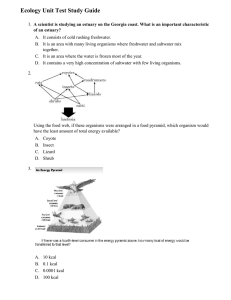
What are the effects of fire on the environment (3)
... Describe the soil of a desert. Describe the vegetation of a desert. Describe the typical desert animals. How have humans altered the desert? What is the climate of a savanna? Describe the soil of a savanna. Describe the vegetation of the savanna. What are the animal species of the savanna What are s ...
... Describe the soil of a desert. Describe the vegetation of a desert. Describe the typical desert animals. How have humans altered the desert? What is the climate of a savanna? Describe the soil of a savanna. Describe the vegetation of the savanna. What are the animal species of the savanna What are s ...
Ecology Review Game! Chapters 34, 35, 36, 38
... Organisms are organized! Name the terms that biologist use to describe the levels of ...
... Organisms are organized! Name the terms that biologist use to describe the levels of ...
Section 01
... resembles the deciduous forests because during dry season □ trees lose their leaves □ to conserve water ...
... resembles the deciduous forests because during dry season □ trees lose their leaves □ to conserve water ...
Biome Photostory Topic Quiz
... 1. Which of the following is not true about temperate deciduous forests? • A. Trees grow lush green leaves in the spring, but lose their leaves in late summer. • B. The soil is rich, and plants cover much of the forest floor. • C. Animals such as squirrels, bears, and deer find food in the form of ...
... 1. Which of the following is not true about temperate deciduous forests? • A. Trees grow lush green leaves in the spring, but lose their leaves in late summer. • B. The soil is rich, and plants cover much of the forest floor. • C. Animals such as squirrels, bears, and deer find food in the form of ...
Organisms and Ecosystems
... Objective: To know that climates and the types of life that they support define biomes on Earth. Ecological roles are the same in different biomes but may be filled by different species. ...
... Objective: To know that climates and the types of life that they support define biomes on Earth. Ecological roles are the same in different biomes but may be filled by different species. ...
ecosystem - Teacher Pages
... The temperate deciduous forest contains various species of angiosperm trees, which drop their leaves in the autumn, plus some species of coniferous trees. This forest type is widespread south of the boreal forest. ...
... The temperate deciduous forest contains various species of angiosperm trees, which drop their leaves in the autumn, plus some species of coniferous trees. This forest type is widespread south of the boreal forest. ...
Biomes of the World
... • Very few reptiles • Snow is primary form of precipitation (40 – 100 cm annually) Biodiversity: evergreen tree: pine, spruce, Animals: owls, mice, moose, bears and abundant insects in summer attract many birds that migrate south in winter. Human Impact: Tree harvesting ...
... • Very few reptiles • Snow is primary form of precipitation (40 – 100 cm annually) Biodiversity: evergreen tree: pine, spruce, Animals: owls, mice, moose, bears and abundant insects in summer attract many birds that migrate south in winter. Human Impact: Tree harvesting ...
Biomes of the World - Mrs.Cain's World Geography
... • Most trees will lose their leaves in the winter • Temperatures range between – 30oC and 30oC • Averages from 75 to 150 cm of precipitation • Well developed understory ...
... • Most trees will lose their leaves in the winter • Temperatures range between – 30oC and 30oC • Averages from 75 to 150 cm of precipitation • Well developed understory ...
chapt05_lecture_Terrestrial Biomes Fall 2014
... trees between 50° and 60° N latitude Dominated by pines, hemlock, spruce, cedar and fir with some deciduous trees mixed in ...
... trees between 50° and 60° N latitude Dominated by pines, hemlock, spruce, cedar and fir with some deciduous trees mixed in ...
Tropical Rain Forest
... Tropical rain forests are home to more species than all other land biomes combined. The leafy tops of tall trees- extending up to 70 meters above the forest floor – form a dense covering called a canopy. In the shade below the canopy a second layer of shorter trees and vines forms an understory. Org ...
... Tropical rain forests are home to more species than all other land biomes combined. The leafy tops of tall trees- extending up to 70 meters above the forest floor – form a dense covering called a canopy. In the shade below the canopy a second layer of shorter trees and vines forms an understory. Org ...
populations
... 7. What types of factors are considered limiting factors that restrict population growth? 8. What is density? 9. What are the two types of limiting factors? 10. What are the three types of density dependent factors? 12. What are the three types of density-independent factors? GLOBAL ...
... 7. What types of factors are considered limiting factors that restrict population growth? 8. What is density? 9. What are the two types of limiting factors? 10. What are the three types of density dependent factors? 12. What are the three types of density-independent factors? GLOBAL ...
Cartoon Guide to Terrestrial Biomes
... 4. Describe how humans have changed temperate deciduous forests. What are the different layers of this biome? Identify some primary consumers and some secondary/tertiary consumers. 5. How is the climate for grassland different from that of a forest or desert? What is the correlation between the avai ...
... 4. Describe how humans have changed temperate deciduous forests. What are the different layers of this biome? Identify some primary consumers and some secondary/tertiary consumers. 5. How is the climate for grassland different from that of a forest or desert? What is the correlation between the avai ...
Regional Effects
... defined by climate (temperature and precipitation) and vegetation type • Climate is influenced by ...
... defined by climate (temperature and precipitation) and vegetation type • Climate is influenced by ...
Biomes 3 - Decatur ISD
... How are biomes formed? Biomes are distributed across the Earth based primarily on climate. Therefore, in areas that are far apart, you will sometimes find similar plants and animals because the climate is similar. One factor affecting climate is latitude. Typically, the farther you move north or so ...
... How are biomes formed? Biomes are distributed across the Earth based primarily on climate. Therefore, in areas that are far apart, you will sometimes find similar plants and animals because the climate is similar. One factor affecting climate is latitude. Typically, the farther you move north or so ...
Canadian Perspectives: Major Zones in Canada
... the dominant evergreen spruces, firs and pines. This transcontinental forest is continuous with similar coniferous forests in the Cordillera, which extend far to the south. Like the arctic, the boreal forest of Canada is characterized by cold winters, but the greater snow cover ameliorates ground-su ...
... the dominant evergreen spruces, firs and pines. This transcontinental forest is continuous with similar coniferous forests in the Cordillera, which extend far to the south. Like the arctic, the boreal forest of Canada is characterized by cold winters, but the greater snow cover ameliorates ground-su ...
ecology unit study guide
... An oak and a maple tree grow larger to absorb the sunlight. What type of relationship is occurring? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... An oak and a maple tree grow larger to absorb the sunlight. What type of relationship is occurring? A. B. C. D. E. ...
Levels of Organization
... • Group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time • Species= organisms with similar characteristics that are able to breed and produce fertile offspring • Compete for food water, mates, resources • Adaptations may lead to no competition • Ex) School of Tangs ...
... • Group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time • Species= organisms with similar characteristics that are able to breed and produce fertile offspring • Compete for food water, mates, resources • Adaptations may lead to no competition • Ex) School of Tangs ...
Biomes of the World - Dublin City Schools
... Temperate Boreal Forest • Also known as Taiga • Typically found between 45o and 60o North latitude • Cold climate with summer rains • Very few reptiles • Limited understory • Snow is primary form of precipitation (40 – 100 cm annually) ...
... Temperate Boreal Forest • Also known as Taiga • Typically found between 45o and 60o North latitude • Cold climate with summer rains • Very few reptiles • Limited understory • Snow is primary form of precipitation (40 – 100 cm annually) ...
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities
... O2 than still water. 2. Standing-Water—lakes, ponds. These contain phytoplankton (single-celled algae) and zooplankton. 3. Freshwater wetlands—water either covers soil or is at or near the surface of the soil for at least part of the year. ...
... O2 than still water. 2. Standing-Water—lakes, ponds. These contain phytoplankton (single-celled algae) and zooplankton. 3. Freshwater wetlands—water either covers soil or is at or near the surface of the soil for at least part of the year. ...
THE BIOSPHERE - Bishop Amat Memorial High School
... allow many animals and plants to reproduce. Many rivers, ponds, lakes, and bogs provide homes for small birds and mammals either hibernate or move to warmer regions during the long, cold winters. Typical inhabitants • black bears, grizzlies, wolves, moose, elk, and dozens of ...
... allow many animals and plants to reproduce. Many rivers, ponds, lakes, and bogs provide homes for small birds and mammals either hibernate or move to warmer regions during the long, cold winters. Typical inhabitants • black bears, grizzlies, wolves, moose, elk, and dozens of ...
Temperate forest
... number of geographic areas distinguished by particular types of dominant vegetation. These categories of plant life are called biomes. Often biomes are thought of as climatic regions E.g. grassland, savanna, temperate forest, desert, boreal forest, tropical rain forest, tundra Factors that can effec ...
... number of geographic areas distinguished by particular types of dominant vegetation. These categories of plant life are called biomes. Often biomes are thought of as climatic regions E.g. grassland, savanna, temperate forest, desert, boreal forest, tropical rain forest, tundra Factors that can effec ...
Introduction to Ecology
... Are distinguished by the presence of characteristic plants and animals Commonly identified by their dominant plant life Biomes are distributed over the Earth based on climate (temperature and precipitation) and latitude 8 major categories of Major Biomes Tundra Tropical forest Temperate ...
... Are distinguished by the presence of characteristic plants and animals Commonly identified by their dominant plant life Biomes are distributed over the Earth based on climate (temperature and precipitation) and latitude 8 major categories of Major Biomes Tundra Tropical forest Temperate ...
Taiga

Taiga (/ˈtaɪɡə/; Russian: тайга́; IPA: [tɐjˈɡa]; from Turkic) also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces and larches.The taiga is the world's largest terrestrial biome. In North America it covers most of inland Canada and Alaska as well as parts of the extreme northern continental United States (northern Minnesota through the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to Upstate New York and northern New England), where it is known as the Northwoods. In Eurasia, it covers most of Sweden, Finland, much of Norway, some lowland/coastal areas of Iceland, much of Russia from Karelia in the west to the Pacific Ocean (including much of Siberia), and areas of northern Kazakhstan, northern Mongolia, and northern Japan (on the island of Hokkaidō). However, the main tree species, the length of the growing season and summer temperatures vary. For example, the taiga of North America mostly consists of spruces; Scandinavian and Finnish taiga consists of a mix of spruce, pines and birch; Russian taiga has spruces, pines and larches depending on the region, while the Eastern Siberian taiga is a vast larch forest.A different use of the term taiga is often encountered in the English language, with ""boreal forest"" used in the United States and Canada to refer to only the more southerly part of the biome, while ""taiga"" is used to describe the more barren areas of the northernmost part of the biome approaching the tree line and the tundra biome. Hoffman (1958) discusses the origin of this differential use in North America and why it is an inappropriate differentiation of the Russian term. Although at high elevations taiga grades into alpine tundra through Krummholz, it is not an alpine biome only like subalpine forest, and much of taiga is lowlands.