downloading
... KBOs (blue), and 2:5 resonant objects (green). Orbits of other KBOs are gray. (Orbital axes have been aligned for comparison.) ...
... KBOs (blue), and 2:5 resonant objects (green). Orbits of other KBOs are gray. (Orbital axes have been aligned for comparison.) ...
Moro_Martin`s Talk - CIERA
... Cold KB-like disks are more common than AB-like disks. Individual collisional events may dominate disk properties. Inner gaps appear to be common in cold KB-like disks ...
... Cold KB-like disks are more common than AB-like disks. Individual collisional events may dominate disk properties. Inner gaps appear to be common in cold KB-like disks ...
Sidereal vs. Synodic Motion
... A synodic or solar day is the time it takes the sun to successively pass the meridian (astronomical noon). ...
... A synodic or solar day is the time it takes the sun to successively pass the meridian (astronomical noon). ...
A Unit 5 Videoscript
... Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.” Zeek: “Our beautiful blue Earth is the third planet.” SC: “Yes, Commander.” Zeek: “Venus is the hottest planet, even though Mercury is closest to the sun.” SC: “Venus is hotter than Mercury because it has thick gas clouds all over it that trap in the sun’s h ...
... Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.” Zeek: “Our beautiful blue Earth is the third planet.” SC: “Yes, Commander.” Zeek: “Venus is the hottest planet, even though Mercury is closest to the sun.” SC: “Venus is hotter than Mercury because it has thick gas clouds all over it that trap in the sun’s h ...
The Naked Eye Era
... rotation carried him from east to west. And if it belonged to the realm of the planets he should also see proper motions from day to day as the object moved in its orbit. The fact that he could detect neither kind of motion during the whole year that he could observe it indicated to him that the sup ...
... rotation carried him from east to west. And if it belonged to the realm of the planets he should also see proper motions from day to day as the object moved in its orbit. The fact that he could detect neither kind of motion during the whole year that he could observe it indicated to him that the sup ...
Galileo & the Telescope—Sept 21
... in a few days she was reduced to a semicircle. She maintained this shape for many days, all the while, however, growing in size. At present, she is becoming sickle-shaped… ...
... in a few days she was reduced to a semicircle. She maintained this shape for many days, all the while, however, growing in size. At present, she is becoming sickle-shaped… ...
Universal Gravitation Chapter 12
... Yet there is another way to look at gravitational interactions. We can study it in terms of what is called a gravitational field. In the simplest form, we define a gravitational field as a region in which gravitational force can be experienced. For example here on earth at sea level we can experien ...
... Yet there is another way to look at gravitational interactions. We can study it in terms of what is called a gravitational field. In the simplest form, we define a gravitational field as a region in which gravitational force can be experienced. For example here on earth at sea level we can experien ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. Define Horizontal parallax. 5. State any one of Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. 6. What is Equation of time? 7. Define Synodic month. 8. What is meant by ‘phase of moon’? 9. What are inner planets? 10. Define ‘Stationary points’. ...
... 4. Define Horizontal parallax. 5. State any one of Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. 6. What is Equation of time? 7. Define Synodic month. 8. What is meant by ‘phase of moon’? 9. What are inner planets? 10. Define ‘Stationary points’. ...
Sky Notes - February 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... M41 Mentioned in a work by Aristotle from the year 325 BC, this open cluster could lay some claim to being the longest-known deep-sky object of all. However, the first formal identification of what would later be called M41 dates to 1654, and the object was catalogued by Messier in January 1765 as a ...
... M41 Mentioned in a work by Aristotle from the year 325 BC, this open cluster could lay some claim to being the longest-known deep-sky object of all. However, the first formal identification of what would later be called M41 dates to 1654, and the object was catalogued by Messier in January 1765 as a ...
Physics 1010: The Physics of Everyday Life
... A black body is easy to construct: Consider a a large cavity with a tiny hole drilled into it. Of all the light that goes through the hole, only an insignificantly small amount gets reflected back out. The rest is bounced around the interior of the cavity so many times, that it is finally totally a ...
... A black body is easy to construct: Consider a a large cavity with a tiny hole drilled into it. Of all the light that goes through the hole, only an insignificantly small amount gets reflected back out. The rest is bounced around the interior of the cavity so many times, that it is finally totally a ...
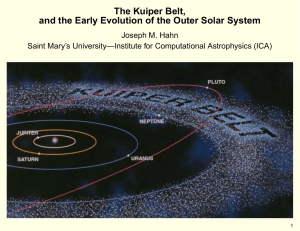
The Kuiper Belt, and the Early Evolution of the Outer Solar System
... a relic that was left–over from when the giant planets formed • this Belt is interesting, since it appears to preserve evidence of planet migration – the KBOs trapped at Neptune’s resonances suggest that Neptune’s orbit expanded ∼ 30% • the Kuiper Belt is also the source of the short–period comets, ...
... a relic that was left–over from when the giant planets formed • this Belt is interesting, since it appears to preserve evidence of planet migration – the KBOs trapped at Neptune’s resonances suggest that Neptune’s orbit expanded ∼ 30% • the Kuiper Belt is also the source of the short–period comets, ...
Gravity: Motivation • An initial theory describing the nature of the
... observing session. • Extra credit is available by attending an Astronomical Video and Public Telescope Observing session (up to 5% of final grade) and submitting a two page word processed paper describing the session’s video and celestial objects observed with the telescope(s) no later than one week ...
... observing session. • Extra credit is available by attending an Astronomical Video and Public Telescope Observing session (up to 5% of final grade) and submitting a two page word processed paper describing the session’s video and celestial objects observed with the telescope(s) no later than one week ...
3 mark - Department of Physics, Engineering Physics & Astronomy
... Part B. Explain a physical law (16 marks) Example 2: Explain Kepler’s third law, including the equation and units used to describe it. More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower average speeds, obeying the relationship ...
... Part B. Explain a physical law (16 marks) Example 2: Explain Kepler’s third law, including the equation and units used to describe it. More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower average speeds, obeying the relationship ...
Balloon Animals
... Kepler’s Laws of planetary motion 1. Planets travel in elliptical paths with one focus at the Sun. 2. At all times, a planet’s path traces out equal areas. 3. The square of a planet’s orbital period is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit. ...
... Kepler’s Laws of planetary motion 1. Planets travel in elliptical paths with one focus at the Sun. 2. At all times, a planet’s path traces out equal areas. 3. The square of a planet’s orbital period is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit. ...
7.4 – Universal Gravitation
... The moon’s orbit around the Earth is slightly tilted (about 5º) with respect to Earth’s orbit around the sun. Therefore, most months neither the Earth’s shadow nor the moon’s shadow affects one another. However, an ellipse occurs when the moon’s shadow is cast onto the Earth or the Earth’s shadow is ...
... The moon’s orbit around the Earth is slightly tilted (about 5º) with respect to Earth’s orbit around the sun. Therefore, most months neither the Earth’s shadow nor the moon’s shadow affects one another. However, an ellipse occurs when the moon’s shadow is cast onto the Earth or the Earth’s shadow is ...
How Old Is The Earth?
... salinity of the oceans could be used to estimate the age of the planet. Halley observed that oceans and lakes fed by streams were constantly receiving more salt, which then stuck around as the wat ...
... salinity of the oceans could be used to estimate the age of the planet. Halley observed that oceans and lakes fed by streams were constantly receiving more salt, which then stuck around as the wat ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Rocky fragments ranging from 940 km across (Ceres) to < 0.1 km. 100,000 known. Most in Asteroid Belt, at about 2-3 AU, between Mars and Jupiter. The Trojan asteroids orbit 60 o ahead of and behind Jupiter. Some asteroids cross Earth's orbit. Their orbits were probably disrupted by Jupiter's gravity. ...
... Rocky fragments ranging from 940 km across (Ceres) to < 0.1 km. 100,000 known. Most in Asteroid Belt, at about 2-3 AU, between Mars and Jupiter. The Trojan asteroids orbit 60 o ahead of and behind Jupiter. Some asteroids cross Earth's orbit. Their orbits were probably disrupted by Jupiter's gravity. ...
Implications of the Search and Discovery
... times is only 400,000 years. • So why aren’t they all around us? – Recall the Fermi Paradox ...
... times is only 400,000 years. • So why aren’t they all around us? – Recall the Fermi Paradox ...
HW6 class solution
... At first glance, this seems to show that the circular orbit assumption is also valid for Mercury and Pluto! One reason for this may be that the standard mean radii are calculated from the orbital period. Mercury and Pluto don’t have very circular orbits because their orbital eccentricities are too f ...
... At first glance, this seems to show that the circular orbit assumption is also valid for Mercury and Pluto! One reason for this may be that the standard mean radii are calculated from the orbital period. Mercury and Pluto don’t have very circular orbits because their orbital eccentricities are too f ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.