What is an operating system?
... Concurrent threads may interfere one with another. This leads to the necessity for resource protection by using user/supervisor modes. For example, the I/O instructions are privileged, it can be run only in supervisor mode. The system calls are making the transfer from user mode into supervisor mode ...
... Concurrent threads may interfere one with another. This leads to the necessity for resource protection by using user/supervisor modes. For example, the I/O instructions are privileged, it can be run only in supervisor mode. The system calls are making the transfer from user mode into supervisor mode ...
Objects and Concurrency
... – 26 Graphical Tools: TkTools • deals with graphics • you won’t need this because we have done it for you Part VII: Miscellaneous – 27 Support Classes for Objects: ObjectSupport ...
... – 26 Graphical Tools: TkTools • deals with graphics • you won’t need this because we have done it for you Part VII: Miscellaneous – 27 Support Classes for Objects: ObjectSupport ...
Programming Languages
... Determines the memory locations that code from each module will occupy and relocates instructions by adjusting absolute references Resolves references among files Chapter 17 Programming Tools ...
... Determines the memory locations that code from each module will occupy and relocates instructions by adjusting absolute references Resolves references among files Chapter 17 Programming Tools ...
Module 3: Operating
... – creating the output file – if a file named file2 already existed: delete a previous file file2, or return an error, or ask user for action – in case of errors: print message and exit – if no error: a loop where characters are read from file1 and copied to file2 (2 system calls, with possible error ...
... – creating the output file – if a file named file2 already existed: delete a previous file file2, or return an error, or ask user for action – in case of errors: print message and exit – if no error: a loop where characters are read from file1 and copied to file2 (2 system calls, with possible error ...
An Overview of Visual Basic .NET
... start of the task to its completion. The programmer determines and controls the order in which the computer processes the instructions. Examples of procedure-oriented high-level languages include COBOL, BASIC (Beginner’s All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code), and C. Procedure-oriented high-level la ...
... start of the task to its completion. The programmer determines and controls the order in which the computer processes the instructions. Examples of procedure-oriented high-level languages include COBOL, BASIC (Beginner’s All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code), and C. Procedure-oriented high-level la ...
Exception Handling and System Calls
... For the system calls like Create, Open, Read, Write and Close, these member functions of openfile and filesys classes directly call unix system calls in order to actually perform the above tasks. You would be required to use the global fileSystem object to call these member functions (create and ope ...
... For the system calls like Create, Open, Read, Write and Close, these member functions of openfile and filesys classes directly call unix system calls in order to actually perform the above tasks. You would be required to use the global fileSystem object to call these member functions (create and ope ...
Intro to UNIX - Regis University: Academic Web Server for Faculty
... UNIX is less secure than some operating systems – Developed to be used as a software development environment, in which all users are working together cooperatively. Security was traded for more convenience and flexibility. – Well-documented open code makes hacking easier. ...
... UNIX is less secure than some operating systems – Developed to be used as a software development environment, in which all users are working together cooperatively. Security was traded for more convenience and flexibility. – Well-documented open code makes hacking easier. ...
Answers to Even-numbered Exercises
... that is frequently related to the operating system. A utility is simpler than an application program, although no clear line separates the two. Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu Linux, include many utilities. You can also download many utilities from the Internet. Examples of utilities are cp (cop ...
... that is frequently related to the operating system. A utility is simpler than an application program, although no clear line separates the two. Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu Linux, include many utilities. You can also download many utilities from the Internet. Examples of utilities are cp (cop ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS QUESTIONS
... 10. What is the cause of thrashing? How does the system detect thrashing? Once it detects thrashing, what can the system do to eliminate this problem? - Thrashing is caused by under allocation of the minimum number of pages required by a process, forcing it to continuously page fault. The system can ...
... 10. What is the cause of thrashing? How does the system detect thrashing? Once it detects thrashing, what can the system do to eliminate this problem? - Thrashing is caused by under allocation of the minimum number of pages required by a process, forcing it to continuously page fault. The system can ...
System Call - KOVAN Research Lab
... System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and ...
... System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and ...
Chapter 16 PowerPoint
... Microsoft Windows 95 was the first 32-bit version. All applications designed for Windows have standard interfaces. Multitasking allows users to have more than one application open. ...
... Microsoft Windows 95 was the first 32-bit version. All applications designed for Windows have standard interfaces. Multitasking allows users to have more than one application open. ...
Introduction to Unix
... subroutines to be executed first if they do not exist. Finally the command (or rule) is to be executed if all if the dependencies exist; it takes the dependencies and turns them into the target. There are two important things to remember: The file names must start on the first character of a line. ...
... subroutines to be executed first if they do not exist. Finally the command (or rule) is to be executed if all if the dependencies exist; it takes the dependencies and turns them into the target. There are two important things to remember: The file names must start on the first character of a line. ...
Linux Kernel—File Systems
... A directory is a file containing a list of entries. Each entry contains an inode number and a file name When a process uses a pathname, the kernel code searches in the directories to find the corresponding inode number, the Inode is loaded into memory for requests. ...
... A directory is a file containing a list of entries. Each entry contains an inode number and a file name When a process uses a pathname, the kernel code searches in the directories to find the corresponding inode number, the Inode is loaded into memory for requests. ...
Operating Systems
... Course Description: Operating Systems, types, characteristics, historical development of operating systems, Linux and Windows operating system structures, Linux system calls, Windows API calls, processes, states, process applications in Linux and Windows, threads, multithread programming, Linux and ...
... Course Description: Operating Systems, types, characteristics, historical development of operating systems, Linux and Windows operating system structures, Linux system calls, Windows API calls, processes, states, process applications in Linux and Windows, threads, multithread programming, Linux and ...
Getting started in UNIX is easy
... jEdit is a text editor created to be particularly useful for editing programs in a variety of languages. It was written with Java in mind and provides syntax highlighting and formatting for your source files. It also has facilities for providing formatting several other languages. jEdit may be launc ...
... jEdit is a text editor created to be particularly useful for editing programs in a variety of languages. It was written with Java in mind and provides syntax highlighting and formatting for your source files. It also has facilities for providing formatting several other languages. jEdit may be launc ...
Operating systems
... It is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs. Operating systems, in general, control the functions of a computer and the running of application programs. They perform basic tasks, such as recognizing inpu ...
... It is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs. Operating systems, in general, control the functions of a computer and the running of application programs. They perform basic tasks, such as recognizing inpu ...
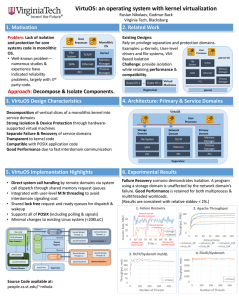
operating systems structures
... I/O Operations: A running program may require I/O, which may involve a file or an I/O device. For efficiency and protection user usually cannot control I/O devices directly. The OS provides a means to do I/O. ƒ File System Manipulation: Programs need to read, write files. Also they should be able to ...
... I/O Operations: A running program may require I/O, which may involve a file or an I/O device. For efficiency and protection user usually cannot control I/O devices directly. The OS provides a means to do I/O. ƒ File System Manipulation: Programs need to read, write files. Also they should be able to ...
Computer components
... and the other takes nearly 3 minutes. What could explain the difference? 2. In this example, we loaded and executed Microsoft Word by double-clicking the name of the program in the Start menu. What would we have done if instead of creating a new document, we wanted to go back and modify the old docu ...
... and the other takes nearly 3 minutes. What could explain the difference? 2. In this example, we loaded and executed Microsoft Word by double-clicking the name of the program in the Start menu. What would we have done if instead of creating a new document, we wanted to go back and modify the old docu ...
Chapter I Introduction
... blocks hoping they will be accessed again – Caching • Works very well because we keep accessing again and again the data we are working with • Caching is a fundamental technique of OS and database design ...
... blocks hoping they will be accessed again – Caching • Works very well because we keep accessing again and again the data we are working with • Caching is a fundamental technique of OS and database design ...
Lecture 11
... Is similar to multiuser systems in many respects. The major burden of program execution has been shifted from the multiuser system to individual clients connected to the server through network. The server may have no direct user facilities of its own, other than those required for management of the ...
... Is similar to multiuser systems in many respects. The major burden of program execution has been shifted from the multiuser system to individual clients connected to the server through network. The server may have no direct user facilities of its own, other than those required for management of the ...
Slide 1
... Is similar to multiuser systems in many respects. The major burden of program execution has been shifted from the multiuser system to individual clients connected to the server through network. The server may have no direct user facilities of its own, other than those required for management of the ...
... Is similar to multiuser systems in many respects. The major burden of program execution has been shifted from the multiuser system to individual clients connected to the server through network. The server may have no direct user facilities of its own, other than those required for management of the ...
CENG334 Introduction to Operating Systems
... System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and ...
... System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and ...
Library (computing)
In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often to develop software. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets.In computer science, a library is a collection of implementations of behavior, written in terms of a language, that has a well-defined interface by which the behavior is invoked. This means that as long as a higher level program uses a library to make system calls, it does not need to be re-written to implement those system calls over and over again. In addition, the behavior is provided for reuse by multiple independent programs. A program invokes the library-provided behavior via a mechanism of the language. For example, in a simple imperative language such as C, the behavior in a library is invoked by using C's normal function-call. What distinguishes the call as being to a library, versus being to another function in the same program, is the way that the code is organized in the system. Library code is organized in such a way that it can be used by multiple programs that have no connection to each other, while code that is part of a program is organized to only be used within that one program. This distinction can gain a hierarchical notion when a program grows large, such as a multi-million-line program. In that case, there may be internal libraries that are reused by independent sub-portions of the large program. The distinguishing feature is that a library is organized for the purposes of being reused by independent programs or sub-programs, and the user only needs to know the interface, and not the internal details of the library.The value of a library is the reuse of the behavior. When a program invokes a library, it gains the behavior implemented inside that library without having to implement that behavior itself. Libraries encourage the sharing of code in a modular fashion, and ease the distribution of the code. The behavior implemented by a library can be connected to the invoking program at different program lifecycle phases. If the code of the library is accessed during the build of the invoking program, then the library is called a static library. An alternative is to build the executable of the invoking program and distribute that, independently from the library implementation. The library behavior is connected after the executable has been invoked to be executed, either as part of the process of starting the execution, or in the middle of execution. In this case the library is called a dynamic library. A dynamic library can be loaded and linked as part of preparing a program for execution, by the linker. Alternatively, in the middle of execution, an application may explicitly request that a module be loaded.Most compiled languages have a standard library although programmers can also create their own custom libraries. Most modern software systems provide libraries that implement the majority of system services. Such libraries have commoditized the services which a modern application requires. As such, most code used by modern applications is provided in these system libraries.