Chapter 19: Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
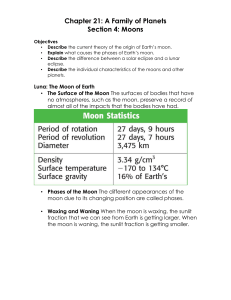
... • Explain what causes the phases of Earth’s moon. • Describe the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse. • Describe the individual characteristics of the moons and other planets. ...
... • Explain what causes the phases of Earth’s moon. • Describe the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse. • Describe the individual characteristics of the moons and other planets. ...
UBD - Solar System
... What is the difference between a star, a planet and a moon? What are the names of the 8 planets in our solar system? What is the difference between a terrestrial and gas planet? How do these planets differ in terms of size and distance from the sun? What are the physical properties of these planets? ...
... What is the difference between a star, a planet and a moon? What are the names of the 8 planets in our solar system? What is the difference between a terrestrial and gas planet? How do these planets differ in terms of size and distance from the sun? What are the physical properties of these planets? ...
Astronomy and Space articles
... The other craft that have done this are Pioneers 10 and 11, and Voyagers 1 and 2, which investigated the planets in the outer solar system in the 1970s and 1980s. The Voyagers are still transmitting information about the conditions way out beyond Pluto, but did not go anywhere close to Pluto itself. ...
... The other craft that have done this are Pioneers 10 and 11, and Voyagers 1 and 2, which investigated the planets in the outer solar system in the 1970s and 1980s. The Voyagers are still transmitting information about the conditions way out beyond Pluto, but did not go anywhere close to Pluto itself. ...
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory
... 43. How many rotations on its axis will Venus complete in 1 of its years? 44. Explain the relationship between a planet’s period of rotation and period of revolution that would cause one side of a planet to face the Sun throughout its year. (Hint: think about our Moon, we typically only see one side ...
... 43. How many rotations on its axis will Venus complete in 1 of its years? 44. Explain the relationship between a planet’s period of rotation and period of revolution that would cause one side of a planet to face the Sun throughout its year. (Hint: think about our Moon, we typically only see one side ...
3/r -- this talks about the surface area vs the volume of a planet
... model. he saw that there were gibbous and full phases which meant that the sun had to be in center with Venus orbiting around it. Giordano Bruno liked the idea of an infinite number of worlds. he believed that no body could be called the center of the universe. Sept 22 2009 Newton - born in 1642, th ...
... model. he saw that there were gibbous and full phases which meant that the sun had to be in center with Venus orbiting around it. Giordano Bruno liked the idea of an infinite number of worlds. he believed that no body could be called the center of the universe. Sept 22 2009 Newton - born in 1642, th ...
Page 1 of 10 Name: Space Systems Learning Target #1: I CAN
... 4. When the Earth is tilted AWAY from the sun, what season is experienced? _______Winter_____________ 5. The ___Solstice___ is the day when the sun reaches its greatest distance north or south of the equator. 6. In the northern hemisphere, when is summer solstice? June 21 or 22 7. In the northern he ...
... 4. When the Earth is tilted AWAY from the sun, what season is experienced? _______Winter_____________ 5. The ___Solstice___ is the day when the sun reaches its greatest distance north or south of the equator. 6. In the northern hemisphere, when is summer solstice? June 21 or 22 7. In the northern he ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... 6. What is the central and largest body of our solar system? A. Jupiter B. the Milky Way C. Earth D. the sun 7. The fates of the sun and the Earth are linked. Which of the following explains why this statement is true? A. Without the Earth in orbit, the sun would quickly burn up. B. Without the heat ...
... 6. What is the central and largest body of our solar system? A. Jupiter B. the Milky Way C. Earth D. the sun 7. The fates of the sun and the Earth are linked. Which of the following explains why this statement is true? A. Without the Earth in orbit, the sun would quickly burn up. B. Without the heat ...
Scale and Distance
... Take two sheets of paper and fold them in half like a book. Tape them together in one long sheet. You will create a map of the solar system on this paper. Label 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 at the ends and the folds. ...
... Take two sheets of paper and fold them in half like a book. Tape them together in one long sheet. You will create a map of the solar system on this paper. Label 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 at the ends and the folds. ...
CONCEPT OF BHAVOTTAMA
... Placement in kendra, Trikona and 2nd and 11th houses. Even if planets are in exaltation, Mooltrikona and own sign, but placed in , 3,6,8 and 12 houses, are of not much use. In Rasi chart, the signs which are placed in 4,5,9 and 10 house, the planets in such signs in Vargas show merit, particular ...
... Placement in kendra, Trikona and 2nd and 11th houses. Even if planets are in exaltation, Mooltrikona and own sign, but placed in , 3,6,8 and 12 houses, are of not much use. In Rasi chart, the signs which are placed in 4,5,9 and 10 house, the planets in such signs in Vargas show merit, particular ...
DATE - cloudfront.net
... 5. The solar system consists of planets and other bodies that orbit the Sun in predictable paths. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know the Sun, an average star, is the central and largest body in the solar system and is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium. b. Students kn ...
... 5. The solar system consists of planets and other bodies that orbit the Sun in predictable paths. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know the Sun, an average star, is the central and largest body in the solar system and is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium. b. Students kn ...
Week #2: Mars!
... How do we measure the diameters of the planets? • know distances (from Newton, Kepler) • observe angular size (α, in arcseconds) • derive the diameter from the angular size equation: D=α*d/206265 Sun ~ 100x Earth ...
... How do we measure the diameters of the planets? • know distances (from Newton, Kepler) • observe angular size (α, in arcseconds) • derive the diameter from the angular size equation: D=α*d/206265 Sun ~ 100x Earth ...
grade vii and viii - Sacred Heart CMI Public School
... brightness was 70% that of what it is today. The Solar System will remain roughly as we know it today until the hydrogen in the core of the Sun has been entirely converted to helium, which will occur roughly 5 billion years from now. This will mark the end of the Sun's main-sequence life. At this ti ...
... brightness was 70% that of what it is today. The Solar System will remain roughly as we know it today until the hydrogen in the core of the Sun has been entirely converted to helium, which will occur roughly 5 billion years from now. This will mark the end of the Sun's main-sequence life. At this ti ...
FREE Sample Here
... 30. The inability to observe parallax of stars contributed to the ancient Greek astronomers rejection of the idea that the Earth revolves around the Sun. ...
... 30. The inability to observe parallax of stars contributed to the ancient Greek astronomers rejection of the idea that the Earth revolves around the Sun. ...
Nearest star`s wobbles could reveal Earth`s twin
... smaller star, Alpha Centauri B, an Earth-like world often coalesced in or near the star's habitable zone, where liquid water could exist on the planet's surface. Finding these planets could be time-consuming, but it does not require any new techniques, they say. They suggest using the "radial veloci ...
... smaller star, Alpha Centauri B, an Earth-like world often coalesced in or near the star's habitable zone, where liquid water could exist on the planet's surface. Finding these planets could be time-consuming, but it does not require any new techniques, they say. They suggest using the "radial veloci ...
Chapter 7
... •Sidereal rotation period: -72 earth days •Much smaller than Jupiter and Saturn, but much larger than Earth • Made of H, He gas, hydrogen compounds (gas and ices of H2O, NH3, CH4) •The bluish green color is due to the presence of methane in the atmosphere. Methane absorb the red part of spectrum and ...
... •Sidereal rotation period: -72 earth days •Much smaller than Jupiter and Saturn, but much larger than Earth • Made of H, He gas, hydrogen compounds (gas and ices of H2O, NH3, CH4) •The bluish green color is due to the presence of methane in the atmosphere. Methane absorb the red part of spectrum and ...
FREE Sample Here
... © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part ...
... © 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part ...
What else is in our solar system, besides the sun, the planets, and
... What else is in our solar system, besides the sun, the planets, and their moons ...
... What else is in our solar system, besides the sun, the planets, and their moons ...
ASTR 150
... • If fall perpendicular to spin axis Need to speed up resistance: centrifugal force • If fall parallel to spin axis: same speed, so no resistance forms protoplanetary disk swirling gas and dust raw material for planets – Origin of planet’s orbits! – Origin of Ecliptic plane – Organizes spins along i ...
... • If fall perpendicular to spin axis Need to speed up resistance: centrifugal force • If fall parallel to spin axis: same speed, so no resistance forms protoplanetary disk swirling gas and dust raw material for planets – Origin of planet’s orbits! – Origin of Ecliptic plane – Organizes spins along i ...
HORARY Chart Setup
... Planetary Hours are not directly related to standardized clock time. Planetary Hour lengths differ between day and night, and the exact lengths depend on the Suns location along the Alma. 1) Determine from a calendar the horary Weekday of the nativity. Horary Weekdays last from local (i.e., sundial) ...
... Planetary Hours are not directly related to standardized clock time. Planetary Hour lengths differ between day and night, and the exact lengths depend on the Suns location along the Alma. 1) Determine from a calendar the horary Weekday of the nativity. Horary Weekdays last from local (i.e., sundial) ...
Not too hot, not too cold: New Earth-like planet could
... Gliese 581g has a mass about three to four times that of Earth. It orbits its sun in 37 days and is thought to be a rocky world. It has enough gravity to possibly have an atmosphere. ...
... Gliese 581g has a mass about three to four times that of Earth. It orbits its sun in 37 days and is thought to be a rocky world. It has enough gravity to possibly have an atmosphere. ...
Planets in astrology
Planets in astrology have a meaning different from the modern astronomical understanding of what a planet is. Before the age of telescopes, the night sky was thought to consist of two very similar components: fixed stars, which remained motionless in relation to each other, and ""wandering stars"" (Ancient Greek: ἀστέρες πλανῆται asteres planetai), which moved relative to the fixed stars over the course of the year.To the Greeks and the other earliest astronomers, this group comprised the five planets visible to the naked eye, and excluded the Earth. Although strictly the term ""planet"" applied only to those five objects, the term was latterly broadened, particularly in the Middle Ages, to include the Sun and the Moon (sometimes referred to as ""Lights""), making a total of seven planets. Astrologers retain this definition today.To ancient astrologers, the planets represented the will of the gods and their direct influence upon human affairs. To modern astrologers the planets represent basic drives or urges in the unconscious, or energy flow regulators representing dimensions of experience. They express themselves with different qualities in the twelve signs of the zodiac and in the twelve houses. The planets are also related to each other in the form of aspects.Modern astrologers differ on the source of the planets' influence. Hone writes that the planets exert it directly through gravitation or another, unknown influence. Others hold that the planets have no direct influence in themselves, but are mirrors of basic organizing principles in the universe. In other words, the basic patterns of the universe repeat themselves everywhere, in fractal-like fashion, and ""as above so below"". Therefore, the patterns that the planets make in the sky reflect the ebb and flow of basic human impulses. The planets are also associated, especially in the Chinese tradition, with the basic forces of nature.Listed below are the specific meanings and domains associated with the astrological planets since ancient times, with the main focus on the Western astrological tradition. The planets in Hindu astrology are known as the Navagraha or ""nine realms"". In Chinese astrology, the planets are associated with the life forces of yin and yang and the five elements, which play an important role in the Chinese form of geomancy known as Feng Shui.