a PDF version of the Uniglobe Manual.
... A system of coordinates similar to that described in Figures 11 and 12 is used to label directions in the sky. These directions are represented as positions on the CELESTIAL GLOBE of the Uniglobe. The effect of the size of the earth on measurement of angle is shown in Figure 13. The extremely large ...
... A system of coordinates similar to that described in Figures 11 and 12 is used to label directions in the sky. These directions are represented as positions on the CELESTIAL GLOBE of the Uniglobe. The effect of the size of the earth on measurement of angle is shown in Figure 13. The extremely large ...
RV Metric_new_8
... to the center of mass, from parameters ii–ix, for both the face-on and edge-on inclinations. Second, knowing the planet’s position, we compute the apparent separation (s), the radial distance (r) from star to the planet, and the phase angle ( b ), which is the planetocentric angle between the star a ...
... to the center of mass, from parameters ii–ix, for both the face-on and edge-on inclinations. Second, knowing the planet’s position, we compute the apparent separation (s), the radial distance (r) from star to the planet, and the phase angle ( b ), which is the planetocentric angle between the star a ...
Comets - Images
... The comet was first recorded in 240 BC and was also visible in 1066 after the Battle of Hastings. It is shown in the Bayeaux Tapestry. ...
... The comet was first recorded in 240 BC and was also visible in 1066 after the Battle of Hastings. It is shown in the Bayeaux Tapestry. ...
Stellarium – a valuable resource for teaching astronomy in the
... The movement of the planets (their name in Greek means wanderers) against the backdrop of the celestial sphere can easily be seen by using the magnifying glass symbol to locate the planet (e.g. Jupiter) and advancing the date a month at a time. The planet will move relative to the constellations. (T ...
... The movement of the planets (their name in Greek means wanderers) against the backdrop of the celestial sphere can easily be seen by using the magnifying glass symbol to locate the planet (e.g. Jupiter) and advancing the date a month at a time. The planet will move relative to the constellations. (T ...
Where do Comets come from?
... The Kuiper Belt is 3,000 times smaller and closer in than the Oort cloud. The ice worlds in the Kuiper Belt are more like an extension of the planets: they are orbiting roughly in the same plane, and roughly in the same direction as the planets. So - this is getting pretty silly. We now have not on ...
... The Kuiper Belt is 3,000 times smaller and closer in than the Oort cloud. The ice worlds in the Kuiper Belt are more like an extension of the planets: they are orbiting roughly in the same plane, and roughly in the same direction as the planets. So - this is getting pretty silly. We now have not on ...
ted_2012_power_of_design
... meet earthquake requirements, maintain cultural identity, and take the environment into consideration. A light-steel component system dramatically reducing construction time was developed with donated Autodesk design software. Local materials were used wherever possible, and due to the simple design ...
... meet earthquake requirements, maintain cultural identity, and take the environment into consideration. A light-steel component system dramatically reducing construction time was developed with donated Autodesk design software. Local materials were used wherever possible, and due to the simple design ...
What is our place in the universe?
... Earth orbits the Sun (revolves) once every year: • at an average distance of 1 AU ≈ 150 million km. • with Earth’s axis tilted by 23.5º (pointing to Polaris) • and rotating in the same direction it orbits, counterclockwise as viewed from above the North Pole. ...
... Earth orbits the Sun (revolves) once every year: • at an average distance of 1 AU ≈ 150 million km. • with Earth’s axis tilted by 23.5º (pointing to Polaris) • and rotating in the same direction it orbits, counterclockwise as viewed from above the North Pole. ...
Minor Bodies of the Solar System Standardized Test Prep
... Read the passage below. Then, answer questions 8–11. Kuiper Belt Objects To explain the source of short-period comets, or comets that have a relatively short orbit around the sun, the Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper proposed in 1949 that a belt of icy bodies must lie beyond the orbits of Nep ...
... Read the passage below. Then, answer questions 8–11. Kuiper Belt Objects To explain the source of short-period comets, or comets that have a relatively short orbit around the sun, the Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper proposed in 1949 that a belt of icy bodies must lie beyond the orbits of Nep ...
Birth of Stars - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... producing energy through nuclear fusion in their cores. Generating energy by fusion defines a star. Hydrogen is being converted to helium, but eventually the supply of hydrogen will run out. Stars range in mass from about 1/12 Msun to 200 Msun. Low mass stars are more common. For main sequence stars ...
... producing energy through nuclear fusion in their cores. Generating energy by fusion defines a star. Hydrogen is being converted to helium, but eventually the supply of hydrogen will run out. Stars range in mass from about 1/12 Msun to 200 Msun. Low mass stars are more common. For main sequence stars ...
Glossary Topics - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... This system may seem to be awkward and lack sense, but in fact it is based on the natural capabilities of the human eye. Hipparchus was the first to catalogue star brightness this way in 120 BCE, assigning a number from 1 to 6 where 1 represented the brightest stars. Astronomers are now able to prec ...
... This system may seem to be awkward and lack sense, but in fact it is based on the natural capabilities of the human eye. Hipparchus was the first to catalogue star brightness this way in 120 BCE, assigning a number from 1 to 6 where 1 represented the brightest stars. Astronomers are now able to prec ...
Our Star and Solar System
... carbon, gold, iron, and others. Many of these elements were originally forged in supernova explosions. So we, and everything in our solar system, are made of “star stuff”1. Every second, the Sun fuses 614 million metric tons of hydrogen into 609 metric tons of helium in its core. The difference is c ...
... carbon, gold, iron, and others. Many of these elements were originally forged in supernova explosions. So we, and everything in our solar system, are made of “star stuff”1. Every second, the Sun fuses 614 million metric tons of hydrogen into 609 metric tons of helium in its core. The difference is c ...
The Planets The Moons of Jupiter Two Types of Starsnd at
... Name _______________________________________ Date _____________________________ Block _____ You weight on different planets. ...
... Name _______________________________________ Date _____________________________ Block _____ You weight on different planets. ...
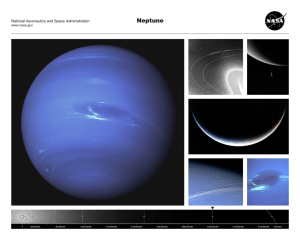
Neptune - TeacherLINK
... a French mathematician, Urbain Joseph Le Verrier, proposed the position and mass of another as yet unknown planet that could cause the observed changes to Uranus’ orbit. After being ignored by French astronomers, Le Verrier sent his predictions to Johann Gottfried Galle at the Berlin Observatory, wh ...
... a French mathematician, Urbain Joseph Le Verrier, proposed the position and mass of another as yet unknown planet that could cause the observed changes to Uranus’ orbit. After being ignored by French astronomers, Le Verrier sent his predictions to Johann Gottfried Galle at the Berlin Observatory, wh ...
A Jupiter-mass companion to a solar-type star
... The presence of a Jupiter-mass companion to the star 51 Pegasi is inferred from observations of periodic variations in the star's radial velocity. The companion lies only about eight million kilometres from the star, which would be well inside the orbit of Mercury in our Solar System. This object mi ...
... The presence of a Jupiter-mass companion to the star 51 Pegasi is inferred from observations of periodic variations in the star's radial velocity. The companion lies only about eight million kilometres from the star, which would be well inside the orbit of Mercury in our Solar System. This object mi ...
Astronomy & the Process of Science
... How it rises & sets depends on position! Near Equator, almost straight up/down Near Poles, very “shallow” angle! ...
... How it rises & sets depends on position! Near Equator, almost straight up/down Near Poles, very “shallow” angle! ...
Astronomy and the Coal Age of Alabama
... If the Sun was born in a cluster, where are its “siblings”? Answer: most of these clusters disperse after several tens of millions of years. Very few hang together more than a billion years. It is likely the Sun had long since left its cluster by the time of the Minkin site. ...
... If the Sun was born in a cluster, where are its “siblings”? Answer: most of these clusters disperse after several tens of millions of years. Very few hang together more than a billion years. It is likely the Sun had long since left its cluster by the time of the Minkin site. ...
ASTR 330: The Solar System
... Callisto, with crater ghosts and concentric ridges from long-ago impacts. This terrain has a similar level of cratering, and hence age, as Callisto. The albedo is about 25%, suggesting a relatively low admixture of ice with the ‘dirt’. 2. The rest of Ganymede is a lighter colored, less-cratered type ...
... Callisto, with crater ghosts and concentric ridges from long-ago impacts. This terrain has a similar level of cratering, and hence age, as Callisto. The albedo is about 25%, suggesting a relatively low admixture of ice with the ‘dirt’. 2. The rest of Ganymede is a lighter colored, less-cratered type ...
The Origin of Mercury - Institute of Planetary Science
... smaller than those of any of the other terrestrial planets or the Moon. A variety of hypotheses have been suggested to account for the anomalously high mean density of Mercury. In all cases, the close proximity of Mercury to the Sun plays a crucial role and all theories invoke processes that result ...
... smaller than those of any of the other terrestrial planets or the Moon. A variety of hypotheses have been suggested to account for the anomalously high mean density of Mercury. In all cases, the close proximity of Mercury to the Sun plays a crucial role and all theories invoke processes that result ...
jun14
... The full Moon is exactly opposite the Sun or 180 degrees away in the sky. Astronomers would measure this angle in hours and say it is 12 hours from the Sun. If sunset is at 6:00 P.M. the full Moon rises at 6:00 P.M., crosses the meridian at midnight and sets at sunrise at 6:00 A.M., 12 hours differ ...
... The full Moon is exactly opposite the Sun or 180 degrees away in the sky. Astronomers would measure this angle in hours and say it is 12 hours from the Sun. If sunset is at 6:00 P.M. the full Moon rises at 6:00 P.M., crosses the meridian at midnight and sets at sunrise at 6:00 A.M., 12 hours differ ...
Isotopic Ratios In Titanʼs Atmosphere: Clues and Challenges
... ⇒ Tight constraint on time since release, e.g. if KIE ~1%, not very many ‘lifetimes’ allowed before noticeably different from 89. 2. Methane constantly replenished: we can show that carbon ratio stabilzes at (89/f) – where f (enrichment per lifetime) is not much above unity. ...
... ⇒ Tight constraint on time since release, e.g. if KIE ~1%, not very many ‘lifetimes’ allowed before noticeably different from 89. 2. Methane constantly replenished: we can show that carbon ratio stabilzes at (89/f) – where f (enrichment per lifetime) is not much above unity. ...
giant planet formation i. introduction
... 1993). Even if giant planets would have kept this angular momentum, they still would not rotate critically! Giant planets, unlike stars, therefore do not have an angular momentum problem. This may justify why most studies of proto-giant planets neglect rotation or treat it as a small perturbation. W ...
... 1993). Even if giant planets would have kept this angular momentum, they still would not rotate critically! Giant planets, unlike stars, therefore do not have an angular momentum problem. This may justify why most studies of proto-giant planets neglect rotation or treat it as a small perturbation. W ...
EARTH SCIENCE - Westhampton Beach School District
... (3) upward away from Earth’s surface (4) downward toward Earth’s surface ...
... (3) upward away from Earth’s surface (4) downward toward Earth’s surface ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.