The history of gene duplication Phylogenies are not just useful for
... lineage split to give rise to two living species, X and Y? Species X and Y would each have three gene copies, A1, A2a, and A2b, meaning there would be six tips. But how would they be related to each other? One way to think through this problem is to first draw the population lineages as though they ...
... lineage split to give rise to two living species, X and Y? Species X and Y would each have three gene copies, A1, A2a, and A2b, meaning there would be six tips. But how would they be related to each other? One way to think through this problem is to first draw the population lineages as though they ...
Nobel Laureate 1995
... homeotic ge nes, a word coined more than a hundred years ago co mean a type of variat ion in which "something has been changed into the likeness of something else." Calvin Bridges found the first homeotic gene in 19 15, and hypothesized th at gene dupl ications occur naturally and in tande m . Lewis ...
... homeotic ge nes, a word coined more than a hundred years ago co mean a type of variat ion in which "something has been changed into the likeness of something else." Calvin Bridges found the first homeotic gene in 19 15, and hypothesized th at gene dupl ications occur naturally and in tande m . Lewis ...
OB35
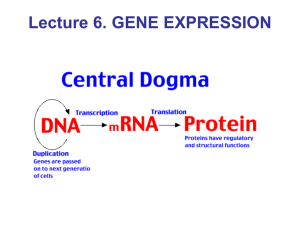
... • DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid • it is a molecule built in a particular code • the code contains instructions for every structure and function the body will ever need • the DNA code for each separate structure or function is called a gene • this makes it a very very long molecule…so how does ...
... • DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid • it is a molecule built in a particular code • the code contains instructions for every structure and function the body will ever need • the DNA code for each separate structure or function is called a gene • this makes it a very very long molecule…so how does ...
Genes
... complexed with proteins called histones. Chromosomes together carry the genetic blueprint of an individual. DNA is a long molecule that’s made up of thousands of segments called genes. Each of the traits that a person inherits is coded in their genes. All human somatic (body) cells contain 23 pairs ...
... complexed with proteins called histones. Chromosomes together carry the genetic blueprint of an individual. DNA is a long molecule that’s made up of thousands of segments called genes. Each of the traits that a person inherits is coded in their genes. All human somatic (body) cells contain 23 pairs ...
Designer Genes - Heredity
... The steps of translation: 1. Initiation: mRNA enters the cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes (rRNA + proteins). tRNAs, each carrying a specific amino acid, pair up with the mRNA codons inside the ribosomes. Base pairing (A-U, G-C) between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons determines the or ...
... The steps of translation: 1. Initiation: mRNA enters the cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes (rRNA + proteins). tRNAs, each carrying a specific amino acid, pair up with the mRNA codons inside the ribosomes. Base pairing (A-U, G-C) between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons determines the or ...
Document
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
... • This occurs at the beginning of transcription. The 5' cap is used as a recognition signal for ribosomes to bind to the mRNA. • At the 3' end, a poly(A) tail of 150 or more adenine nucleotides is added. The tail plays a role in the stability of the mRNA. ...
Mixed questions
... (a) high threonine, high lysine (b) high threonine, low lysine (c) low threonine, high lysine (c) low threonine, low lysine 30. What elements make up the lac operon and what roles do they play? 31. The lac operon is an inducible operon. Why and what does this mean? 32. Describe the process of induct ...
... (a) high threonine, high lysine (b) high threonine, low lysine (c) low threonine, high lysine (c) low threonine, low lysine 30. What elements make up the lac operon and what roles do they play? 31. The lac operon is an inducible operon. Why and what does this mean? 32. Describe the process of induct ...
Lecture 2 4285 2015 - Scheid Signalling Lab @ York University
... • Oocytes sit like this for decades • Complete meiosis II once each month • While arrested at the diplotene stage, the tetrad chromosomes are held together by chiasmata (formed during recombination) • If a pair of chromosomes don’t undergo recombination, the lack of chiasmata can contribute to non-d ...
... • Oocytes sit like this for decades • Complete meiosis II once each month • While arrested at the diplotene stage, the tetrad chromosomes are held together by chiasmata (formed during recombination) • If a pair of chromosomes don’t undergo recombination, the lack of chiasmata can contribute to non-d ...
chromosomes
... 2) autosomes => two and two fully identical – homologous, pair chromosomes chromosomes of one pair have the same shape, size and the same genes they may not have the same forms of expressing genes– alleles ...
... 2) autosomes => two and two fully identical – homologous, pair chromosomes chromosomes of one pair have the same shape, size and the same genes they may not have the same forms of expressing genes– alleles ...
Chapter 13 - Warren County Schools
... Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes Genes Segments of DNA that code for heredity Transmitted from generation to generation Gametes are the reproductive cells that do this ...
... Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes Genes Segments of DNA that code for heredity Transmitted from generation to generation Gametes are the reproductive cells that do this ...
Transcription AND Translation
... • While polypeptides are being made, they fold and coil. This is responsible for the tertiary structure of proteins. • Quaternary structure occurs when many polypeptides join together. ...
... • While polypeptides are being made, they fold and coil. This is responsible for the tertiary structure of proteins. • Quaternary structure occurs when many polypeptides join together. ...
MEIOSIS - Oakland-Craig Public School
... 1. Plant breeders purposely cause polyploidy to improve their produce a. Bananas (3n), Wheat (6n) ...
... 1. Plant breeders purposely cause polyploidy to improve their produce a. Bananas (3n), Wheat (6n) ...
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
... see if the separation of one pair of alleles affects the separation of another pair of alleles. Instead of crossing a yellow seed with a green seed; he observed seed color and seed shape together Seeds that are round (R) and yellow (Y) are ...
... see if the separation of one pair of alleles affects the separation of another pair of alleles. Instead of crossing a yellow seed with a green seed; he observed seed color and seed shape together Seeds that are round (R) and yellow (Y) are ...
The ovine callipyge locus: a paradigm illustrating the - HAL
... schemes, but it should lead to a better fundamental understanding of the so-called black box, ie, the functioning of the network of involved polygenes. The first whole genome scans performed during the last 5 years have already led to the mapping of a number of production genes (reviewed in Georges ...
... schemes, but it should lead to a better fundamental understanding of the so-called black box, ie, the functioning of the network of involved polygenes. The first whole genome scans performed during the last 5 years have already led to the mapping of a number of production genes (reviewed in Georges ...
Annotation Practice Activity [Based on materials from the GEP
... The Genome Brower window will display one or more gene models that prediction programs have identified in the contig. (Note: your image may not look exactly like this depending on your settings. Feel free to experiment with the menu’s found below the browser image to control what is seen in the ima ...
... The Genome Brower window will display one or more gene models that prediction programs have identified in the contig. (Note: your image may not look exactly like this depending on your settings. Feel free to experiment with the menu’s found below the browser image to control what is seen in the ima ...
Introduction to Microarray Analysis (Section D1)
... turned on, however, and it is the subset that is "expressed" that confers unique properties to each cell type. "Gene expression" is the term used to describe the transcription of the information contained within the DNA, the repository of genetic ...
... turned on, however, and it is the subset that is "expressed" that confers unique properties to each cell type. "Gene expression" is the term used to describe the transcription of the information contained within the DNA, the repository of genetic ...
Molecular-Pathology2010
... genes revealed (for the first time) that crossing over — with genetic recombination — occasionally occurs in mitosis (as it always does in meiosis). ...
... genes revealed (for the first time) that crossing over — with genetic recombination — occasionally occurs in mitosis (as it always does in meiosis). ...
Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics.notebook
... 1. Biological inheritance is determined by factors that are passed from generation to generation. Trait specific characteristic Each original plant was the parent plant P Generation Offspring from the P Generation F1 or First Filial Hybrids offspring with two different traits Genes che ...
... 1. Biological inheritance is determined by factors that are passed from generation to generation. Trait specific characteristic Each original plant was the parent plant P Generation Offspring from the P Generation F1 or First Filial Hybrids offspring with two different traits Genes che ...
Genetics: Inherited Traits
... different, there is one trait that will appear over the other. He also discovered that when there is a dominant gene then there is usually a recessive gene that will only appear if both the genes you get from both parents are for that recessive trait. ...
... different, there is one trait that will appear over the other. He also discovered that when there is a dominant gene then there is usually a recessive gene that will only appear if both the genes you get from both parents are for that recessive trait. ...