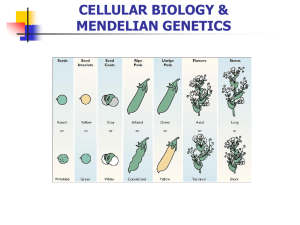
Chapter 3
... • Can result from mistakes during DNA replication • Are fixed by mechanisms in your body • In somatic cells can affect individuals but not necessarily the next generation • In gametes may be passed on to the next generation ...
... • Can result from mistakes during DNA replication • Are fixed by mechanisms in your body • In somatic cells can affect individuals but not necessarily the next generation • In gametes may be passed on to the next generation ...
Ch.6: Sexual Identity
... expressed in both sexes but the results of the expression from allele is dominant in one sex but recessive in the other. Ex: Male pattern baldness ...
... expressed in both sexes but the results of the expression from allele is dominant in one sex but recessive in the other. Ex: Male pattern baldness ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any one codon, there can be only o ...
... 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any one codon, there can be only o ...
DNA - heredity2
... • The different traits for a specific gene are called alleles – e.g. Blue, green and brown eyes are different alleles for eye colour. ...
... • The different traits for a specific gene are called alleles – e.g. Blue, green and brown eyes are different alleles for eye colour. ...
Homology and developmental genes.
... Although the domains of gene expression are strikingly similar in all three phyla, and might reflect a homologous role specifying proximodistal axes, the appendages themselves are clearly not homologous t9. This and other case.~ demonstrate that orthologous regulatory genes can be expressed in struc ...
... Although the domains of gene expression are strikingly similar in all three phyla, and might reflect a homologous role specifying proximodistal axes, the appendages themselves are clearly not homologous t9. This and other case.~ demonstrate that orthologous regulatory genes can be expressed in struc ...
How do I find a list of genes in a genomic region using the UCSC
... How do I find a list of genes in a genomic region using the UCSC Genome Browser? This tutorial will show how to use the UCSC genome browser to find a list of genes in a given genomic region. To navigate to the Genome Browser go to genome.ucsc.edu. This page shows the main page for the Genome Browser ...
... How do I find a list of genes in a genomic region using the UCSC Genome Browser? This tutorial will show how to use the UCSC genome browser to find a list of genes in a given genomic region. To navigate to the Genome Browser go to genome.ucsc.edu. This page shows the main page for the Genome Browser ...
Characterizing the Imprintome
... expression so that one parent’s allele is selectively expressed. Together, these imprinted genes make up the imprintome. Scientists used to search for imprinted genes one by one, but thanks to modern sequencing techniques, they can now scan entire genomes. The precise size of the imprintome is uncer ...
... expression so that one parent’s allele is selectively expressed. Together, these imprinted genes make up the imprintome. Scientists used to search for imprinted genes one by one, but thanks to modern sequencing techniques, they can now scan entire genomes. The precise size of the imprintome is uncer ...
Chapter 7
... 12. Interference: Usually one cross-over will interfere with formation of another crossover near it. Leads to: reduction (or increase) in observed number of double cross-overs versus the number expected, when genes are close. observed DCO = 8/755 = 0.0105 expected DCO = (Prob. of st--ss CO)(Prob. of ...
... 12. Interference: Usually one cross-over will interfere with formation of another crossover near it. Leads to: reduction (or increase) in observed number of double cross-overs versus the number expected, when genes are close. observed DCO = 8/755 = 0.0105 expected DCO = (Prob. of st--ss CO)(Prob. of ...
Chapter 2
... A prokaryotic gene is expressed by transcription into mRNA and then by translation of the mRNA into protein. In eukaryotes, a gene may contain internal regions that are not represented in protein. ...
... A prokaryotic gene is expressed by transcription into mRNA and then by translation of the mRNA into protein. In eukaryotes, a gene may contain internal regions that are not represented in protein. ...
Fundamentals of Biotechnology
... An alternative to conventional gene therapy involves repair of a mutant sequence in vivo. In principle, this can be done by a variety of different experimental strategies at both the level of the mutant gene or its transcript. ...
... An alternative to conventional gene therapy involves repair of a mutant sequence in vivo. In principle, this can be done by a variety of different experimental strategies at both the level of the mutant gene or its transcript. ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 15 Notes
... **Loss of heterochromatin affects longevity (shortens life span) **Loss of heterochromatin increases non-dysjunction ...
... **Loss of heterochromatin affects longevity (shortens life span) **Loss of heterochromatin increases non-dysjunction ...
11-3: exploring mendelian genetics
... 1. Inheritance is determined by genes, which are passed from parents to offspring. 2. Some forms of a gene may be dominant and others recessive. 3. You get one copy of each gene from each parent. These genes segregate when gametes are formed. 4. Different genes segregate independently from one anoth ...
... 1. Inheritance is determined by genes, which are passed from parents to offspring. 2. Some forms of a gene may be dominant and others recessive. 3. You get one copy of each gene from each parent. These genes segregate when gametes are formed. 4. Different genes segregate independently from one anoth ...
Protein-protein interactions
... across different, distantly related genomes are likely to be part of the same protein complex or functional process across all species – They have been selected to remain as a co-regulated unit throughout the extensive shuffling of gene order that takes place in prokaryote genomes ...
... across different, distantly related genomes are likely to be part of the same protein complex or functional process across all species – They have been selected to remain as a co-regulated unit throughout the extensive shuffling of gene order that takes place in prokaryote genomes ...
Chapter 11
... chromosome inactivation in interphase cells of female mammals – In each cell line, the X chromosome from either parent may be inactivated – Leads to a random mosaic of expression of the two X chromosomes – Example: coat color in tortoiseshell cat ...
... chromosome inactivation in interphase cells of female mammals – In each cell line, the X chromosome from either parent may be inactivated – Leads to a random mosaic of expression of the two X chromosomes – Example: coat color in tortoiseshell cat ...
Lecture: Mendelian Genetics
... has 2 alleles with different instructions for developing a certain phenotype ...
... has 2 alleles with different instructions for developing a certain phenotype ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... nondisjunction during meiosis II in the father; d) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the mother; e) we can not specifically determine where non-disjunction occurred from the information given. 4. The expression of the dysplastic (i.e. mutant) tissue phenotype in the mutant sectors is best explaine ...
... nondisjunction during meiosis II in the father; d) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the mother; e) we can not specifically determine where non-disjunction occurred from the information given. 4. The expression of the dysplastic (i.e. mutant) tissue phenotype in the mutant sectors is best explaine ...
Sutton-Boveri theory: The chromosome theory of inheritance
... • hemophilia A; 75% of the cases; more severe form; factor VIII is missing • hemophilia B; 25% of the cases; less severe form factor IX is missing • therapy: administration of missing factor isolated from blood or produced from the cloned gene ...
... • hemophilia A; 75% of the cases; more severe form; factor VIII is missing • hemophilia B; 25% of the cases; less severe form factor IX is missing • therapy: administration of missing factor isolated from blood or produced from the cloned gene ...
Pathway/Genome Navigator
... regulated by ArcA. Highlight all reactions in EcoCyc that are inhibited by ADP. ...
... regulated by ArcA. Highlight all reactions in EcoCyc that are inhibited by ADP. ...
I. Introduction
... 6. Mode of inheritance refers to whether a trait is dominant or recessive, autosomal or carried on a sex chromosome. 7. An autosomal condition is equally likely to affect either sex. 8. X-linked characteristics affect males much more than females. 9. Recessive conditions can skip a generation becaus ...
... 6. Mode of inheritance refers to whether a trait is dominant or recessive, autosomal or carried on a sex chromosome. 7. An autosomal condition is equally likely to affect either sex. 8. X-linked characteristics affect males much more than females. 9. Recessive conditions can skip a generation becaus ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... Human mtDNA does NOT have introns. Introns are non-coding SEQUENCES of the double helix. The absence of INTRONS in human mtDNA means that mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA co ...
... Human mtDNA does NOT have introns. Introns are non-coding SEQUENCES of the double helix. The absence of INTRONS in human mtDNA means that mutations will have a greater impact because all of the information is needed for normal cell structure and function; there is no “fluff” What does human mtDNA co ...
All life is based on the same genetic code
... DNA is coiled tightly into an x-like called a chromosome stored in the nucleus of every cell. ...
... DNA is coiled tightly into an x-like called a chromosome stored in the nucleus of every cell. ...
PCB 6528 Exam – Organelle genomes and gene expression
... http://www.arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?name=AT2G21640&type=locus). The transcript is up-regulated in response to a wide suite of hydrogen peroxide, superoxide and singlet oxygen generating agents (Gadjev et al. , Plant Physiol. 141: 436). The protein product, however, was up-regulated in Ara ...
... http://www.arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?name=AT2G21640&type=locus). The transcript is up-regulated in response to a wide suite of hydrogen peroxide, superoxide and singlet oxygen generating agents (Gadjev et al. , Plant Physiol. 141: 436). The protein product, however, was up-regulated in Ara ...