Glossary
... Mars- It is the fourth planet from the Sun. In some ways it’s like our Earth. Mars has volcanoes, valleys and sandy desert. Mercury- It is the closest planet to the Sun. It is a barren rocky planet and its surface is covered with huge holes or craters where rocks called meteorites have crashed into ...
... Mars- It is the fourth planet from the Sun. In some ways it’s like our Earth. Mars has volcanoes, valleys and sandy desert. Mercury- It is the closest planet to the Sun. It is a barren rocky planet and its surface is covered with huge holes or craters where rocks called meteorites have crashed into ...
Science 9 Unit E Section 1.0
... Venus is similar to Earth in diameter, mass, and gravity, and is often called Earth’s twin. A closer look at conditions on Venus’s surface shows where the similarities end. Venus would be horrific for humans to visit. Surface temperatures are kept hot due to a greenhouse effect caused by thick cloud ...
... Venus is similar to Earth in diameter, mass, and gravity, and is often called Earth’s twin. A closer look at conditions on Venus’s surface shows where the similarities end. Venus would be horrific for humans to visit. Surface temperatures are kept hot due to a greenhouse effect caused by thick cloud ...
a 3 (in astronomical units)
... • Venus showed complete set of phases only explainable if it was in orbit around the Sun not the Earth. Because of his insistence of the Heliocentric model based on his observations, Galileo was arrested by the church and was not forgiven of his “crimes” until 1992. ...
... • Venus showed complete set of phases only explainable if it was in orbit around the Sun not the Earth. Because of his insistence of the Heliocentric model based on his observations, Galileo was arrested by the church and was not forgiven of his “crimes” until 1992. ...
Playground planets - Earth Learning Idea
... • The solar system is 4·6 billion years old. • The Universe from the Big Bang to the present day is about 13 billion years old. ...
... • The solar system is 4·6 billion years old. • The Universe from the Big Bang to the present day is about 13 billion years old. ...
practice exam #1
... 3. When Eratosthenes calculated Earth’s circumference, he used measurements of shadows cast at two different cities on the same day, and a. b. c. d. e. f. g. ...
... 3. When Eratosthenes calculated Earth’s circumference, he used measurements of shadows cast at two different cities on the same day, and a. b. c. d. e. f. g. ...
DeKalb Middle School Weekly Lesson Plan Teacher: Angela
... discover more bodies in the solar system? (telescope) ...
... discover more bodies in the solar system? (telescope) ...
Unit Assesment
... 6) True or False: There are 9 planets in the Solar System. a) True b) False 7) True or False: Mercury is the smallest planet in our Solar System. a) True b) False ...
... 6) True or False: There are 9 planets in the Solar System. a) True b) False 7) True or False: Mercury is the smallest planet in our Solar System. a) True b) False ...
The Solar System - University of Sioux Falls
... There is only one satellite known to Pluto that is named Charon ...
... There is only one satellite known to Pluto that is named Charon ...
Chapter 4 Chapter 4 - The Solar System The Solar System
... Nebular Theory for Solar System formation Our sun and the planets began from a cloud of dust and gas (nebula) As the cloud contracts under its own gravity, the Sun is formed at the ...
... Nebular Theory for Solar System formation Our sun and the planets began from a cloud of dust and gas (nebula) As the cloud contracts under its own gravity, the Sun is formed at the ...
2. Universe, Solar System and Earth`s formation
... 3. External source of energy: Early in the Earth’s history there is still plenty of material in the path of the protoplanet’s orbit, which is constantly being attracted by the Earth’s gravity to the every enlarging planet. Collisions of these meteorites into the Earth’s surface are a constant source ...
... 3. External source of energy: Early in the Earth’s history there is still plenty of material in the path of the protoplanet’s orbit, which is constantly being attracted by the Earth’s gravity to the every enlarging planet. Collisions of these meteorites into the Earth’s surface are a constant source ...
Solar_System - UF :: Astronomy
... •Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune •Far from Sun •Large masses and radii •Gaseous surface •Low densities •Fast rotation •Strong magnetic field •Many rings •Many moons ...
... •Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune •Far from Sun •Large masses and radii •Gaseous surface •Low densities •Fast rotation •Strong magnetic field •Many rings •Many moons ...
Chapter 20 Questions
... 11. What do we call the motion of a body as it orbits another body in space? 12. What do we call the time it takes for an object to revolve around the sun once? 13. What are the differences between prograde rotation and retrograde rotation? Which applies to the Earth? 14. Which planet is considered ...
... 11. What do we call the motion of a body as it orbits another body in space? 12. What do we call the time it takes for an object to revolve around the sun once? 13. What are the differences between prograde rotation and retrograde rotation? Which applies to the Earth? 14. Which planet is considered ...
The Earth and Other Planets
... Resources: Celestia, Virginia SOL Enhanced Scopes and Sequence Lesson Plan Outline: Topic Introduction to the planets of the Solar System – relative size and distance from the sun. Instructional Objective(s) Students will be able to: - describe the relative sizes of the planets compared to each othe ...
... Resources: Celestia, Virginia SOL Enhanced Scopes and Sequence Lesson Plan Outline: Topic Introduction to the planets of the Solar System – relative size and distance from the sun. Instructional Objective(s) Students will be able to: - describe the relative sizes of the planets compared to each othe ...
Name Class Date
... a. heat produced when planetesimals collided with one another. b. heat generated when the increasing weight of its outer layers compressed its inner layers. c. the conversion of moving radioactive particles into heat energy. d. an irregular orbit that brought it closer to the sun. ______ 24. Dense m ...
... a. heat produced when planetesimals collided with one another. b. heat generated when the increasing weight of its outer layers compressed its inner layers. c. the conversion of moving radioactive particles into heat energy. d. an irregular orbit that brought it closer to the sun. ______ 24. Dense m ...
Space 2006
... A. A year would be shorter. B. A year would be longer. C. A day would be shorter. D. A day would be longer. ...
... A. A year would be shorter. B. A year would be longer. C. A day would be shorter. D. A day would be longer. ...
the free PDF resource
... 11. What S is the nearest star to Neptune? 12. What M is often known as ‘the Red Planet’ due to red iron oxide on its surface? ...
... 11. What S is the nearest star to Neptune? 12. What M is often known as ‘the Red Planet’ due to red iron oxide on its surface? ...
Pocket Solar System - Skynet Junior Scholars
... 3. Given this spacing, why do you think little, rocky Venus can outshine giant Jupiter in the night sky? Both are covered with highly reflective clouds, and although it is much smaller, Venus is also much, much closer. ...
... 3. Given this spacing, why do you think little, rocky Venus can outshine giant Jupiter in the night sky? Both are covered with highly reflective clouds, and although it is much smaller, Venus is also much, much closer. ...
ASTR 1010 – Spring 2016 – Study Notes Dr. Magnani
... Samos, who argued for a heliocentric model based on his estimates of the relative sizes of Sun, Earth, and Moon. He determined that the Sun was the largest body and so should be at the cent ...
... Samos, who argued for a heliocentric model based on his estimates of the relative sizes of Sun, Earth, and Moon. He determined that the Sun was the largest body and so should be at the cent ...
Worksheet 1
... N. A region from which some comets come. The region extends from the orbit of Neptune to beyond Pluto O. A region between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter in which most of the Solar System’s asteroids are located P. A rocky planet similar to the Earth in size and structure Q. A vast region in which co ...
... N. A region from which some comets come. The region extends from the orbit of Neptune to beyond Pluto O. A region between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter in which most of the Solar System’s asteroids are located P. A rocky planet similar to the Earth in size and structure Q. A vast region in which co ...
Pocket Solar System - California Academy of Sciences
... planet: In the solar system, a planet is a large round object that orbits the Sun and has cleared out most of the other objects in its orbit. dwarf planet: A large round object that orbits the Sun but is NOT the dominant object in its orbit. solar system: The Sun and all of the planets, comets, etc. ...
... planet: In the solar system, a planet is a large round object that orbits the Sun and has cleared out most of the other objects in its orbit. dwarf planet: A large round object that orbits the Sun but is NOT the dominant object in its orbit. solar system: The Sun and all of the planets, comets, etc. ...
2. Universe, Solar System and Earth`s formation
... 3. External source of energy: Early in the Earth’s history there is still plenty of material in the path of the protoplanet’s orbit, which is constantly being attracted by the Earth’s gravity to the every enlarging planet. Collisions of these meteorites into the Earth’s surface are a constant source ...
... 3. External source of energy: Early in the Earth’s history there is still plenty of material in the path of the protoplanet’s orbit, which is constantly being attracted by the Earth’s gravity to the every enlarging planet. Collisions of these meteorites into the Earth’s surface are a constant source ...
What is Astronomy?
... of celestial objects using the scientific method. • Has its origins in ancient history. ...
... of celestial objects using the scientific method. • Has its origins in ancient history. ...
Solar System Vocab terms geocentric — discredited theory that
... gibbous phase — when a moon or planet shows more than half, but not all, of its face. gravity — seeming force of attraction felt between two or more objects with mass. heliocentric — theory that the sun is in the center of the solar system. infrared — invisible part of light, with longer wavelengths ...
... gibbous phase — when a moon or planet shows more than half, but not all, of its face. gravity — seeming force of attraction felt between two or more objects with mass. heliocentric — theory that the sun is in the center of the solar system. infrared — invisible part of light, with longer wavelengths ...
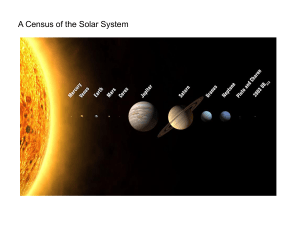
A Census of the Solar System
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
... 1. Planets and their satellites all lie in the same plane - the ecliptic – to within a few degrees 2. Sun’s rotational equator aligned with ecliptic 3. Planetary orbits are nearly circular ellipses 4. Planets all revolve in same W -> E direction 5. Sun and planets all rotate on axes in same W –E dir ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.