AS 701 - INTRODUCTION TO ASTROPHYSICS COURSE OVERVIEW - FALL 2013
... and gravitational physics, properties of stars, stellar structure, stellar evolution, dynamics of binary stars systems and star clusters, types of galaxies, galactic structure and dynamics, active galaxies and some cosmological topics. COURSE STRUCTURE AND PHILOSOPHY: The course is intended to provi ...
... and gravitational physics, properties of stars, stellar structure, stellar evolution, dynamics of binary stars systems and star clusters, types of galaxies, galactic structure and dynamics, active galaxies and some cosmological topics. COURSE STRUCTURE AND PHILOSOPHY: The course is intended to provi ...
Lecture 2: Gravitational wave sources
... Do we have evidence that these formulae actually work? Yes! Nature has been kind enough to provide us with the perfect test sources: binary neutron stars. Several such systems are known, all of which have binary separations orders of magnitude greater than the size of a neutron star, so the lowest o ...
... Do we have evidence that these formulae actually work? Yes! Nature has been kind enough to provide us with the perfect test sources: binary neutron stars. Several such systems are known, all of which have binary separations orders of magnitude greater than the size of a neutron star, so the lowest o ...
Hawking Radiation and Black Hole Evaporation
... Refutations (from the purely classical point of view): ✘ The temperature of a black hole vanishes! ✘ Entropy is dimensionless, the horizon area is a length squared! ✘ The area is separately non-decreasing, whereas only the total thermodynamical entropy is non-decreasing! ✘ Numerically, the black hol ...
... Refutations (from the purely classical point of view): ✘ The temperature of a black hole vanishes! ✘ Entropy is dimensionless, the horizon area is a length squared! ✘ The area is separately non-decreasing, whereas only the total thermodynamical entropy is non-decreasing! ✘ Numerically, the black hol ...
10.1 Introduction
... Figure 10.7: A schematic HR diagram for the most luminous known stars. The continuous black line shows the empirical upper luminosity boundary known as the HumphreysDavidson limit. (Figure reproduced from Humphreys & Davidson 1994, PASP, 106, 1025). ...
... Figure 10.7: A schematic HR diagram for the most luminous known stars. The continuous black line shows the empirical upper luminosity boundary known as the HumphreysDavidson limit. (Figure reproduced from Humphreys & Davidson 1994, PASP, 106, 1025). ...
Death of the Stars
... from the Earth. Instead we must rely on indirect methods of observation. First, if a star seems to be rotating around “nothing”, that nothing is probably very small to be observed from the Earth, but very massive, hence it can be a black hole. ...
... from the Earth. Instead we must rely on indirect methods of observation. First, if a star seems to be rotating around “nothing”, that nothing is probably very small to be observed from the Earth, but very massive, hence it can be a black hole. ...
b) How to Create Large Disks despite Major Mergers
... Clumpy Gas transfers orbital energy to DM via dynamical friction ...
... Clumpy Gas transfers orbital energy to DM via dynamical friction ...
Conference Summary Richard Ellis (Caltech) ITALIA
... • Keck can probe redshift-dependent Lyα emitting fraction within continuumselected Lyman break population • Via z~7 WFC3/IR candidates can test for reduced Lyα fraction claimed by Subaru narrow band surveys ...
... • Keck can probe redshift-dependent Lyα emitting fraction within continuumselected Lyman break population • Via z~7 WFC3/IR candidates can test for reduced Lyα fraction claimed by Subaru narrow band surveys ...
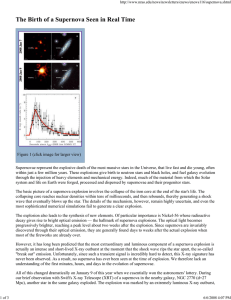
The Birth of a Supernova Seen in Real Time
... Twenty days after the outburst, the radio emission peaked at 8.46 GHz with radio spectral luminosity of 1027 erg s-1 Hz-1, a factor of 104 lower than those of typical GRB afterglows, but comparable to the radio luminosities observed for nearby core-collapse SNe. Based on our modeling of the temporal ...
... Twenty days after the outburst, the radio emission peaked at 8.46 GHz with radio spectral luminosity of 1027 erg s-1 Hz-1, a factor of 104 lower than those of typical GRB afterglows, but comparable to the radio luminosities observed for nearby core-collapse SNe. Based on our modeling of the temporal ...
Extragalactic Astrophysics 1 AA 2011-2012 Prof. LA Antonelli
... on the contrary, stars and globular clusters born during collapse do not lose a significant amount of energy in collisions and move on elongated orbits with random orientations, and with negligible total angular momentum Bulge stars are younger than globular clusters (age < ~8-10 Gyr). they could ha ...
... on the contrary, stars and globular clusters born during collapse do not lose a significant amount of energy in collisions and move on elongated orbits with random orientations, and with negligible total angular momentum Bulge stars are younger than globular clusters (age < ~8-10 Gyr). they could ha ...
Chandra - Cosmos
... solar panels) both key for this research. • Large fraction of Galactic LMXBs that exhibit bright (>1037 erg/s) transient outbursts have been shown to contain black holes (McClintock & Remillard 2004). • There are only ~20 such objects in the Galaxy, and each is vital for studies of accretion physics ...
... solar panels) both key for this research. • Large fraction of Galactic LMXBs that exhibit bright (>1037 erg/s) transient outbursts have been shown to contain black holes (McClintock & Remillard 2004). • There are only ~20 such objects in the Galaxy, and each is vital for studies of accretion physics ...
Booklet 5 – Stellar Processes and Evolution
... mass allows stellar collapse to take place and the outer layers to reignite. A cross section through the star at this point would show an outer shell of hydrogen burning, an inner shell of helium burning and the core, where there is now sufficient energy for the carbon to fuse with helium into oxyge ...
... mass allows stellar collapse to take place and the outer layers to reignite. A cross section through the star at this point would show an outer shell of hydrogen burning, an inner shell of helium burning and the core, where there is now sufficient energy for the carbon to fuse with helium into oxyge ...
Galactic Evolution:
... typically assumed. There are models with quick pre-enrichment. This includes pre-galactic enrichment, or protogalactic processes, or preenrichment from other more evolved system. ...
... typically assumed. There are models with quick pre-enrichment. This includes pre-galactic enrichment, or protogalactic processes, or preenrichment from other more evolved system. ...
Document
... (spheromaks) that become planetary cores. The reconnection radiation and winds heat and compress the disk causing agglomeration out to the snow line. The cores grow by collecting material infalling toward the star. They are in unstable orbits that can change radically or they can be ejected from the ...
... (spheromaks) that become planetary cores. The reconnection radiation and winds heat and compress the disk causing agglomeration out to the snow line. The cores grow by collecting material infalling toward the star. They are in unstable orbits that can change radically or they can be ejected from the ...
dynamical models of winds from rotating hot stars
... 2.1 Spherical-star nite disk (FD) factors, plotted for both a uniformly bright star and a linearly limb-darkened star. : ...
... 2.1 Spherical-star nite disk (FD) factors, plotted for both a uniformly bright star and a linearly limb-darkened star. : ...
Astrophysics - Part 2
... Stefan’s law and Wien’s displacement law.General shape of black body curves, experimental verification is not required. Use of Wien’s displacement law to estimate black-body temperature of sources λmaxT = constant = 2.9 × 10-3 mK. Inverse square law, assumptions in its application. Use of Stefan’s l ...
... Stefan’s law and Wien’s displacement law.General shape of black body curves, experimental verification is not required. Use of Wien’s displacement law to estimate black-body temperature of sources λmaxT = constant = 2.9 × 10-3 mK. Inverse square law, assumptions in its application. Use of Stefan’s l ...
Nova
... Roche lobe, gas moves into the Roche lobe of the companion star and is pulled in toward that star. This process of mass transfer is referred to as Roche lobe overflow. Binaries in this stage of mass transfer are called semi-detached binaries, because only one of the stars is actually in contact with ...
... Roche lobe, gas moves into the Roche lobe of the companion star and is pulled in toward that star. This process of mass transfer is referred to as Roche lobe overflow. Binaries in this stage of mass transfer are called semi-detached binaries, because only one of the stars is actually in contact with ...
Calculations on space-time curvature within the Earth and Sun
... value for Vrel about 18% greater than the Euclidean volume. This suggests that relativistic space-time curvature is a significant consideration when modelling the interiors of neutron stars. ...
... value for Vrel about 18% greater than the Euclidean volume. This suggests that relativistic space-time curvature is a significant consideration when modelling the interiors of neutron stars. ...
talk
... brings the "outer" disk further in by at least one scale length using thewhat gas ≥ was stars outer definition. The inner disk was then about half the size of what it is today for evolution without major mergers. If the HI --> H2 --> stars process varies with the gas/star mass ratio, then the stud ...
... brings the "outer" disk further in by at least one scale length using thewhat gas ≥ was stars outer definition. The inner disk was then about half the size of what it is today for evolution without major mergers. If the HI --> H2 --> stars process varies with the gas/star mass ratio, then the stud ...
Binary star formation
... part of binary systems: Solar mass stars: about 2 / 3 are part of binaries Separations from: • < 0.1 au • > 103 au ...
... part of binary systems: Solar mass stars: about 2 / 3 are part of binaries Separations from: • < 0.1 au • > 103 au ...
L5 Protoplanetary disks Part I
... dissipation (liberated potential energy), and by re-radiated stellar irradiation. Excess over the photospheric (stellar) contribution. The shape of the SED in the IR is used to classify sources (Class 0, I, II, III) ...
... dissipation (liberated potential energy), and by re-radiated stellar irradiation. Excess over the photospheric (stellar) contribution. The shape of the SED in the IR is used to classify sources (Class 0, I, II, III) ...
Chapter 14
... Stars evolve in the sense that they pass through different stages of a stellar life cycle that is measured in billions of years. The longer the amount of time a star spends in a particular stage of evolution, the greater the number of stars that one observes in that stage. Stars evolve at different ...
... Stars evolve in the sense that they pass through different stages of a stellar life cycle that is measured in billions of years. The longer the amount of time a star spends in a particular stage of evolution, the greater the number of stars that one observes in that stage. Stars evolve at different ...
cifutielu`s Astronomy Test 2014
... Kelvin and a luminosity 250,000 to 1,000,000 times that of the Sun’s. 2. _____ Pre-main sequence stars that are very young (less than a million years old) and have a mass that is between a fifth and a third of the Sun’s mass. 3. _____ Giants/supergiants whose periods range from 20 to 2000 days. 4. _ ...
... Kelvin and a luminosity 250,000 to 1,000,000 times that of the Sun’s. 2. _____ Pre-main sequence stars that are very young (less than a million years old) and have a mass that is between a fifth and a third of the Sun’s mass. 3. _____ Giants/supergiants whose periods range from 20 to 2000 days. 4. _ ...
Source Variability - Center for Astrophysics and Space
... • 1995 – Future Concepts for X-ray Astronomy Chosen by Competition ...
... • 1995 – Future Concepts for X-ray Astronomy Chosen by Competition ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.