Every reaction is reversible: A chemical reaction is in equilibrium
... This particular equilibrium constant, K, is known as the Partition Coefficient. It depends on the two immiscible liquids involved, the solute and the temperature. Iodine is much more soluble in Methylbenzene than in Water. The value of the partition coefficient is quite high. Solvent extraction is a ...
... This particular equilibrium constant, K, is known as the Partition Coefficient. It depends on the two immiscible liquids involved, the solute and the temperature. Iodine is much more soluble in Methylbenzene than in Water. The value of the partition coefficient is quite high. Solvent extraction is a ...
Energy
... is usually surrounded by water • Apparatus is closed • Initial temperature is measured • Final temperature is taken to be the ...
... is usually surrounded by water • Apparatus is closed • Initial temperature is measured • Final temperature is taken to be the ...
Grades 9-12 Physics
... a dozen of the brightest stars and constellations in the San Marino winter sky. ...
... a dozen of the brightest stars and constellations in the San Marino winter sky. ...
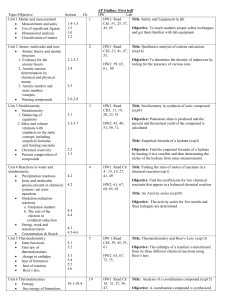
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 4. Define boiling point? 5. What is the difference between normal boiling point and boiling point? 6. What happens to vapor pressure as temperature increases? 7. What happens to boiling point as altitude increases? 8. Who has a higher boiling point; Mount McKinley or Charlotte, NC? 9. What 2 tempera ...
... 4. Define boiling point? 5. What is the difference between normal boiling point and boiling point? 6. What happens to vapor pressure as temperature increases? 7. What happens to boiling point as altitude increases? 8. Who has a higher boiling point; Mount McKinley or Charlotte, NC? 9. What 2 tempera ...
7. Heat capacity
... When C is large > a given amount of heating results in only a small temperature rise (the system has a large capacity for heat) The heat capacity depends on conditions: - system constrained to have constant volume > Cv (heat capacity at constant volume, or isochoric heat capacity) - system subject t ...
... When C is large > a given amount of heating results in only a small temperature rise (the system has a large capacity for heat) The heat capacity depends on conditions: - system constrained to have constant volume > Cv (heat capacity at constant volume, or isochoric heat capacity) - system subject t ...
Physics - Hinsdale Township High School District 86
... radioactivity, nuclear reactions, and fundamental particles D. Relativity, such as time dilation, length contraction, and mass-energy equivalence ...
... radioactivity, nuclear reactions, and fundamental particles D. Relativity, such as time dilation, length contraction, and mass-energy equivalence ...
Chapter Six Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... Energy needed to break attractions between H2O molecules Heat goes from surroundings into the system ...
... Energy needed to break attractions between H2O molecules Heat goes from surroundings into the system ...
Standard answers: 1 Basic concepts, Fuels, alkanes and alkenes
... More electrons – greater VDW forces of attraction 2. Effect of branching on the boiling point / volatility of the isomers More branching decreases the boiling point / increases volatility Same number of electrons but smaller surface area Decreases VDW forces of attraction ...
... More electrons – greater VDW forces of attraction 2. Effect of branching on the boiling point / volatility of the isomers More branching decreases the boiling point / increases volatility Same number of electrons but smaller surface area Decreases VDW forces of attraction ...
sample problem - KFUPM Resources
... The Third Law of Thermodynamics According to the third law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a perfect crystalline substance is zero at absolute zero. ...
... The Third Law of Thermodynamics According to the third law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a perfect crystalline substance is zero at absolute zero. ...
Heat Capacity (C)
... conditions of 1 atmosphere and 25 0C. (The standard state of oxygen is O2 (g) at a pressure of 1 atmosphere, the standard state of sodium is Na(s); the standard state of mercury is Hg (l); and so on. 2. The ΔH of a reaction is equal to the difference between the sum of the enthalpy of formation of a ...
... conditions of 1 atmosphere and 25 0C. (The standard state of oxygen is O2 (g) at a pressure of 1 atmosphere, the standard state of sodium is Na(s); the standard state of mercury is Hg (l); and so on. 2. The ΔH of a reaction is equal to the difference between the sum of the enthalpy of formation of a ...
Phase, Q, Curves
... a thermometer. If the chart above is based on 4 grams of Gold, how much energy does it take to melt 12 grams of Gold? ___________. How long would it take to melt 4 grams? _____________. How long it would it probably take to melt 12 grams? ________________________. ...
... a thermometer. If the chart above is based on 4 grams of Gold, how much energy does it take to melt 12 grams of Gold? ___________. How long would it take to melt 4 grams? _____________. How long it would it probably take to melt 12 grams? ________________________. ...