Chemistry - Nagpur University
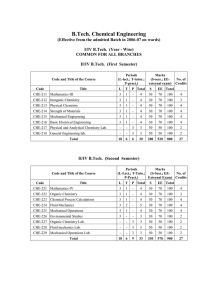
... CH – 202: Paper- II ( Physical Chemistry) UNIT-I : Thermodynamics 7.5 Hrs (A) Recapitulation of thermodynamic terms : system, surrounding, types of system (closed, open & isolated), Thermodynamic, variables, intensive & extensive properties, thermodynamic processes isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, i ...
... CH – 202: Paper- II ( Physical Chemistry) UNIT-I : Thermodynamics 7.5 Hrs (A) Recapitulation of thermodynamic terms : system, surrounding, types of system (closed, open & isolated), Thermodynamic, variables, intensive & extensive properties, thermodynamic processes isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, i ...
Chemical Reactions
... A decomposition reaction is a reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances – The reactant in a decomposition reaction must be a compound – the products may be elements or compounds AB → A + B ...
... A decomposition reaction is a reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances – The reactant in a decomposition reaction must be a compound – the products may be elements or compounds AB → A + B ...
Chapter 6. Therrnochemistry
... where AEsys is the change in the internal energy of the system and AEsu,r is the change in the energy of the surroundings. If we could relate q and w directly to the reactants and products (Ainitiat and A,o~=), we’d have the quantitative description we’re looking for. The problem is that q and w are ...
... where AEsys is the change in the internal energy of the system and AEsu,r is the change in the energy of the surroundings. If we could relate q and w directly to the reactants and products (Ainitiat and A,o~=), we’d have the quantitative description we’re looking for. The problem is that q and w are ...
Chem - Andhra University
... Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperature on Heat of Reaction. Second law of Thermodynamics, spontaneous processes, ...
... Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperature on Heat of Reaction. Second law of Thermodynamics, spontaneous processes, ...
Chapter 5
... The loss of energy by one part is equal to the energy gained by another part; overall, energy is conserved (meaning neither created/destroyed) ...
... The loss of energy by one part is equal to the energy gained by another part; overall, energy is conserved (meaning neither created/destroyed) ...
Property calculation I
... MC method is based on directly computing the ensemble average Define a series of microscopic states that reflect the appropriate ensemble average; weights intrinsically captured since states more likely are visited more frequently and vice versa Egodicity: The ensemble average is equal to the ti ...
... MC method is based on directly computing the ensemble average Define a series of microscopic states that reflect the appropriate ensemble average; weights intrinsically captured since states more likely are visited more frequently and vice versa Egodicity: The ensemble average is equal to the ti ...
Channel arc model of DC hydrogen plasma: influence of radiation and very high pressure
... 3.3. Net emission coefficient In most plasma studies, radiation is neglected or estimated with empirical formulas [6]. However, at high current and pressure, the heat transfer is mostly related with radiation [9]. For higher accuracy, there is then need to consider the latter in the mathematical for ...
... 3.3. Net emission coefficient In most plasma studies, radiation is neglected or estimated with empirical formulas [6]. However, at high current and pressure, the heat transfer is mostly related with radiation [9]. For higher accuracy, there is then need to consider the latter in the mathematical for ...
Power Point for Equilibrium
... • Therefore, the larger K the more products are present at equilibrium. • Conversely, the smaller K the more reactants are present at equilibrium. • If K >> 1, then products dominate at equilibrium and equilibrium lies to the right. • If K << 1, then reactants dominate at equilibrium and the equilib ...
... • Therefore, the larger K the more products are present at equilibrium. • Conversely, the smaller K the more reactants are present at equilibrium. • If K >> 1, then products dominate at equilibrium and equilibrium lies to the right. • If K << 1, then reactants dominate at equilibrium and the equilib ...
Chemical reactions
... tabulation of standard enthalpies of formation is presented aside, including the chemical elements, for which the surname 'formation' added to the standard enthalpy is irrelevant: hf⊕= h⊕=h(T⊕,p⊕)=0. Notice that standard enthalpies of formation are usually negative because the formation reaction is ...
... tabulation of standard enthalpies of formation is presented aside, including the chemical elements, for which the surname 'formation' added to the standard enthalpy is irrelevant: hf⊕= h⊕=h(T⊕,p⊕)=0. Notice that standard enthalpies of formation are usually negative because the formation reaction is ...
5 Thermochemistry
... ball lands. Some energy is released as heat through friction between the ball and the sand. ...
... ball lands. Some energy is released as heat through friction between the ball and the sand. ...