Earth 351, Forming a Habitable Planet
... 4. A challenge in thinking about life on earth or other planets is the very long time scales. To help you, mark key dates and events on two time lines corresponding to the main sequence life of the sun. Turn one in and keep the other to use and update during the quarter. Label the following with he ...
... 4. A challenge in thinking about life on earth or other planets is the very long time scales. To help you, mark key dates and events on two time lines corresponding to the main sequence life of the sun. Turn one in and keep the other to use and update during the quarter. Label the following with he ...
What is a Planet
... There are FIVE Dwarf Planets in our Solar System; Pluto, Eris, Makemake and Haumea (found in the Kupier Belt) and a very large asteroid called Ceres. What is a Planet? – In 2006 the International Astronomical Union define a planet as an object that orbits the sun with sufficient mass and gravity. – ...
... There are FIVE Dwarf Planets in our Solar System; Pluto, Eris, Makemake and Haumea (found in the Kupier Belt) and a very large asteroid called Ceres. What is a Planet? – In 2006 the International Astronomical Union define a planet as an object that orbits the sun with sufficient mass and gravity. – ...
Suns .n. Stars
... • The sun rises in the east every morning. • The sun gives us light and heat. • The sun has a core in the centre of it. • The sun is about 5,000 degrees but the core is 3 times as hot. • It takes light about 8 minutes 70 seconds to get from Sun to Earth. ...
... • The sun rises in the east every morning. • The sun gives us light and heat. • The sun has a core in the centre of it. • The sun is about 5,000 degrees but the core is 3 times as hot. • It takes light about 8 minutes 70 seconds to get from Sun to Earth. ...
1448
... a planet, we count at least 110 known planets in our Solar System (Figure 1). This number continues to grow as astronomers discover more planets in the Kuiper Belt [e.g., 7]. Certainly 110 planets is more than students should be expected to memorize, and indeed they ought not. Instead, students shou ...
... a planet, we count at least 110 known planets in our Solar System (Figure 1). This number continues to grow as astronomers discover more planets in the Kuiper Belt [e.g., 7]. Certainly 110 planets is more than students should be expected to memorize, and indeed they ought not. Instead, students shou ...
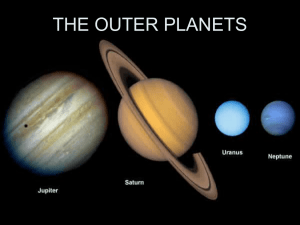
The Outer Planets
... in 1610 (Galilean moons) Many more have been discovered as technology improved – latest count is 63 The four largest are very different from each other ...
... in 1610 (Galilean moons) Many more have been discovered as technology improved – latest count is 63 The four largest are very different from each other ...
Mission 1 Glossary
... to plan, record and control the movement of a ship or plane Moon - can be any natural object orbiting around another; often refers to the Moon of the Earth (but other planets have moons too.) The Moon of the Earth was probably formed when a large object struck the Earth a long time ago. ...
... to plan, record and control the movement of a ship or plane Moon - can be any natural object orbiting around another; often refers to the Moon of the Earth (but other planets have moons too.) The Moon of the Earth was probably formed when a large object struck the Earth a long time ago. ...
vert strand 6
... Observe the change in time and location of moon rise, moon set, and the moon’s appearance relative to time of day and month over several months, and note the pattern in this change Recognize the moon rises later each day due to its revolution around the Earth in a counterclockwise direction Recogniz ...
... Observe the change in time and location of moon rise, moon set, and the moon’s appearance relative to time of day and month over several months, and note the pattern in this change Recognize the moon rises later each day due to its revolution around the Earth in a counterclockwise direction Recogniz ...
Boy Scout Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
... a. Describe the composition of the Sun, its relationship to other stars, and some effects of its radiation on Earth’s weather. Define sunspots and describe some of the effects they may have on solar radiation. b. Identify at least one red star, one blue star, and one yellow star (other than the Sun) ...
... a. Describe the composition of the Sun, its relationship to other stars, and some effects of its radiation on Earth’s weather. Define sunspots and describe some of the effects they may have on solar radiation. b. Identify at least one red star, one blue star, and one yellow star (other than the Sun) ...
Earth, Moon, and Sun - Sloan Creek Intermediate School
... Characteristics of the Sun The Sun has SUNSPOTS that are areas of the sun’s surface that are cooler than the rest of the sun. ...
... Characteristics of the Sun The Sun has SUNSPOTS that are areas of the sun’s surface that are cooler than the rest of the sun. ...
Physics - Gravity and Gravity Applications
... 7) Which force-pair is greater – that between the moon and earth, or that between the sun and earth? 8) Which is more effective in raising ocean tides – the moon or the sun? Explain. ...
... 7) Which force-pair is greater – that between the moon and earth, or that between the sun and earth? 8) Which is more effective in raising ocean tides – the moon or the sun? Explain. ...
Sun and Planets.notebook
... http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/howtheuniverseworkssolarwinds.html http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XuD82q4Fxgk ...
... http://dsc.discovery.com/videos/howtheuniverseworkssolarwinds.html http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XuD82q4Fxgk ...
Summary of week 1:
... The Visible Universe: The part of the Universe that can be observed from the Earth at the present time. Note: This is not a fixed volume, and some objects currently outside our visible universe may be within it in the future. The Universe: “All that there is (was; will be)” Astronomical Unit: The av ...
... The Visible Universe: The part of the Universe that can be observed from the Earth at the present time. Note: This is not a fixed volume, and some objects currently outside our visible universe may be within it in the future. The Universe: “All that there is (was; will be)” Astronomical Unit: The av ...
Dark Skies Above Downeast Maine
... January 3 – The Quadrantid Meteor Shower Peaks. Look for this beautiful shower to be at its best during the early hours of January 3rd. The Quadrantids have a very small window for when the met ...
... January 3 – The Quadrantid Meteor Shower Peaks. Look for this beautiful shower to be at its best during the early hours of January 3rd. The Quadrantids have a very small window for when the met ...
Astronomical scale - Monash University
... A light year is the distance that light travels in 1 year. The light from the sun takes about eight minutes to reach the earth because it is only a relatively short astronomical distance (about 149 million km) away. The light from distant astronomical objects takes so long to get to us that we see t ...
... A light year is the distance that light travels in 1 year. The light from the sun takes about eight minutes to reach the earth because it is only a relatively short astronomical distance (about 149 million km) away. The light from distant astronomical objects takes so long to get to us that we see t ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Earth`s Place in the Universe Test 1
... D) the time it takes light to travel from Earth to the Sun. 3) Hunter goes outside and notices that the sun looks larger than the other stars he has seen. Why does the sun appear larger than the other stars? The Sun looks larger because it's closer to A) The Sun is the largest star in the sky. C) Ea ...
... D) the time it takes light to travel from Earth to the Sun. 3) Hunter goes outside and notices that the sun looks larger than the other stars he has seen. Why does the sun appear larger than the other stars? The Sun looks larger because it's closer to A) The Sun is the largest star in the sky. C) Ea ...
THE OUTER PLANETS
... • Uranus is about 4 times the diameter of Earth, but is still much smaller than Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus is a very far from the sun, making it colder than Saturn, and is surrounded by a group of thin, flat rings that are much darker than Saturn’s rings. ...
... • Uranus is about 4 times the diameter of Earth, but is still much smaller than Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus is a very far from the sun, making it colder than Saturn, and is surrounded by a group of thin, flat rings that are much darker than Saturn’s rings. ...
Solar System Scale
... The nearest star to Earth is Alpha Centauri, 274,332 AU away. Where would this star be placed in your scale model of Solar System distances. ...
... The nearest star to Earth is Alpha Centauri, 274,332 AU away. Where would this star be placed in your scale model of Solar System distances. ...
Looking out at the Night Sky What questions do you have?
... When do we see the stars? How long does it take the earth to revolve around the sun? Ok: the north star, or Polaris, or “the star that does not walk”; why does it have this name? Use your planisphere (star wheel) for this. ...
... When do we see the stars? How long does it take the earth to revolve around the sun? Ok: the north star, or Polaris, or “the star that does not walk”; why does it have this name? Use your planisphere (star wheel) for this. ...
ppt
... When do we see the stars? How long does it take the earth to revolve around the sun? Ok: the north star, or Polaris, or “the star that does not walk”; why does it have this name? Use your planisphere (star wheel) for this. ...
... When do we see the stars? How long does it take the earth to revolve around the sun? Ok: the north star, or Polaris, or “the star that does not walk”; why does it have this name? Use your planisphere (star wheel) for this. ...
A Short History of Venus
... “greenhouse” gases. As the temperature increased, all of the existing water became vapor, circulated high into the atmosphere. This vapor was split apart by solar UV radiation, the hydrogen released was lost to the planet. Without a hydrological cycle, all of the outgassed CO2 remained in the atmosp ...
... “greenhouse” gases. As the temperature increased, all of the existing water became vapor, circulated high into the atmosphere. This vapor was split apart by solar UV radiation, the hydrogen released was lost to the planet. Without a hydrological cycle, all of the outgassed CO2 remained in the atmosp ...
Planetary Science Vocabulary #2 1. Asteroids Objects made of rock
... Piece of rock from space that makes it through Earth’s atmosphere and lands on Earth ...
... Piece of rock from space that makes it through Earth’s atmosphere and lands on Earth ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.