ZXTC6720MC Features and Benefits Mechanical Data
... 4. For a dual device surface mounted on 28mm x 28mm (8cm ) FR4 PCB with high coverage of single sided 2 oz copper, in still air conditions; the device is measured when operating in a steady-state condition. The heatsink is split in half with the exposed collector pads connected to each half. 5. Same ...
... 4. For a dual device surface mounted on 28mm x 28mm (8cm ) FR4 PCB with high coverage of single sided 2 oz copper, in still air conditions; the device is measured when operating in a steady-state condition. The heatsink is split in half with the exposed collector pads connected to each half. 5. Same ...
The Cathodyne Phase Inverter
... always worth checking. A load line can be now drawn for the cathodyne in exactly the same way as for any gain stage, remembering that it must represent the total load in series with the valve, Za + Zk (it is useful to learn to mentally ‘flip-flop’ between viewing individual outputs, and the total be ...
... always worth checking. A load line can be now drawn for the cathodyne in exactly the same way as for any gain stage, remembering that it must represent the total load in series with the valve, Za + Zk (it is useful to learn to mentally ‘flip-flop’ between viewing individual outputs, and the total be ...
Question: How do I apply an instrument`s accuracy specification?
... Question: Why does my picoammeter (or electrometer in the current mode) give a non-zero reading when I short the input? Answer: When measuring current, the input circuit is an op amp in a current-to-voltage converter configuration, also known as a transimpedance amplifier. As such, the feedback is 1 ...
... Question: Why does my picoammeter (or electrometer in the current mode) give a non-zero reading when I short the input? Answer: When measuring current, the input circuit is an op amp in a current-to-voltage converter configuration, also known as a transimpedance amplifier. As such, the feedback is 1 ...
Voltage Reference Circuits
... temperature coefficient ,we write VREF 1VBE 2 (VT ln n) VT ln n is the difference between the base-emitter voltages of the two bipolar transistors operating at different current ...
... temperature coefficient ,we write VREF 1VBE 2 (VT ln n) VT ln n is the difference between the base-emitter voltages of the two bipolar transistors operating at different current ...
J. Lu, D.J. Perreault and K.L. Afridi, “Impedance Control Network Resonant Converter for Wide-Range High-Efficiency Operation,” 2015 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference , pp. 1440-1447, March 2015.
... outphasing is increased further the transistors in the lagging inverter leg lose ZVS turn-on capability. These factors result in extra losses and lead to lower converter efficiency at partial loads, and consequently to poor design tradeoffs. Other fixed frequency control techniques have also been de ...
... outphasing is increased further the transistors in the lagging inverter leg lose ZVS turn-on capability. These factors result in extra losses and lead to lower converter efficiency at partial loads, and consequently to poor design tradeoffs. Other fixed frequency control techniques have also been de ...
BDX53/A/B/C NPN Epitaxial Silicon Transistor BDX53/A/B/C — NP N Epit
... 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) 2. A critical component in any component of a life support, device, or are intended for surgical implant into the body or (b) support or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to sustain life, and (c) whose fail ...
... 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) 2. A critical component in any component of a life support, device, or are intended for surgical implant into the body or (b) support or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to sustain life, and (c) whose fail ...
NCP1380 - ONSemi
... controller stops and stays latched for option A and C or enters auto−recovery mode for option B and D. Particularly well suited for adapter applications, the controller features a pin to implement either a combined overvoltage / overtemperature protection (Version A and B) or a combined brown−out/ov ...
... controller stops and stays latched for option A and C or enters auto−recovery mode for option B and D. Particularly well suited for adapter applications, the controller features a pin to implement either a combined overvoltage / overtemperature protection (Version A and B) or a combined brown−out/ov ...
DMS-20LCD Series - Murata Power Solutions
... Therefore, the 9V battery voltage appears to the meter inputs as 0.9V. With the decimal point moved to its DP2 position (pin 5 tied to pin 3), the meter reads 9.00 Volts. ...
... Therefore, the 9V battery voltage appears to the meter inputs as 0.9V. With the decimal point moved to its DP2 position (pin 5 tied to pin 3), the meter reads 9.00 Volts. ...
Unit I
... In n-well fabrication, n-well is protected with resist material. Because, it should not be affected by Boron implantation. The boron is implanexcept n-well. It is done using photoresist mask. This type of implantation is known as channel implantation. ...
... In n-well fabrication, n-well is protected with resist material. Because, it should not be affected by Boron implantation. The boron is implanexcept n-well. It is done using photoresist mask. This type of implantation is known as channel implantation. ...
3.4 Pulsed and Steady-State Power Supplies
... the 69 kV busbar has to be restored. The minimum charge/discharge time is about half an hour. The energy stored in the TF coils at the maximum (68 kA) current is about 40 GJ. In case of quench or a failure in the power supply system requiring immediate extraction of the coil energy, 9 fast discharge ...
... the 69 kV busbar has to be restored. The minimum charge/discharge time is about half an hour. The energy stored in the TF coils at the maximum (68 kA) current is about 40 GJ. In case of quench or a failure in the power supply system requiring immediate extraction of the coil energy, 9 fast discharge ...
LM258A-EP DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
... TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or the design of Buyers’ products. Buyers are responsible for their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with Buyers’ products and applications, Buyers should provide adequate design and operating safeguar ...
... TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or the design of Buyers’ products. Buyers are responsible for their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with Buyers’ products and applications, Buyers should provide adequate design and operating safeguar ...
HFA3101 - Intersil
... The process of frequency doubling is also understood by having the same signal being fed to both modulating and carrier ports. The output frequency will be the sum of ωC and ωM which is equivalent to the product of the input frequency by 2 and a zero Hz or DC frequency equivalent to the difference o ...
... The process of frequency doubling is also understood by having the same signal being fed to both modulating and carrier ports. The output frequency will be the sum of ωC and ωM which is equivalent to the product of the input frequency by 2 and a zero Hz or DC frequency equivalent to the difference o ...
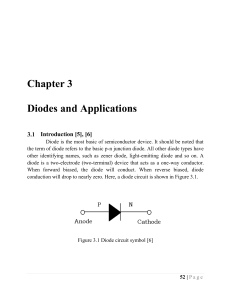
Chapter 3 Diodes and Applications
... Figure 3.38 illustrates the process called half-wave rectification. A diode is connected to an ac source and to a load resistor, RL, forming a half-wave rectifier. Let’s examine what happens during one cycle of the input voltage using the CVD model for the diode. When the sinusoidal input voltage (V ...
... Figure 3.38 illustrates the process called half-wave rectification. A diode is connected to an ac source and to a load resistor, RL, forming a half-wave rectifier. Let’s examine what happens during one cycle of the input voltage using the CVD model for the diode. When the sinusoidal input voltage (V ...
MAX8513/MAX8514 Wide-Input, High-Frequency, Triple-Output Supplies with Voltage Monitor and Power-On Reset General Description
... Current limiting is accomplished by inductor current sensing for improved efficiency, or by an external sense resistor for better accuracy. The MAX8513/MAX8514s’ first LDO controller is designed to provide a low-cost, high-current regulated output from 0.8V to 5.5V using an N-channel MOSFET or a low ...
... Current limiting is accomplished by inductor current sensing for improved efficiency, or by an external sense resistor for better accuracy. The MAX8513/MAX8514s’ first LDO controller is designed to provide a low-cost, high-current regulated output from 0.8V to 5.5V using an N-channel MOSFET or a low ...
Power Plant Electrical Distribution Systems
... shown as a three winding transformer. It has a primary winding and two separate secondary windings at different voltages. This allows the station to have two different voltage levels one at 6900 Volts or 6.9kV and the other at 4160 Volts or 4.16KV. The higher voltage afforded by the 6.9KV windings a ...
... shown as a three winding transformer. It has a primary winding and two separate secondary windings at different voltages. This allows the station to have two different voltage levels one at 6900 Volts or 6.9kV and the other at 4160 Volts or 4.16KV. The higher voltage afforded by the 6.9KV windings a ...
Rectifier

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a ""cat's whisker"" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or ""crystal detector"".Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.