part of Earth crust and inner core. 2. Large clouds of gas and dust, mostly made up of hydrogen, are ...
Black Holes : A lecture to 6th Formers
... By altering angular momentum, can get stable orbits at different radii. A stable circular orbit lies at a minimum of V. At r=6GM/c2 the minimum becomes a point of inflection. This is the innermost stable orbit and can be observed. ...
... By altering angular momentum, can get stable orbits at different radii. A stable circular orbit lies at a minimum of V. At r=6GM/c2 the minimum becomes a point of inflection. This is the innermost stable orbit and can be observed. ...
Stellar Physics 2
... C. Hawking radiation will exceed in-falling matter and radiation, so the black hole will evaporate. y D. None of the above. ...
... C. Hawking radiation will exceed in-falling matter and radiation, so the black hole will evaporate. y D. None of the above. ...
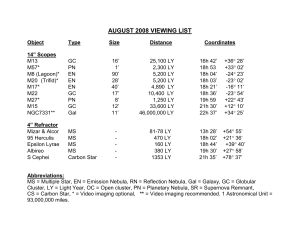
August
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
Name Physics 130 Astronomy Exam 2 August 2, 2004 Multiple Choice
... b.) The twinkling and blurring of the image due to air currents in the Earth’s atmosphere. c.) The amount of haze or thin cloud in the atmosphere, that affects the brightness of the telescope image. d.) The effect of the wind, that can cause the telescope to vibrate blurring the image. ...
... b.) The twinkling and blurring of the image due to air currents in the Earth’s atmosphere. c.) The amount of haze or thin cloud in the atmosphere, that affects the brightness of the telescope image. d.) The effect of the wind, that can cause the telescope to vibrate blurring the image. ...
Lecture 18
... Initial mass M0 = 10 Solar masses Final mass M= 10 x exp(109 / 4.5 x 107) = 4 x 1010 Solar masses Conclude: if the record breaking quasars at z > 6 have black hole masses of ~ 1010 Solar masses, and are being seen when the Universe was about 1 Gyr old, just enough time for them to have grown from sm ...
... Initial mass M0 = 10 Solar masses Final mass M= 10 x exp(109 / 4.5 x 107) = 4 x 1010 Solar masses Conclude: if the record breaking quasars at z > 6 have black hole masses of ~ 1010 Solar masses, and are being seen when the Universe was about 1 Gyr old, just enough time for them to have grown from sm ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... of energy since the rest of the star collapses and then bounces off the neutron core • 1044-46 Joules • Annual energy generation of Sun is 1034 Joules ...
... of energy since the rest of the star collapses and then bounces off the neutron core • 1044-46 Joules • Annual energy generation of Sun is 1034 Joules ...
Astronomy - Test 3
... E) Although such objects could occur, they would be so rare that we ignore them 26. Which of the following was not a method for making black holes that was discussed? A) Very high mass star supernova B) White dwarf supernova C) Accretion of matter onto a neutron star D) Merger of neutron stars E) Ac ...
... E) Although such objects could occur, they would be so rare that we ignore them 26. Which of the following was not a method for making black holes that was discussed? A) Very high mass star supernova B) White dwarf supernova C) Accretion of matter onto a neutron star D) Merger of neutron stars E) Ac ...
Document
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.