Block ______ minutes spent on DH:______ Last name First name
... Freshman Physics Honors with Dr. Leopold DH42 – Voltage, Resistance and Ohm’s Law (Goes with day 62. Self-grade out of 23.) 1. The source in an electric circuit performs two functions. What are they? ...
... Freshman Physics Honors with Dr. Leopold DH42 – Voltage, Resistance and Ohm’s Law (Goes with day 62. Self-grade out of 23.) 1. The source in an electric circuit performs two functions. What are they? ...
TS321_B15
... more than –0.3 VDC (at 25 C). An input clamp diode with a resistor to the IC input terminal can be used. To reduce the power supply drain, the amplifier has a class A output stage for small signal levels which converts to class B in a large signal mode. This allows the amplifiers to both source and ...
... more than –0.3 VDC (at 25 C). An input clamp diode with a resistor to the IC input terminal can be used. To reduce the power supply drain, the amplifier has a class A output stage for small signal levels which converts to class B in a large signal mode. This allows the amplifiers to both source and ...
Protek PM150 Series
... 1. To order a model with PFD signal, please consult factory to get an exclusive part number distinguishing it from the standard model without PFD signal. 2. Peak output current with 10% duty cycle maximum for less than 15 seconds, average power not to exceed maximum power rating. 3. The first value ...
... 1. To order a model with PFD signal, please consult factory to get an exclusive part number distinguishing it from the standard model without PFD signal. 2. Peak output current with 10% duty cycle maximum for less than 15 seconds, average power not to exceed maximum power rating. 3. The first value ...
dmt 121/3 electronic i
... a) An external voltage is applied that is positive at anode and negative at cathode. b) An external voltage is applied that is negative at anode and positive at cathode. c) An external voltage is applied that is positive at the p region and negative at n region. d) Answer (a) and (c). 12. When a dio ...
... a) An external voltage is applied that is positive at anode and negative at cathode. b) An external voltage is applied that is negative at anode and positive at cathode. c) An external voltage is applied that is positive at the p region and negative at n region. d) Answer (a) and (c). 12. When a dio ...
Unit 8: Electronic Circuit Design and Construction
... Draw and label a diagram of the 1N4001 general purpose diode connected in forward bias and reverse bias mode Measure the forward characteristic of the diode between 0.5 volts and 0.7 volts using steps of 0.01 of a volt by adjusting the resistance box R1 Measure and record the reverse characteristic ...
... Draw and label a diagram of the 1N4001 general purpose diode connected in forward bias and reverse bias mode Measure the forward characteristic of the diode between 0.5 volts and 0.7 volts using steps of 0.01 of a volt by adjusting the resistance box R1 Measure and record the reverse characteristic ...
Download T3000 Datasheet
... relays. The output relay for under frequency is activated at frequencies higher than the preset value, while the output relay for over frequency is activated at frequencies lower than the preset value. This means that both output relays are activated at frequencies within the interval between the un ...
... relays. The output relay for under frequency is activated at frequencies higher than the preset value, while the output relay for over frequency is activated at frequencies lower than the preset value. This means that both output relays are activated at frequencies within the interval between the un ...
Lab 7
... R1 with C2 forms a low pass filter. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative inpu ...
... R1 with C2 forms a low pass filter. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative inpu ...
Differentiator
... If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo vari ...
... If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo is relatively constant, C1 acts like an open circuit and all of the current through R2 and C1 will flow through R1. If the difference in the voltage between the negative input terminal on the op amp and Vo vari ...
CN-0023 利用AD5546/AD5556 DAC实现精密、单极性、同相配置
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
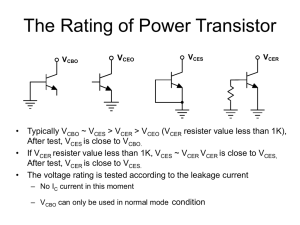
The Rating of Power Transistor
... After test, VCES is close to VCBO. • If VCER resister value less than 1K, VCES ~ VCER VCER is close to VCES, After test, VCER is close to VCES. • The voltage rating is tested according to the leakage current – No IC current in this moment – VCBO can only be used in normal mode condition ...
... After test, VCES is close to VCBO. • If VCER resister value less than 1K, VCES ~ VCER VCER is close to VCES, After test, VCER is close to VCES. • The voltage rating is tested according to the leakage current – No IC current in this moment – VCBO can only be used in normal mode condition ...
Science CAPT Review – Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Series
... The picture below illustrates the four basic parts of a circuit – an energy source (battery) which provides the energy to push electrons through the circuit, a wire to carry the electrons, a “load” or device which does some work (i.e. a light bulb), and a switch which can turn on or turn off the flo ...
... The picture below illustrates the four basic parts of a circuit – an energy source (battery) which provides the energy to push electrons through the circuit, a wire to carry the electrons, a “load” or device which does some work (i.e. a light bulb), and a switch which can turn on or turn off the flo ...
Rad T 110
... • Addresses the issue of the divergent beam. • As the beam travels it diverges or spreads out. The further it travels the more spread out it becomes. • However, given that the same number of photons are in the beam their concentration or intensity will be diminished. ...
... • Addresses the issue of the divergent beam. • As the beam travels it diverges or spreads out. The further it travels the more spread out it becomes. • However, given that the same number of photons are in the beam their concentration or intensity will be diminished. ...
Buck Boost Converter Seminar.pdf
... the duty cycle of the switching transistor. One possible drawback of this converter is that the switch does not have a terminal at ground; this complicates the driving circuitry. Also, the polarity of the output voltage is opposite the input voltage. Neither drawback is of any consequence if the pow ...
... the duty cycle of the switching transistor. One possible drawback of this converter is that the switch does not have a terminal at ground; this complicates the driving circuitry. Also, the polarity of the output voltage is opposite the input voltage. Neither drawback is of any consequence if the pow ...
TECHNICAL DATA
... guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. NOTES 2: Power Dissipation is kept in a safe range by current limiting circuitry. Refer to Overload Recovery in Application Notes. NOTES 3: The maximum power dissipation is a function of Tj(MAX), ΘjA and TA . The ...
... guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. NOTES 2: Power Dissipation is kept in a safe range by current limiting circuitry. Refer to Overload Recovery in Application Notes. NOTES 3: The maximum power dissipation is a function of Tj(MAX), ΘjA and TA . The ...
Homework 3
... current through and the voltage across each element. Do not solve. Note: The purpose of this exercise is to give you practice in carefully labeling circuits and writing the circuit equations. Caution: There is a dependent source in this problem; you must decide if it is a voltage source or a current ...
... current through and the voltage across each element. Do not solve. Note: The purpose of this exercise is to give you practice in carefully labeling circuits and writing the circuit equations. Caution: There is a dependent source in this problem; you must decide if it is a voltage source or a current ...
chapter 8 - Power Quality
... linear loads, these waveforms quite often become distorted. Voltage distortion is any deviation from the nominal sine waveform of the AC line voltage. The distorted waveform repeats itself with some basic frequency. The sine wave associated with this frequency, which is usually 60 Hz, is called the ...
... linear loads, these waveforms quite often become distorted. Voltage distortion is any deviation from the nominal sine waveform of the AC line voltage. The distorted waveform repeats itself with some basic frequency. The sine wave associated with this frequency, which is usually 60 Hz, is called the ...
Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments
... An electrical circuit is a collection of components connected together with wires to perform a desired function. The physical realization of the circuit can vary enormously, as long as the connections between components are correct. For this reason, circuits are usually represented by schematic diag ...
... An electrical circuit is a collection of components connected together with wires to perform a desired function. The physical realization of the circuit can vary enormously, as long as the connections between components are correct. For this reason, circuits are usually represented by schematic diag ...
Rectifier

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a ""cat's whisker"" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or ""crystal detector"".Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.