Mapping the evolving strain field during continental breakup from
... successfully explains observations of temporal changes in fast directions. For example, φ at active volcanoes are usually parallel to the regional SHmin, with 90° polarization flips observed before volcanic eruption interpreted as caused by a change in crack orientation induced by magma reservoir in ...
... successfully explains observations of temporal changes in fast directions. For example, φ at active volcanoes are usually parallel to the regional SHmin, with 90° polarization flips observed before volcanic eruption interpreted as caused by a change in crack orientation induced by magma reservoir in ...
Probability of radial anisotropy in the deep mantle Earth and
... In the first stage, we applied waveform fitting using a model space search approach (using the Neighbourhood Algorithm; Sambridge, 1999a,b) to obtain the fundamental and higher mode Love and Rayleigh wave phase velocity measurements (Visser et al., 2007). In the second stage (Visser et al., 2008), we ...
... In the first stage, we applied waveform fitting using a model space search approach (using the Neighbourhood Algorithm; Sambridge, 1999a,b) to obtain the fundamental and higher mode Love and Rayleigh wave phase velocity measurements (Visser et al., 2007). In the second stage (Visser et al., 2008), we ...
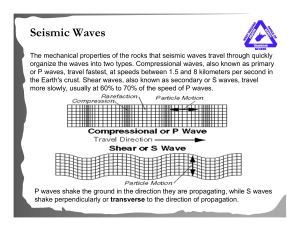
Earthquake destruction and seismic waves Page 1 of 3 I. Factors
... a. due to increased pressure enhancing elastic properties of rock b. results in curved paths of seismic waves through Earth 2.abrupt velocity changes of waves at particular depths—causes refraction of waves a. S waves travel only through solids b. allows us to model Earth’s interior based on seismic ...
... a. due to increased pressure enhancing elastic properties of rock b. results in curved paths of seismic waves through Earth 2.abrupt velocity changes of waves at particular depths—causes refraction of waves a. S waves travel only through solids b. allows us to model Earth’s interior based on seismic ...
Earthquake Test Study Guide
... 10) Which seismic wave travels through the all layers of the Earth? 11) Know which waves move through the earth’s interior (body) and what happens to seismic waves as they travel through materials of different densities. (See Seismic wave graph). 12) Which seismic wave travels only on the surface of ...
... 10) Which seismic wave travels through the all layers of the Earth? 11) Know which waves move through the earth’s interior (body) and what happens to seismic waves as they travel through materials of different densities. (See Seismic wave graph). 12) Which seismic wave travels only on the surface of ...
Thesis of Lamarque Gaëlle
... scattered elsewhere in the TAC. Microstructures and crystallographic preferred orientation (CPO) of minerals (quartz, feldspaths, biotite, amphibole and orthopyroxene) of the MSZ indicate similar characteristics that can be interpreted in terms of conditions, cinematic and rate of deformation, which ...
... scattered elsewhere in the TAC. Microstructures and crystallographic preferred orientation (CPO) of minerals (quartz, feldspaths, biotite, amphibole and orthopyroxene) of the MSZ indicate similar characteristics that can be interpreted in terms of conditions, cinematic and rate of deformation, which ...
2015-defense
... Characters of MTZ Discontinuities Under normal temperature and anhydrous conditions, the estimated Clapeyron slope of the transitions: d410: 1.5 to 3.0 Mpa/K d660: -4.0 to -2.0 Mpa/K The presence of water in the MTZ has similar effects as reducing ...
... Characters of MTZ Discontinuities Under normal temperature and anhydrous conditions, the estimated Clapeyron slope of the transitions: d410: 1.5 to 3.0 Mpa/K d660: -4.0 to -2.0 Mpa/K The presence of water in the MTZ has similar effects as reducing ...
pdf 4.5Mb
... – return of seismic energy to surface – rock layers of different density » boundary reflects energy like a mirror » time since earthquake gives depth to boundary ...
... – return of seismic energy to surface – rock layers of different density » boundary reflects energy like a mirror » time since earthquake gives depth to boundary ...
Lecture Chapter 7 Part 1
... Boundaries between the layers are called discontinuities. – Mohorovičić discontinuity (Moho) between crust and mantle – Gutenberg discontinuity between mantle and core ...
... Boundaries between the layers are called discontinuities. – Mohorovičić discontinuity (Moho) between crust and mantle – Gutenberg discontinuity between mantle and core ...
Chapter 6 – Earthquakes Part 3
... It is Japanese for harbour wave. They result from the vertical displacement of the ocean floor. The energy is transmitted to the water. In the open ocean, they may not appear to be very large, but a they approach land, water piles upward, creating huge towering waves. ...
... It is Japanese for harbour wave. They result from the vertical displacement of the ocean floor. The energy is transmitted to the water. In the open ocean, they may not appear to be very large, but a they approach land, water piles upward, creating huge towering waves. ...
earthquakes - Cloudfront.net
... 1. L-waves (land & last waves) – the slowest and most destructive seismic waves that travel only on the surface/land ...
... 1. L-waves (land & last waves) – the slowest and most destructive seismic waves that travel only on the surface/land ...
Intrinsic versus extrinsic seismic anisotropy: The radial anisotropy in
... can also give rise to observed anisotropy. Cracks (with or without fluid inclusions) embedded in rocks can be aligned parallel to the main compressive stress field through the mechanism of shape-preferred orientation [O’Connell and Budiansky, 1976; Crampin, 1984; Babuska and Cara, 1991; Hudson et al., ...
... can also give rise to observed anisotropy. Cracks (with or without fluid inclusions) embedded in rocks can be aligned parallel to the main compressive stress field through the mechanism of shape-preferred orientation [O’Connell and Budiansky, 1976; Crampin, 1984; Babuska and Cara, 1991; Hudson et al., ...
HERE
... • Can travel through the entire Earth. Through liquids (outer core) and solids (inner core). • The type of wave is called compression. It compresses (squeezes) the matter it’s moving through. (*** your chem teacher might call it longitudinal) • Click HERE for P-waves animation ...
... • Can travel through the entire Earth. Through liquids (outer core) and solids (inner core). • The type of wave is called compression. It compresses (squeezes) the matter it’s moving through. (*** your chem teacher might call it longitudinal) • Click HERE for P-waves animation ...
Structures and deformations correlated to the activation of a
... and crystallographic preferred orientation (CPO) of minerals (quartz, feldspaths, biotite, amphibole and orthopyroxene) of the MSZ indicate similar characteristics that can be interpreted in terms of conditions, cinem ...
... and crystallographic preferred orientation (CPO) of minerals (quartz, feldspaths, biotite, amphibole and orthopyroxene) of the MSZ indicate similar characteristics that can be interpreted in terms of conditions, cinem ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... • Seismic wave studies have provided primary evidence for existence and nature of Earth’s core • Specific areas on the opposite side of the Earth from large earthquakes do not receive seismic waves, resulting in seismic shadow zones • P-wave shadow zone (103°-142° from epicenter) explained by refrac ...
... • Seismic wave studies have provided primary evidence for existence and nature of Earth’s core • Specific areas on the opposite side of the Earth from large earthquakes do not receive seismic waves, resulting in seismic shadow zones • P-wave shadow zone (103°-142° from epicenter) explained by refrac ...
Earthquakes
... and forth in the same direction and the opposite direction as the direction the wave is moving. An S wave, or shear wave, is a seismic body wave that shakes the ground back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is ...
... and forth in the same direction and the opposite direction as the direction the wave is moving. An S wave, or shear wave, is a seismic body wave that shakes the ground back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is ...
Możliwości identyfikacji stref osłabienia w strukturze złoża rud
... This work concerns the identification of weak zones in the structure of a rock mass endangered by outburst of gases and rocks in the Rudna copper ore mine at greater depths (approximately 1200 m). A special project has been undertaken for the recognition of that threat in the wake of an outburst in ...
... This work concerns the identification of weak zones in the structure of a rock mass endangered by outburst of gases and rocks in the Rudna copper ore mine at greater depths (approximately 1200 m). A special project has been undertaken for the recognition of that threat in the wake of an outburst in ...
Tomographic Pn velocity and anisotropy structure beneath
... The event and station distributions in the study area are not uniform. While the ETSE and Syrian National Seismic Network (SNSN) stations provide very dense coverage in a small region, additional stations cover other parts of the region sparsely. In order to take advantage of the high density stati ...
... The event and station distributions in the study area are not uniform. While the ETSE and Syrian National Seismic Network (SNSN) stations provide very dense coverage in a small region, additional stations cover other parts of the region sparsely. In order to take advantage of the high density stati ...
EDWARD J. GARNERO 2. Employer - AGU Elections
... dynamics, and evolution of interiors, especially as it relates to observables at Earth’s surfaces (hotspots, LIPs, subduction zones, plates, etc.). Most of my work has been deep Earth (core-mantle boundary, ultra-low velocity zones, outermost core, D” discontinuities and anisotropy, LLSVPs, etc.), b ...
... dynamics, and evolution of interiors, especially as it relates to observables at Earth’s surfaces (hotspots, LIPs, subduction zones, plates, etc.). Most of my work has been deep Earth (core-mantle boundary, ultra-low velocity zones, outermost core, D” discontinuities and anisotropy, LLSVPs, etc.), b ...
ANTILOPE
... each station showing the measurements calculated by the cross-correlation method. The concentric circles are scales. The diameter of the big one is 2 second and the small one 1 second. The number under each circle is number of the seismic station with 3 in the southern end and 66 as the northern end ...
... each station showing the measurements calculated by the cross-correlation method. The concentric circles are scales. The diameter of the big one is 2 second and the small one 1 second. The number under each circle is number of the seismic station with 3 in the southern end and 66 as the northern end ...
Lecture PowerPoint Slides
... What do seismic waves tell us about Earth’s Interior? • The existence of internal Earth ‘layers’, each characterized by unique density and chemical/mineralogical composition, and identified by a Seismic Discontinuity • Seismic Discontinuity – a region in the Earth which is characterized by an abrupt ...
... What do seismic waves tell us about Earth’s Interior? • The existence of internal Earth ‘layers’, each characterized by unique density and chemical/mineralogical composition, and identified by a Seismic Discontinuity • Seismic Discontinuity – a region in the Earth which is characterized by an abrupt ...
Lithospheric layering in the North American craton
... in the northeastern Superior craton also follows the trends of the geological sutures of the Superior province29. Fossil subductions, revealed as strong mantle reflectors and high-velocity bodies from active and passive seismic studies30–32 are found beneath most of these suture zones and generally ...
... in the northeastern Superior craton also follows the trends of the geological sutures of the Superior province29. Fossil subductions, revealed as strong mantle reflectors and high-velocity bodies from active and passive seismic studies30–32 are found beneath most of these suture zones and generally ...
Solid Earth
... There are approximately 12 lithospheric plates on Earth’s surface. Most scientists believe that convection within Earth’s lower and upper Mantle is the major driving force linked to plate motion. Convection is driven my temperature differences/density differences and gravity. ...
... There are approximately 12 lithospheric plates on Earth’s surface. Most scientists believe that convection within Earth’s lower and upper Mantle is the major driving force linked to plate motion. Convection is driven my temperature differences/density differences and gravity. ...
name________________________
... A. BLAMING SOMEONE ELSE FOR WHAT YOU DID B. THE MOVEMENTS OF ROCK ALONG A FAULT C. THE VIBRATION OF CRUST D. NONE OF THESE 15. IN REGARD TO WAVES, HERTZ IS THE SAME AS A. VELOCITY B. FREQUENCY 16. DRAW IN AND LABEL ALL FOUR BASIC LAYERS OF THE EARTH ...
... A. BLAMING SOMEONE ELSE FOR WHAT YOU DID B. THE MOVEMENTS OF ROCK ALONG A FAULT C. THE VIBRATION OF CRUST D. NONE OF THESE 15. IN REGARD TO WAVES, HERTZ IS THE SAME AS A. VELOCITY B. FREQUENCY 16. DRAW IN AND LABEL ALL FOUR BASIC LAYERS OF THE EARTH ...