Solar evolution and the distant future of Earth
... hydrogen shell-burning zone. At that point, the star disperses the remains of its thin outer layers, ends its active energy production, and only leaves behind its hot core, which would be observed eventually as a “white dwarf”. For a long time, computer models of solar and stellar evolution have dif ...
... hydrogen shell-burning zone. At that point, the star disperses the remains of its thin outer layers, ends its active energy production, and only leaves behind its hot core, which would be observed eventually as a “white dwarf”. For a long time, computer models of solar and stellar evolution have dif ...
SDO | SOLAR DYNAMICS OBSERVATORY HTTP://WWW.NASA
... of other metals (by mass). Of course, the sun is constantly converting hydrogen to helium in its core. In fact, 620 million metric tons of hydrogen are fused every second! That means the concentration of elements will also change over time - lots of time. Since its formation, the sun has used about ...
... of other metals (by mass). Of course, the sun is constantly converting hydrogen to helium in its core. In fact, 620 million metric tons of hydrogen are fused every second! That means the concentration of elements will also change over time - lots of time. Since its formation, the sun has used about ...
Astronomy and the Universe - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... understanding of the universe? What makes up our solar system? What are the stars? Do they last forever? What are galaxies? What do astronomers learn by studying them? How does measuring angles help astronomers learn about objects in the sky? What is powers-of-ten notation, and why is it useful in ...
... understanding of the universe? What makes up our solar system? What are the stars? Do they last forever? What are galaxies? What do astronomers learn by studying them? How does measuring angles help astronomers learn about objects in the sky? What is powers-of-ten notation, and why is it useful in ...
Slide 1
... Retrograde Motion = when planets move in the opposite direction across the sky.. This happens because these planets are moving around the Sun slower than the Earth ...
... Retrograde Motion = when planets move in the opposite direction across the sky.. This happens because these planets are moving around the Sun slower than the Earth ...
Hypothesis vs. Theory ~The Big Bang
... Our study of Astronomy requires us to look UP and not DOWN. Humans today are not used to looking UP, we are not used to observing the sky – it appears to be of little use – and city living with its extensive light pollution often prevents us from seeing, and hence exploring, the “heavens”. Most of u ...
... Our study of Astronomy requires us to look UP and not DOWN. Humans today are not used to looking UP, we are not used to observing the sky – it appears to be of little use – and city living with its extensive light pollution often prevents us from seeing, and hence exploring, the “heavens”. Most of u ...
AST 150: Radioactive Dating Game Activity
... 3. Are there any features of individual planets that stand out as being odd or out of place? If so, which features? 4. Consider the exoplanets we have studied so far, how many more categories would you need to add? ...
... 3. Are there any features of individual planets that stand out as being odd or out of place? If so, which features? 4. Consider the exoplanets we have studied so far, how many more categories would you need to add? ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... Given the information below about some stars, find the distances to each star using the technique of spectroscopic parallax. Use Voyager data panel to find the apparent magnitude (m) and absolute magnitude (M). Then calculate the distance in parsecs using the formula for D below Fig 2. Check your di ...
... Given the information below about some stars, find the distances to each star using the technique of spectroscopic parallax. Use Voyager data panel to find the apparent magnitude (m) and absolute magnitude (M). Then calculate the distance in parsecs using the formula for D below Fig 2. Check your di ...
here - Immersive Theatres
... dimmer – just by fractions of a percent. But this, too, can be measured with high precision, and allows us to determine the size and orbit of the planet. It was discovered that the planet of “51 Pegasi” is rather strange. It is almost as large as Jupiter, but orbits so close to the star that it i ...
... dimmer – just by fractions of a percent. But this, too, can be measured with high precision, and allows us to determine the size and orbit of the planet. It was discovered that the planet of “51 Pegasi” is rather strange. It is almost as large as Jupiter, but orbits so close to the star that it i ...
File
... but share some common components. The list below shows the main components of telescopes. Write a “1” beside the component if it is used in a refracting telescope, a “2” beside a component used in a reflecting telescope, and a “3” if the component is used in both types. ...
... but share some common components. The list below shows the main components of telescopes. Write a “1” beside the component if it is used in a refracting telescope, a “2” beside a component used in a reflecting telescope, and a “3” if the component is used in both types. ...
the solar system and the universe
... Spins in opposite direction to the other terrestrial planets. Volcano-covered surface; most craters erased by volcanic activity. Dense CO2 atmosphere causing greenhouse effect on planet. Hot enough to melt lead; clouds of sulphuric acid. Atmospheric Pressure is x 92 that of Earth. Can be seen from E ...
... Spins in opposite direction to the other terrestrial planets. Volcano-covered surface; most craters erased by volcanic activity. Dense CO2 atmosphere causing greenhouse effect on planet. Hot enough to melt lead; clouds of sulphuric acid. Atmospheric Pressure is x 92 that of Earth. Can be seen from E ...
Science 9 – Unit E - JA Williams High School
... 24. Ancient peoples considered specific times of the year and particular bodies in the sky to be very ...
... 24. Ancient peoples considered specific times of the year and particular bodies in the sky to be very ...
Tue, April 1, 2003
... like on earth. And just as we experience daylit and dark periods on earth, so the moon has both day and night. But the moon’s rotation is slow; a lunar day lasts two weeks, followed by two weeks of night. As the moon orbits the earth, its rotation speed as it spins on its axis matches its revolution ...
... like on earth. And just as we experience daylit and dark periods on earth, so the moon has both day and night. But the moon’s rotation is slow; a lunar day lasts two weeks, followed by two weeks of night. As the moon orbits the earth, its rotation speed as it spins on its axis matches its revolution ...
scale on a string - Big History Project
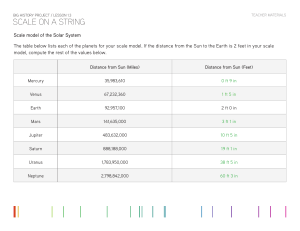
... Note: The last three thresholds are extremely recent on this scale. Students don’t necessarily need to mark these milestones on the string, but they do need to note the very brief period of human history in contrast to the big history of the Universe. ...
... Note: The last three thresholds are extremely recent on this scale. Students don’t necessarily need to mark these milestones on the string, but they do need to note the very brief period of human history in contrast to the big history of the Universe. ...
Astronomer Notes PowerPoint
... Each planet revolves around the sun so that it sweeps over equal areas in equal amounts of time causing it to travel more rapidly in areas closer to the sun. The square of the orbital period is proportional to the cube of its distance from the sun. ...
... Each planet revolves around the sun so that it sweeps over equal areas in equal amounts of time causing it to travel more rapidly in areas closer to the sun. The square of the orbital period is proportional to the cube of its distance from the sun. ...
Eccentric Orbits - Cosmic Connections Workshop
... ECCENTRIC ORBITS Johannes Kepler determined that the planets did not revolve around the sun in circular orbits as previously thought. The purpose of this activity is to understand the nature of these non-circular orbits. ...
... ECCENTRIC ORBITS Johannes Kepler determined that the planets did not revolve around the sun in circular orbits as previously thought. The purpose of this activity is to understand the nature of these non-circular orbits. ...
Giant Planets - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
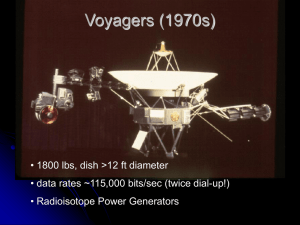
... Far less water was detected in Jupiter's atmosphere than estimated from earlier Voyager observations and from models of the Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 impact Far less lightning activity was found than anticipated The individual lightning events, however, are about ten times stronger on Jupiter than on t ...
... Far less water was detected in Jupiter's atmosphere than estimated from earlier Voyager observations and from models of the Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 impact Far less lightning activity was found than anticipated The individual lightning events, however, are about ten times stronger on Jupiter than on t ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.