Abstract - PG Embedded systems
... achieved by light being generated on one side of a transparent insulating gap and being detected on the other side of the gap without an electrical connection between the two sides (except for a minor amount of coupling capacitance). ...
... achieved by light being generated on one side of a transparent insulating gap and being detected on the other side of the gap without an electrical connection between the two sides (except for a minor amount of coupling capacitance). ...
Existing method
... consists of a three phase induction machine with open stator phase windings and dual bridge inverter supplied from a single DC voltage source. To achieve multi-level output voltage waveforms a floating capacitor bank is used for the second of the dual bridges. The capacitor voltage is regulated usin ...
... consists of a three phase induction machine with open stator phase windings and dual bridge inverter supplied from a single DC voltage source. To achieve multi-level output voltage waveforms a floating capacitor bank is used for the second of the dual bridges. The capacitor voltage is regulated usin ...
Design a simple DC power supply
... this equation comes in two flavors AC and DC. Every circuit designed today needs power to be applied for the circuit to function. DC is the basis for most circuit designs that goes into everyday products. If a circuit has no power a circuit would not be able to perform its desired function. A variab ...
... this equation comes in two flavors AC and DC. Every circuit designed today needs power to be applied for the circuit to function. DC is the basis for most circuit designs that goes into everyday products. If a circuit has no power a circuit would not be able to perform its desired function. A variab ...
LM124/LM224/LM324/LM2902 Low Power Quad Operational
... LM124/LM224/LM324/LM2902 Low Power Quad Operational Amplifiers ...
... LM124/LM224/LM324/LM2902 Low Power Quad Operational Amplifiers ...
CSI23SWI - Circuit Specialists
... though the chassis of the unit is negatively grounded,use correct terminals to connect cable. When plugging the unit into a wall outlet,it must be turned off. Place the unit in a dry and well ventilated area. Never touch the unit while it is working. Even though it is designed for high efficiency,th ...
... though the chassis of the unit is negatively grounded,use correct terminals to connect cable. When plugging the unit into a wall outlet,it must be turned off. Place the unit in a dry and well ventilated area. Never touch the unit while it is working. Even though it is designed for high efficiency,th ...
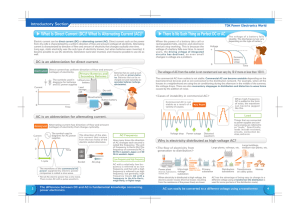
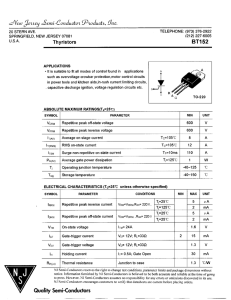
Lecture-19 di / dt and dv / dt protection
... current and recovery charge differences of a thyristors are 12 mA and 120 µC respectively. A derating factor of 20% is applied for the steady state and dynamic (transient) voltage sharing of the thyristors. If the maximum steady sate voltage is 1000V, determine 1) the steady voltage sharing resistor ...
... current and recovery charge differences of a thyristors are 12 mA and 120 µC respectively. A derating factor of 20% is applied for the steady state and dynamic (transient) voltage sharing of the thyristors. If the maximum steady sate voltage is 1000V, determine 1) the steady voltage sharing resistor ...
Lab 1
... Vmcos(t). Assuming an ideal diode, initially Vout charges up to Vm. When Vin falls below Vm, the diode is open, the RC network is isolated, and Vout = Vme-t/RC, as seen in section 7.2 in Nilsson. The exponential decay continues until Vout < Vin, at which time the diode will start conducting again. ...
... Vmcos(t). Assuming an ideal diode, initially Vout charges up to Vm. When Vin falls below Vm, the diode is open, the RC network is isolated, and Vout = Vme-t/RC, as seen in section 7.2 in Nilsson. The exponential decay continues until Vout < Vin, at which time the diode will start conducting again. ...
MEEPP 106-3 High Voltage DC Transmission
... 4. (a) Derive the expression for output voltage across the load for a firing angle less than 60° in the 3-ph bridge circuit. ...
... 4. (a) Derive the expression for output voltage across the load for a firing angle less than 60° in the 3-ph bridge circuit. ...
iD8783 - iDESYN
... There is a cycle-by-cycle current limit on the high-side MOSFET of 3A (typ). When the current flowing out of SW exceeds this limit, the high-side MOSFET turns off and the synchronous rectifier turns on. Unlike the traditional method of current limiting by limiting the voltage at the compensation pin ...
... There is a cycle-by-cycle current limit on the high-side MOSFET of 3A (typ). When the current flowing out of SW exceeds this limit, the high-side MOSFET turns off and the synchronous rectifier turns on. Unlike the traditional method of current limiting by limiting the voltage at the compensation pin ...
Unit 7: Electrical Circuits and Systems Review KEY
... A series circuit contains a 12 volt battery and two identical bulbs for 2 A of current. What is the voltage drop across each bulb? Voltage drop = 12 V/ 2 bulbs = 6 V ...
... A series circuit contains a 12 volt battery and two identical bulbs for 2 A of current. What is the voltage drop across each bulb? Voltage drop = 12 V/ 2 bulbs = 6 V ...
AMG.F.HSQE.001 Electrical Burn while wearing wrist Watch March
... Electrical Burns while wearing wrist Watch ...
... Electrical Burns while wearing wrist Watch ...
EET421 Exp.#2 - Portal UniMAP
... magnet DC motor using items (3) on the frame of the electrical machine trainer. 2) In the first part of this experiment, connect the power diode as the power converter device to a 100 Ohm resistor. After ensure your connection is correct, turn-on the power of the AC supply. 3) On ED-5306, there are ...
... magnet DC motor using items (3) on the frame of the electrical machine trainer. 2) In the first part of this experiment, connect the power diode as the power converter device to a 100 Ohm resistor. After ensure your connection is correct, turn-on the power of the AC supply. 3) On ED-5306, there are ...
Transformers Safety
... Explain what causes physical vibrations in transformers at twice the frequency of the AC power involved. ...
... Explain what causes physical vibrations in transformers at twice the frequency of the AC power involved. ...
Single-Phase Pulse Width Modulated Rectifier
... pulse width modulation. Voltage and current under this control are shown in Fig. 3. One possible way of transistor switching is shown at the bottom of Fig. 3. It can be seen that two states alternate. First, the current flows into the load (D1 and D2 conducts), and second, the input of the rectifier ...
... pulse width modulation. Voltage and current under this control are shown in Fig. 3. One possible way of transistor switching is shown at the bottom of Fig. 3. It can be seen that two states alternate. First, the current flows into the load (D1 and D2 conducts), and second, the input of the rectifier ...
Rectifier

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a ""cat's whisker"" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or ""crystal detector"".Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.